How do environmental exposures and lifestyle factors compare to genetics and clinical factors for predicting risk of type 2 diabetes? Our paper just out in Diabetes Care introduces the polyexposure risk score ( #PXS) to investigate this question:
https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/early/2021/02/08/dc20-2049
1/n
https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/early/2021/02/08/dc20-2049
1/n
We first conducted an exposure-wide association study (XWAS) and subsequently used ML feature selection procedures to build a PXS from an initial set of >100 exposure and lifestyle factors recorded in the UK Biobank. 2/n
What are the factors selected in the T2D PXS?
Alcohol intake
Past tobacco usage
Household income
Insomnia
Snoring
Own/rent
Dietary restriction
Comparative body size at age 10
Major dietary changes in past 5 yrs
Spread type used
Tea intake/day
3/n
Alcohol intake
Past tobacco usage
Household income
Insomnia
Snoring
Own/rent
Dietary restriction
Comparative body size at age 10
Major dietary changes in past 5 yrs
Spread type used
Tea intake/day
3/n
We found that:
PXS > PGS in predicting T2D [C statistics 0.709 and 0.762, respectively]
On top of established clinical risk factors, PXS > PGS in improving T2D classification accuracy
4/n
PXS > PGS in predicting T2D [C statistics 0.709 and 0.762, respectively]
On top of established clinical risk factors, PXS > PGS in improving T2D classification accuracy
4/n
Individuals in the top 10% of PXS had 5.90 fold greater risk than the remaining population. Those in top 10% of PGS had 2.00 fold greater risk.
5/n
5/n
Previous studies on nongenetic exposures (eg factors not measured on a GWAS array) focused on individual/small sets of variables without much consideration for dense correlation between exposures. Our approach considers the #exposome to select for the most important factors. 6/n
Very grateful to @chiragjp, @jotzou, @arjunmanrai, @cmlakhan, Danielle Rasooly, and all the participants and staff from @ukbiobank!! 7/n

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter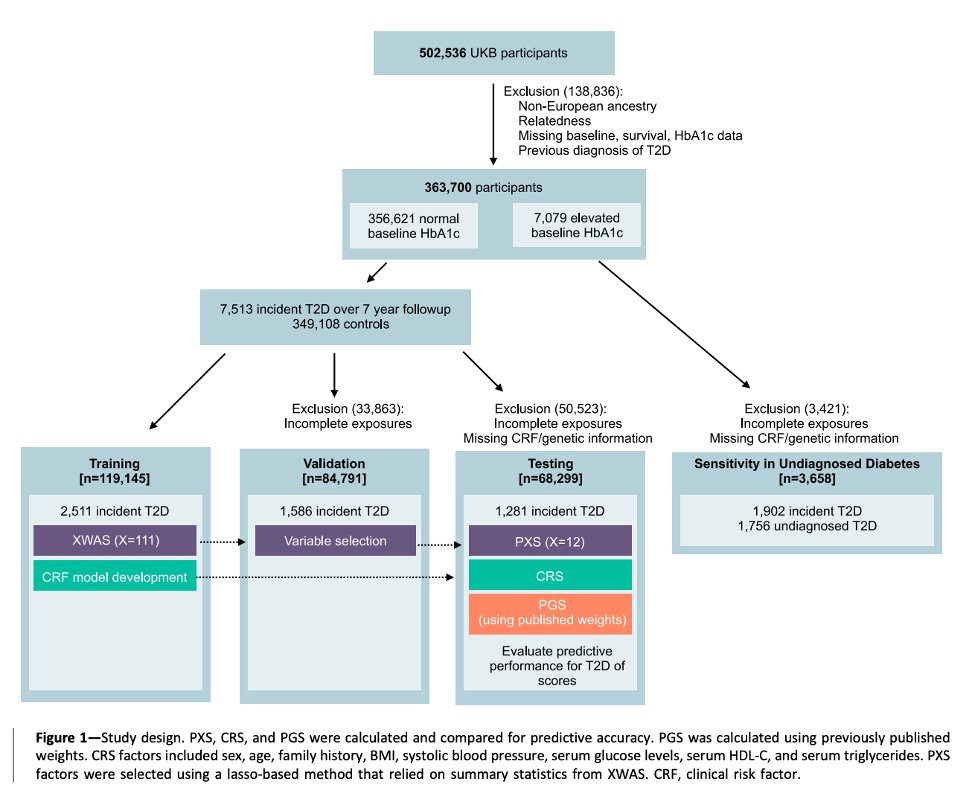
![We found that: PXS > PGS in predicting T2D [C statistics 0.709 and 0.762, respectively]On top of established clinical risk factors, PXS > PGS in improving T2D classification accuracy 4/n We found that: PXS > PGS in predicting T2D [C statistics 0.709 and 0.762, respectively]On top of established clinical risk factors, PXS > PGS in improving T2D classification accuracy 4/n](https://pbs.twimg.com/media/Et5FHGCWYAEHz-9.png)
 Read more:
Read more: 

