Here is the thread of our new pre-print 
Sensitivity of infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 variants to neutralizing antibodies
1/16 https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.02.12.430472v1

Sensitivity of infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 variants to neutralizing antibodies
1/16 https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.02.12.430472v1
In this study, we compared the sensitivity of B.1.1.7, B.1.351 variants and the pre-existing D614G virus to antibody neutralization, using infectious SARS-CoV-2 isolates.
We tested monoclonals antibodies, and convalescent and vaccinees sera.
2/16
We tested monoclonals antibodies, and convalescent and vaccinees sera.
2/16
We isolated B.1.1.7 and B.1.531 from nasal swabs of patients with RT-qPCR and sequence-diagnosed infection. We make 1-2 passages on Vero cells to amplify the virus and re-sequenced to confirm the identity of B.1.1.7 and B.1.531.
3/16
3/16
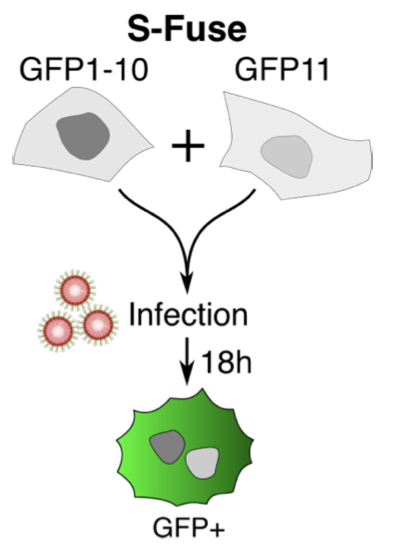
To measure neutralisation titers, we used a high-throughput neutralization assay developed in lab that we called S-Fuse.
It's based on U2OS-ACE2 cells expressing the GFP-split system. Upon infection, the cells fuse together, generating a GFP signal after a few hours.
4/16
It's based on U2OS-ACE2 cells expressing the GFP-split system. Upon infection, the cells fuse together, generating a GFP signal after a few hours.
4/16
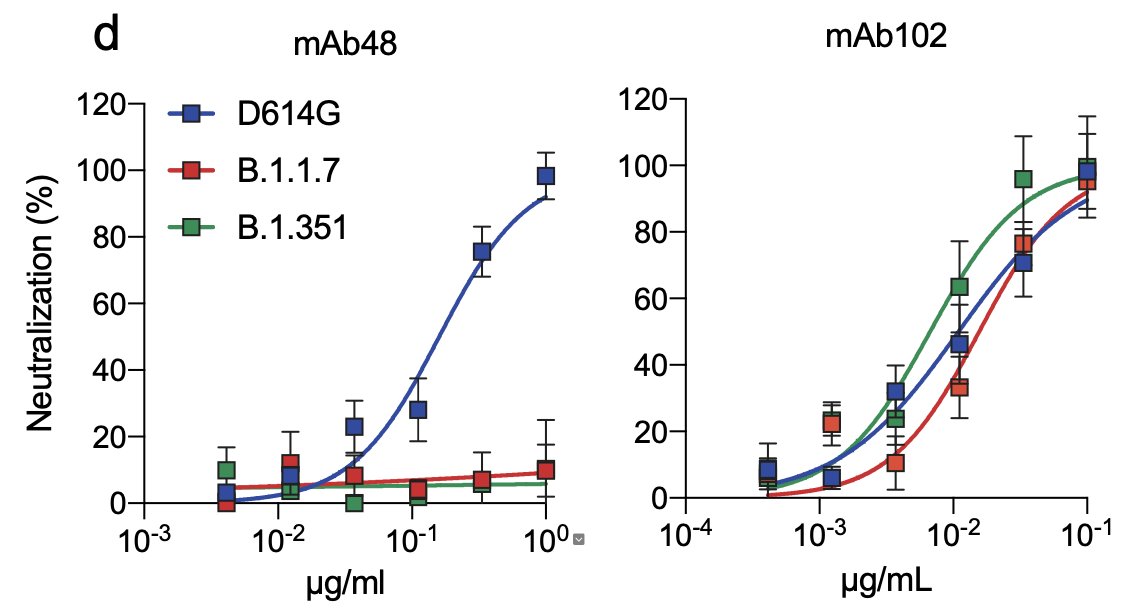
We then test the sensitivity of the three viral strains to two anti-RBD antibodies, mAb102 and mAb48.
MAb102 similarly neutralized the three viral strains, but mAb48 was inactive against B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 variants
6/16
MAb102 similarly neutralized the three viral strains, but mAb48 was inactive against B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 variants
6/16
Next, we randomly selected 28 samples, including critical, severe, and mild cases, all from @CHR_Orleans
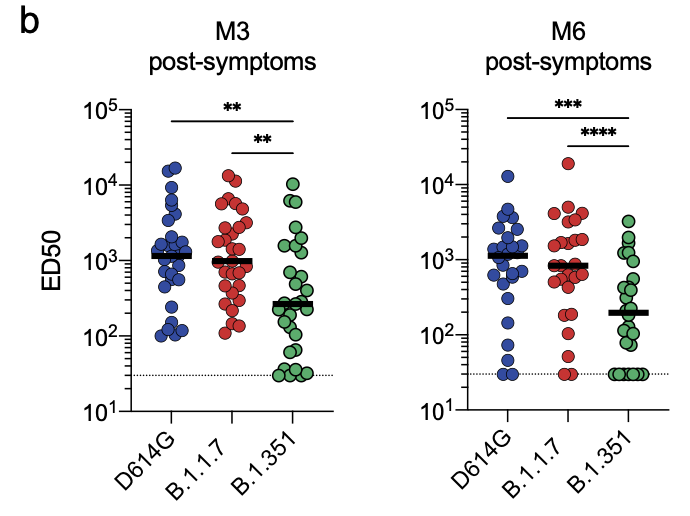
The D614G and B.1.1.7 strains were similarly sensitive to sera, but B1.351 showed a significant decrease of 5 to 10-fold at the two time-points tested (Month 3 and 6).
7/16
The D614G and B.1.1.7 strains were similarly sensitive to sera, but B1.351 showed a significant decrease of 5 to 10-fold at the two time-points tested (Month 3 and 6).
7/16
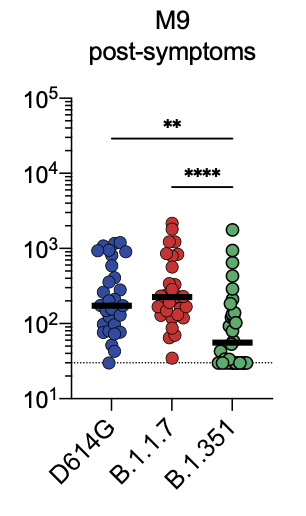
We also tested 30 sera collected 9 month after onset of symptoms from another cohort of staff from @CHRUStrasbourg that experienced a mild disease. We obtained similar results.
8/16
8/16
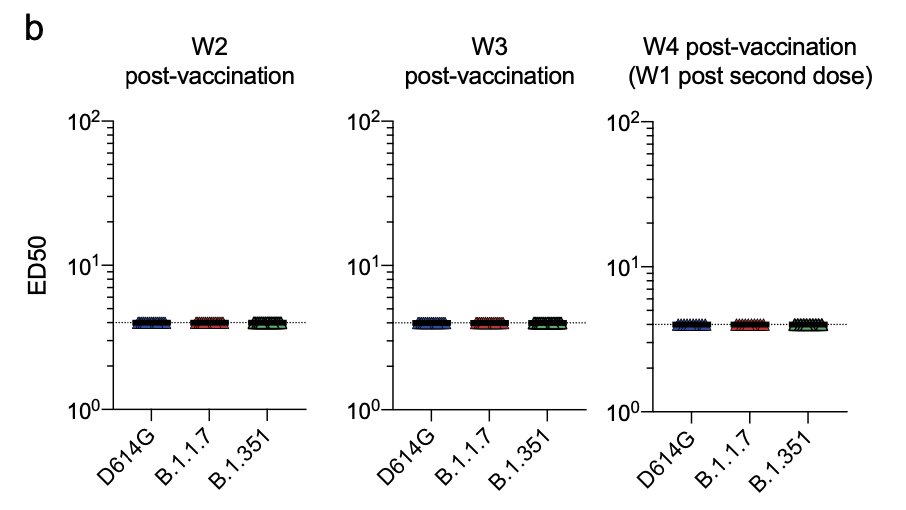
Finally, we asked whether vaccine-elicited antibodies inhibit infection by the different variants in a cohort of 19 individuals. We collected sera and nasal swabs at week 2, 3 and 4 (corresponding to week 1 after the second dose).
9/16
9/16
We observed a delay in the appearance of neutralizing antibodies against B.1.1.7 and B.1.351. The titers remained lower against B.1.351.
10/16
10/16
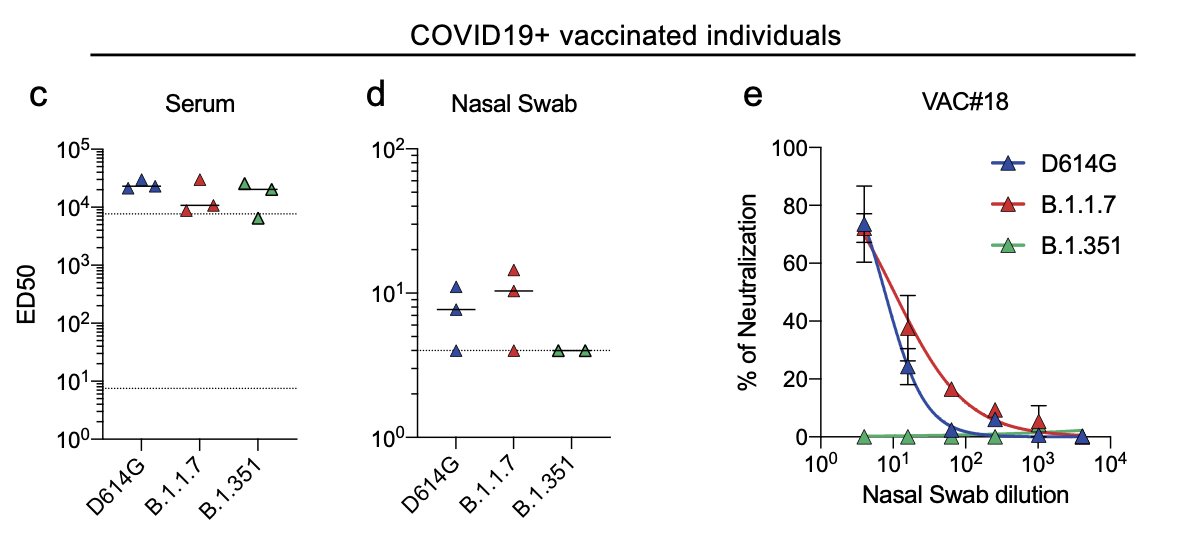
We also analyzed three vaccine recipients who were previously infected by SARS-CoV-2.
Their neutralizing titers were strikingly high at week 2 in their sera and two out of the three displayed a neutralizing activity against D614G and B.1.1.7 in their nasal swabs.
12/16
Their neutralizing titers were strikingly high at week 2 in their sera and two out of the three displayed a neutralizing activity against D614G and B.1.1.7 in their nasal swabs.
12/16
In conclusion, we report that neutralization of sera is slightly reduced but largely preserved activity against B.1.1.7. In contrast, the B.1.351 is less sensitive or even unsensitive to a large part of the sera tested, particularly when global antibody levels are low.
13/16
13/16
Of course so many things remain to be done, cellular immunity, B cell memory, innate immune responses...! All of these is ongoing in @Virus_Immunity Lab, at @institutpasteur and all over the world. Can’t wait the data!
14/16
14/16
HUGE kudos to all people involved!!
The crazy @Delphine_Planas who worked 24/24 7/7

The @Virus_Immunity @OlivierSchwartz Lab, @LudivineGrzelak @JBuchrieser @MaaranRajah. Our outstanding friends @institutpasteur @MOUQUETHugo1 @SimonLoriereLab @NathalieAulner
15/16
The crazy @Delphine_Planas who worked 24/24 7/7


The @Virus_Immunity @OlivierSchwartz Lab, @LudivineGrzelak @JBuchrieser @MaaranRajah. Our outstanding friends @institutpasteur @MOUQUETHugo1 @SimonLoriereLab @NathalieAulner
15/16
And our amazing collaborators @CHRUStrasbourg @FafiKremer, @UnivTours @CHRU_Tours @KarlStefic, @HopitalPompidou @APHP and @CHR_Orleans
16/16
16/16

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter