1/  Hello #MedTwitter
Hello #MedTwitter
This month’s @ASPNeph Renal Imaging Webinar was all about #Pheochromocytoma!
Here are a few “pheo facts” I learned!
#tweetorial #nephtwitter
Let’s start with a poll.
Which of the following is true about pheochromocytoma (PCC)?
 Hello #MedTwitter
Hello #MedTwitter This month’s @ASPNeph Renal Imaging Webinar was all about #Pheochromocytoma!
Here are a few “pheo facts” I learned!
#tweetorial #nephtwitter
Let’s start with a poll.
Which of the following is true about pheochromocytoma (PCC)?
2/Answer: D All of the above
(PMID: 24893135 & 30603807)
 PCC & Paraganglioma (PGL) are catecholamine secreting tumors arising from chromaffin cells
PCC & Paraganglioma (PGL) are catecholamine secreting tumors arising from chromaffin cells
PCC Adrenal medulla = 80-85%
Adrenal medulla = 80-85%
PGL Extra-adrenal =10-15%
Extra-adrenal =10-15%  symp chain (abdo/chest/pelvis) or parasymp chain (head&neck)
symp chain (abdo/chest/pelvis) or parasymp chain (head&neck)
(PMID: 24893135 & 30603807)
 PCC & Paraganglioma (PGL) are catecholamine secreting tumors arising from chromaffin cells
PCC & Paraganglioma (PGL) are catecholamine secreting tumors arising from chromaffin cellsPCC
 Adrenal medulla = 80-85%
Adrenal medulla = 80-85%PGL
 Extra-adrenal =10-15%
Extra-adrenal =10-15%  symp chain (abdo/chest/pelvis) or parasymp chain (head&neck)
symp chain (abdo/chest/pelvis) or parasymp chain (head&neck)
3/ Many will recall the “Rule of 10s”
Many will recall the “Rule of 10s” 
10% Malignant
10% Family history
Family history
10% Bilateral
10% Extra-adrenal
But..
 This rule does not hold true for children
This rule does not hold true for children
 In particular, inherited PCC/PGL more likely in children
In particular, inherited PCC/PGL more likely in children
 Up to 80% in some studies! (PMID:24169644 )
Up to 80% in some studies! (PMID:24169644 )
 Many will recall the “Rule of 10s”
Many will recall the “Rule of 10s” 
10% Malignant
10%
 Family history
Family history10% Bilateral
10% Extra-adrenal
But..
 This rule does not hold true for children
This rule does not hold true for children
 In particular, inherited PCC/PGL more likely in children
In particular, inherited PCC/PGL more likely in children
 Up to 80% in some studies! (PMID:24169644 )
Up to 80% in some studies! (PMID:24169644 )
4/ Which Syndromes are associated with PGLs/PCCs?
5/Ans: D
 Von Hippel Lindau: PCC (often B/L) or PGL in ~10-20%. Noradrenergic phenotype.
Von Hippel Lindau: PCC (often B/L) or PGL in ~10-20%. Noradrenergic phenotype.
Gene: VHL TSG
 MEN2: PCC in ~ 50%. Adrenergic phenotype.
MEN2: PCC in ~ 50%. Adrenergic phenotype.
Gene: RET
 NF1:
NF1:  common ~2-3%. Usually solitary PCC.
common ~2-3%. Usually solitary PCC.
Gene: NF1
 All =AD inheritance
All =AD inheritance
Source: http://UptoDate.com
 Von Hippel Lindau: PCC (often B/L) or PGL in ~10-20%. Noradrenergic phenotype.
Von Hippel Lindau: PCC (often B/L) or PGL in ~10-20%. Noradrenergic phenotype.Gene: VHL TSG
 MEN2: PCC in ~ 50%. Adrenergic phenotype.
MEN2: PCC in ~ 50%. Adrenergic phenotype.Gene: RET
 NF1:
NF1:  common ~2-3%. Usually solitary PCC.
common ~2-3%. Usually solitary PCC.Gene: NF1
 All =AD inheritance
All =AD inheritance
Source: http://UptoDate.com
6/ Many other susceptibility genes identified
Many other susceptibility genes identified 
Genetic mutations can be divided into 2 groups:
 Genes encoding proteins
Genes encoding proteins
 Hypoxia inducible factors: VHL, SDH, EGLN1 & HIF2A
Hypoxia inducible factors: VHL, SDH, EGLN1 & HIF2A
 Kinase Signalling pathway: RET, NF1, TMEM127
Kinase Signalling pathway: RET, NF1, TMEM127
 Genetic Testing is recommended in all children
Genetic Testing is recommended in all children
 Many other susceptibility genes identified
Many other susceptibility genes identified 
Genetic mutations can be divided into 2 groups:
 Genes encoding proteins
Genes encoding proteins Hypoxia inducible factors: VHL, SDH, EGLN1 & HIF2A
Hypoxia inducible factors: VHL, SDH, EGLN1 & HIF2A  Kinase Signalling pathway: RET, NF1, TMEM127
Kinase Signalling pathway: RET, NF1, TMEM127 Genetic Testing is recommended in all children
Genetic Testing is recommended in all children
7/ Approximately how common is the classic triad of episodic headache, sweating and palpitations in children?
8/ The classic triad has been reported in up to 54% of children (PMID: 24825268)
has been reported in up to 54% of children (PMID: 24825268)
 Average age ~ 11-13 years
Average age ~ 11-13 years
 M>F 2:1
M>F 2:1
Other symptoms:
 anxiety
anxiety 
 weight
weight visual change
visual change polydipsia/uria
polydipsia/uria 
 glucose
glucose tremor
tremor  flushing
flushing  abdo pain
abdo pain  diarrhoea
diarrhoea  pallor
pallor  syncope
syncope
 has been reported in up to 54% of children (PMID: 24825268)
has been reported in up to 54% of children (PMID: 24825268) Average age ~ 11-13 years
Average age ~ 11-13 years M>F 2:1
M>F 2:1Other symptoms:
 anxiety
anxiety 
 weight
weight visual change
visual change polydipsia/uria
polydipsia/uria 
 glucose
glucose tremor
tremor  flushing
flushing  abdo pain
abdo pain  diarrhoea
diarrhoea  pallor
pallor  syncope
syncope
9/ Hypertension is common (60-90%)
Hypertension is common (60-90%)
 Sustained > paroxysmal in children
Sustained > paroxysmal in children
 BP can be normal
BP can be normal
 Look for abnormal ABPM eg. “non-dipping”
Look for abnormal ABPM eg. “non-dipping”
 Orthostatic Hypotension can be a presenting feature (epinephrine secreting tumours)
Orthostatic Hypotension can be a presenting feature (epinephrine secreting tumours)
(PMID: 30603807)
 Hypertension is common (60-90%)
Hypertension is common (60-90%) Sustained > paroxysmal in children
Sustained > paroxysmal in children BP can be normal
BP can be normal  Look for abnormal ABPM eg. “non-dipping”
Look for abnormal ABPM eg. “non-dipping” Orthostatic Hypotension can be a presenting feature (epinephrine secreting tumours)
Orthostatic Hypotension can be a presenting feature (epinephrine secreting tumours) (PMID: 30603807)
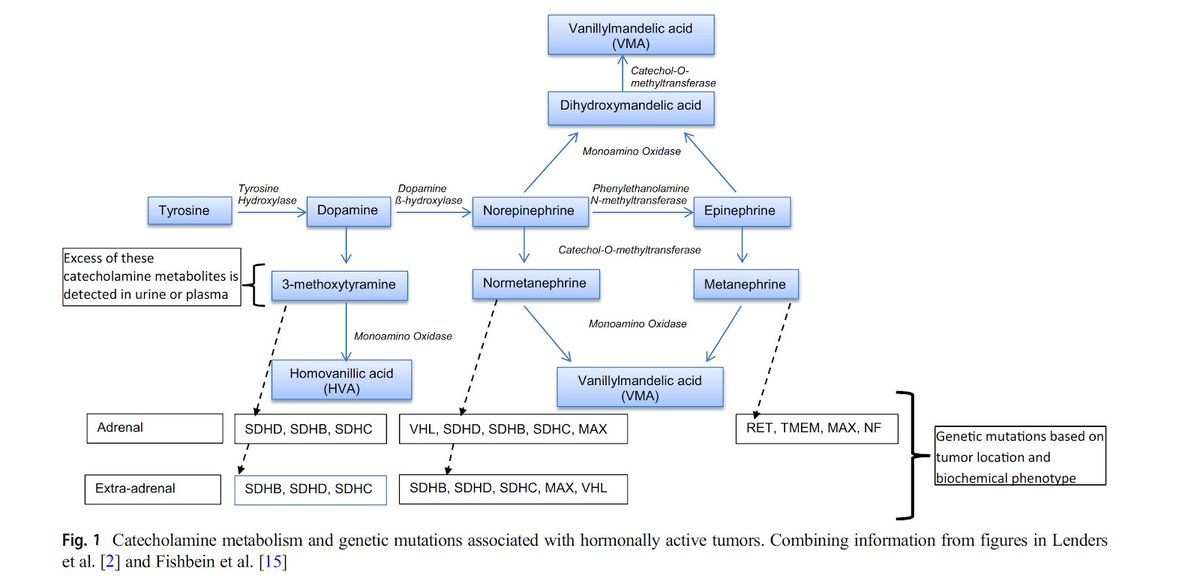
10/ Let’s Review catecholamine production & metabolism!
Catecholamines are produced by metabolism of Tyrosine DOPA
DOPA Dopamine
Dopamine  Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine  Epinephrine
Epinephrine
 Metanephrines are the o-methylated products of catecholamine metabolism
Metanephrines are the o-methylated products of catecholamine metabolism
(PMID: 30603807)
Catecholamines are produced by metabolism of Tyrosine
 DOPA
DOPA Dopamine
Dopamine  Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine  Epinephrine
Epinephrine  Metanephrines are the o-methylated products of catecholamine metabolism
Metanephrines are the o-methylated products of catecholamine metabolism
(PMID: 30603807)
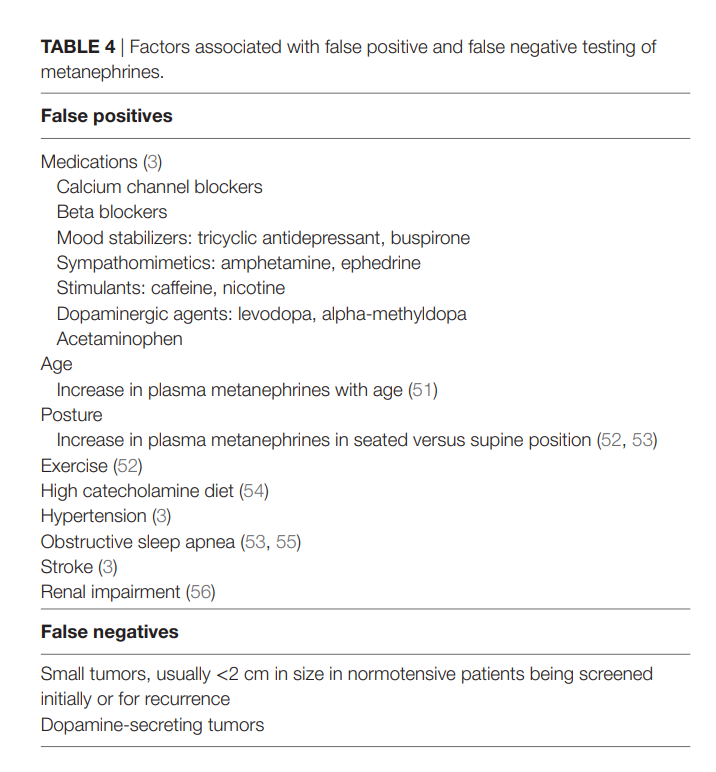
11/ 1st line of invx is biochemical testing
 Catecholamines or metanephrines can be tested
Catecholamines or metanephrines can be tested
 Plasma metanephrines more sens/specific than urine
Plasma metanephrines more sens/specific than urine
 Suspect false
Suspect false  if level <3-4 x normal
if level <3-4 x normal
 Patient should be supine x 30mins for plasma sample
Patient should be supine x 30mins for plasma sample
 Use age appropriate cut-offs
Use age appropriate cut-offs
 Catecholamines or metanephrines can be tested
Catecholamines or metanephrines can be tested  Plasma metanephrines more sens/specific than urine
Plasma metanephrines more sens/specific than urine Suspect false
Suspect false  if level <3-4 x normal
if level <3-4 x normal  Patient should be supine x 30mins for plasma sample
Patient should be supine x 30mins for plasma sample Use age appropriate cut-offs
Use age appropriate cut-offs
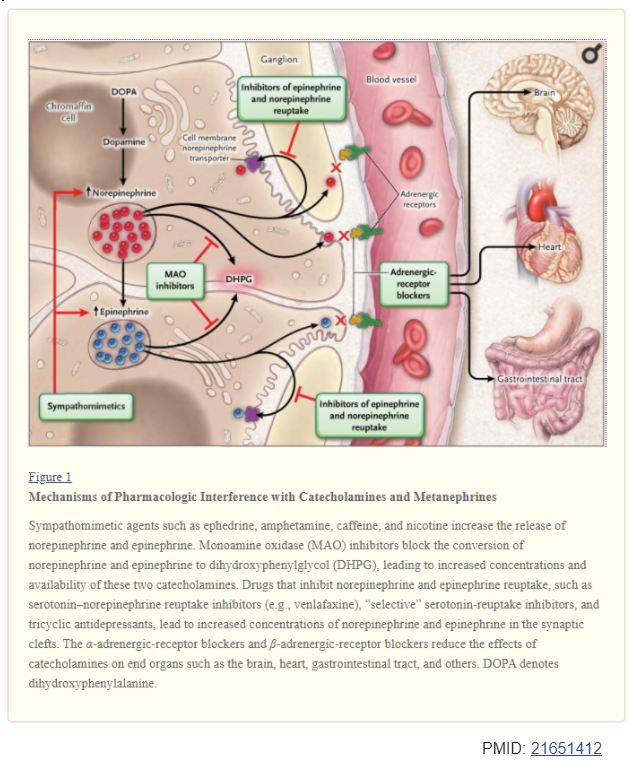
12/ Which of the following medications can cause elevation of catecholamines?
13/ All the above
 Sympathomimetics, SSRIs, MAO inhibitors, α/β blockers
Sympathomimetics, SSRIs, MAO inhibitors, α/β blockers false
false  catecholamines
catecholamines
 Acetaminophen interferes w/ liquid chromatography
Acetaminophen interferes w/ liquid chromatography
 Stop medications ~2 wks prior to testing
Stop medications ~2 wks prior to testing
 If not,
If not, Clonidine suppression test
Clonidine suppression test
(PMID: 21615192, 28752085, 21651412)
 Sympathomimetics, SSRIs, MAO inhibitors, α/β blockers
Sympathomimetics, SSRIs, MAO inhibitors, α/β blockers false
false  catecholamines
catecholamines Acetaminophen interferes w/ liquid chromatography
Acetaminophen interferes w/ liquid chromatography Stop medications ~2 wks prior to testing
Stop medications ~2 wks prior to testing If not,
If not, Clonidine suppression test
Clonidine suppression test (PMID: 21615192, 28752085, 21651412)
14/ Biochemical results can help classify the tumour:
 Adrenergic:
Adrenergic: E&NE, M & NM, VMA
E&NE, M & NM, VMA
 Noradrenergic:
Noradrenergic: NE, NM, VMA
NE, NM, VMA
 Dopaminergic:
Dopaminergic: Dopamine, HVA
Dopamine, HVA
 Adrenergic:
Adrenergic: E&NE, M & NM, VMA
E&NE, M & NM, VMA Noradrenergic:
Noradrenergic: NE, NM, VMA
NE, NM, VMA Dopaminergic:
Dopaminergic: Dopamine, HVA
Dopamine, HVA
15/ Imaging  localise tumour & identify mets
localise tumour & identify mets
CT & MRI both good sens & specificity
good sens & specificity
 Features can include:
Features can include:
 attenuation on non-con CT (most >20 HU)
attenuation on non-con CT (most >20 HU)
 vascularity, cystic or hemorrhagic change
vascularity, cystic or hemorrhagic change
 Delayed contrast washout
Delayed contrast washout
 T2 signal on MRI
T2 signal on MRI
Source: http://uptodate.com
 localise tumour & identify mets
localise tumour & identify metsCT & MRI both
 good sens & specificity
good sens & specificity Features can include:
Features can include: attenuation on non-con CT (most >20 HU)
attenuation on non-con CT (most >20 HU) vascularity, cystic or hemorrhagic change
vascularity, cystic or hemorrhagic change Delayed contrast washout
Delayed contrast washout  T2 signal on MRI
T2 signal on MRISource: http://uptodate.com
16/ Functional imaging can be used to:
 Localise tumour when CT/MRI negative
Localise tumour when CT/MRI negative
 Identify metastatic/multifocal disease
Identify metastatic/multifocal disease
 Follow-up screening
Follow-up screening
Functional imaging may include integrated PET CT/MRI or scintigraphy
Let’s review some options
 Localise tumour when CT/MRI negative
Localise tumour when CT/MRI negative Identify metastatic/multifocal disease
Identify metastatic/multifocal disease Follow-up screening
Follow-up screening Functional imaging may include integrated PET CT/MRI or scintigraphy
Let’s review some options

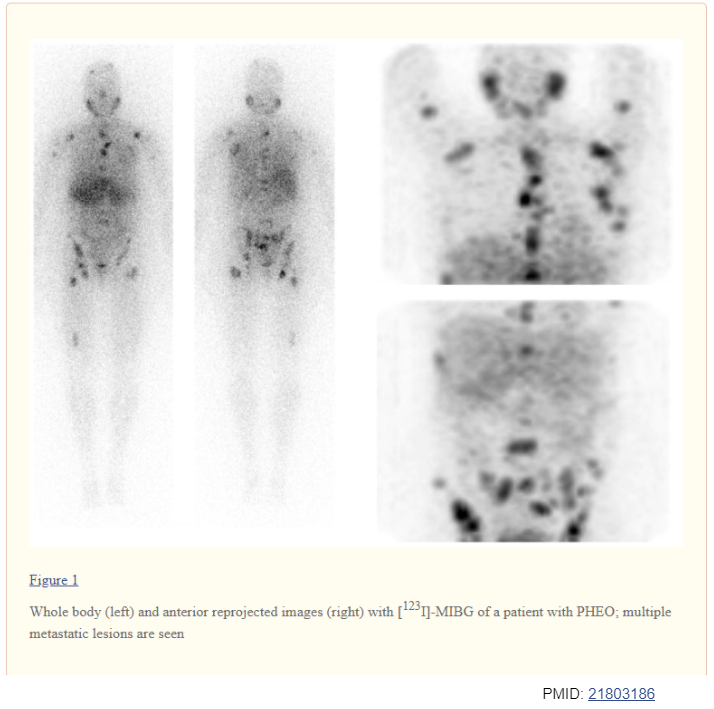
17/ MIBG Scintigraphy:
 Iobenguane I-123 is a compound similar to NE
Iobenguane I-123 is a compound similar to NE
 Uptake at adrenergic tissue
Uptake at adrenergic tissue
 Uptake in normal adrenals can by asymmetrical
Uptake in normal adrenals can by asymmetrical
 Correlate with CT/MRI
Correlate with CT/MRI
PMID: 21803186
 Iobenguane I-123 is a compound similar to NE
Iobenguane I-123 is a compound similar to NE Uptake at adrenergic tissue
Uptake at adrenergic tissue Uptake in normal adrenals can by asymmetrical
Uptake in normal adrenals can by asymmetrical Correlate with CT/MRI
Correlate with CT/MRIPMID: 21803186
18/ FDG PET:
 FDG is a glucose analogue
FDG is a glucose analogue
 Useful in tumours with
Useful in tumours with  glycolytic activity
glycolytic activity
Ga68 DOTATATE PET:
 Somatostatin analogue
Somatostatin analogue
 Good uptake in well-differentiated tumours
Good uptake in well-differentiated tumours

 Sensitivity &
Sensitivity &  Resolution
Resolution

 Radiation
Radiation
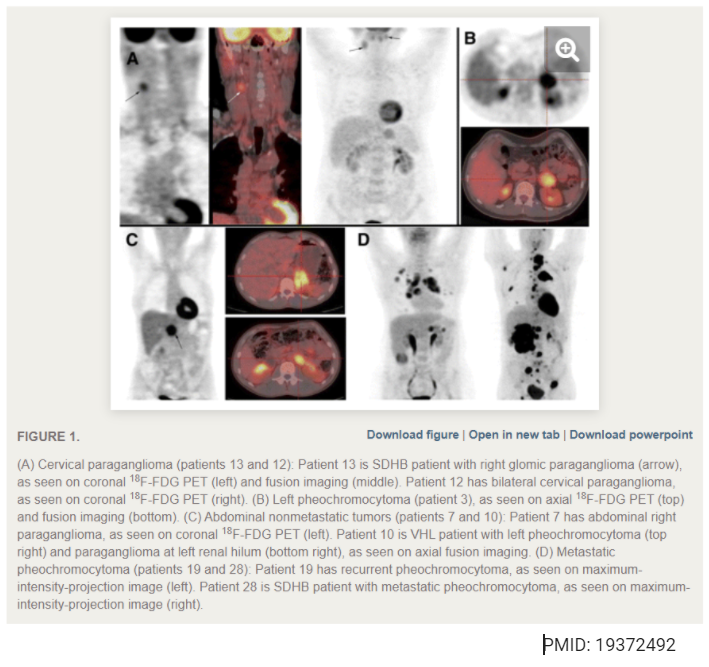
PMID: 19372492
 FDG is a glucose analogue
FDG is a glucose analogue Useful in tumours with
Useful in tumours with  glycolytic activity
glycolytic activityGa68 DOTATATE PET:
 Somatostatin analogue
Somatostatin analogue Good uptake in well-differentiated tumours
Good uptake in well-differentiated tumours
 Sensitivity &
Sensitivity &  Resolution
Resolution 
 Radiation
RadiationPMID: 19372492
19/ This helpful diagram from a comprehensive review or PCC/PGL (PMID:30603807) summarises an approach to diagnostic evaluation:
20/  Surgical removal of a PCC/PGL can trigger a life threatening catecholamine storm
Surgical removal of a PCC/PGL can trigger a life threatening catecholamine storm

This can cause:
 Hypertensive Crisis
Hypertensive Crisis
 Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias
 Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction
 Stroke
Stroke
 Also post-operatively a drop in catecholamines can lead to
Also post-operatively a drop in catecholamines can lead to  BP
BP
 Surgical removal of a PCC/PGL can trigger a life threatening catecholamine storm
Surgical removal of a PCC/PGL can trigger a life threatening catecholamine storm

This can cause:
 Hypertensive Crisis
Hypertensive Crisis Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction Stroke
Stroke Also post-operatively a drop in catecholamines can lead to
Also post-operatively a drop in catecholamines can lead to  BP
BP
21/ Aim of medical management is to prevent fluctuations in BP & post op  BP
BP
Always THINK before
before 
Start with alpha blockers before beta blockers!
 Initial use of beta blockers
Initial use of beta blockers  unopposed alpha action
unopposed alpha action  catecholamine storm
catecholamine storm 

 BP
BP Always THINK
 before
before 
Start with alpha blockers before beta blockers!
 Initial use of beta blockers
Initial use of beta blockers  unopposed alpha action
unopposed alpha action  catecholamine storm
catecholamine storm 

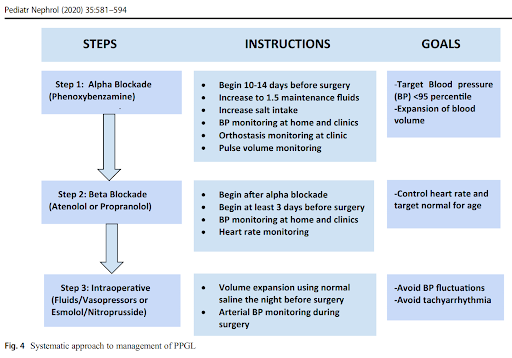
22/ There are no internationally approved protocols for management of PCC/PGLs
The table below summarises a suggested approach (PMID:30603807)
 Metyrosine = tyrosine hydroxylase inhibitor
Metyrosine = tyrosine hydroxylase inhibitor  catecholamine synthesis +/- alpha blockers can
catecholamine synthesis +/- alpha blockers can  BP lability peri-op
BP lability peri-op
The table below summarises a suggested approach (PMID:30603807)
 Metyrosine = tyrosine hydroxylase inhibitor
Metyrosine = tyrosine hydroxylase inhibitor  catecholamine synthesis +/- alpha blockers can
catecholamine synthesis +/- alpha blockers can  BP lability peri-op
BP lability peri-op
23/ Take home points:
 PCC/PGL are rare
PCC/PGL are rare
 Only ~50% have classic symptom triad
Only ~50% have classic symptom triad
 Genetics testing for all children
Genetics testing for all children
 Biochemistry
Biochemistry  CT/MRI
CT/MRI Functional imaging
Functional imaging
 Remember
Remember before
before to avoid a catecholamine storm!!
to avoid a catecholamine storm!!
Thanks #ASPNeph #FellowFOAMgroup @drM_sudha @RoshanPGeorgeMD
 PCC/PGL are rare
PCC/PGL are rare Only ~50% have classic symptom triad
Only ~50% have classic symptom triad Genetics testing for all children
Genetics testing for all children Biochemistry
Biochemistry  CT/MRI
CT/MRI Functional imaging
Functional imaging Remember
Remember before
before to avoid a catecholamine storm!!
to avoid a catecholamine storm!!Thanks #ASPNeph #FellowFOAMgroup @drM_sudha @RoshanPGeorgeMD

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter