Hello Earthlings! In between celebrating the new mission arrivals at #Mars, I have TWO exciting science results to share with you from my mission!
Hello Earthlings! In between celebrating the new mission arrivals at #Mars, I have TWO exciting science results to share with you from my mission! 


 Thread coming up, but if you can’t wait… skip to the full story here
Thread coming up, but if you can’t wait… skip to the full story here 

https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Human_and_Robotic_Exploration/Exploration/ExoMars/ExoMars_discovers_new_gas_and_traces_water_loss_on_Mars
#ExploreFarther
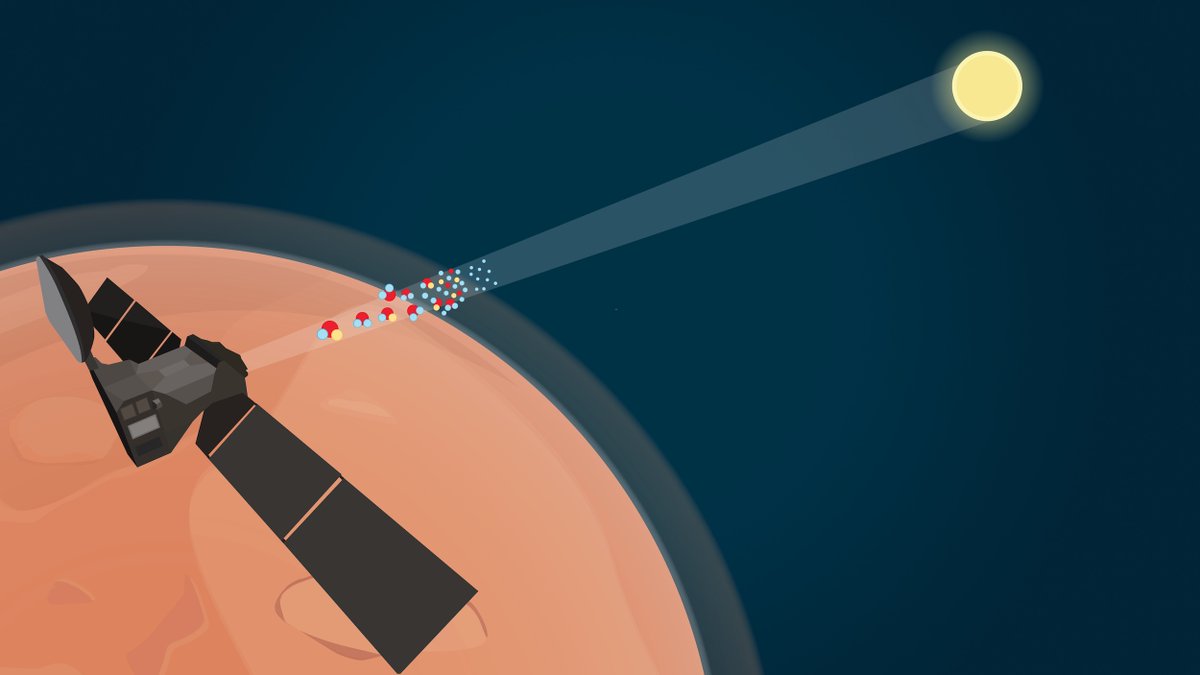
I’m proud to report I’ve discovered my first new trace gas in the atmosphere of #Mars! Exactly what I’m designed to do!  It’s hydrogen chloride (HCl), representing a new chemical cycle to figure out. Let me explain more…
It’s hydrogen chloride (HCl), representing a new chemical cycle to figure out. Let me explain more…
 https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Videos/2021/02/Discovering_new_gases_on_Mars
https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Videos/2021/02/Discovering_new_gases_on_Mars
 It’s hydrogen chloride (HCl), representing a new chemical cycle to figure out. Let me explain more…
It’s hydrogen chloride (HCl), representing a new chemical cycle to figure out. Let me explain more… https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Videos/2021/02/Discovering_new_gases_on_Mars
https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Videos/2021/02/Discovering_new_gases_on_Mars
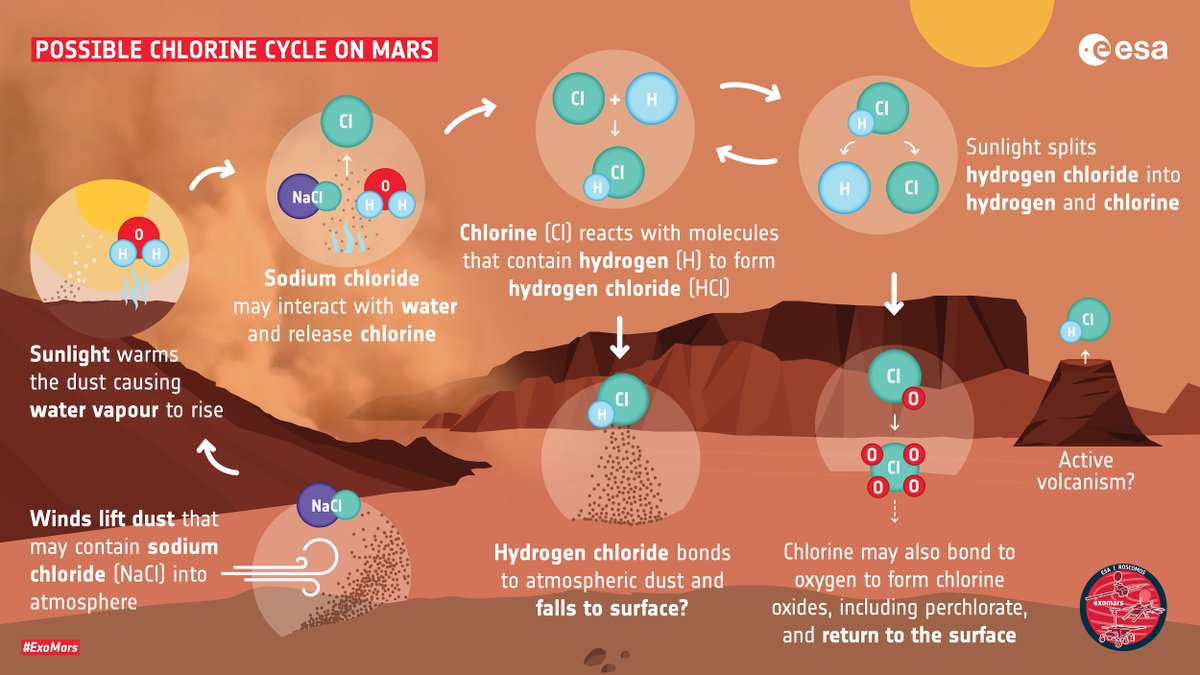
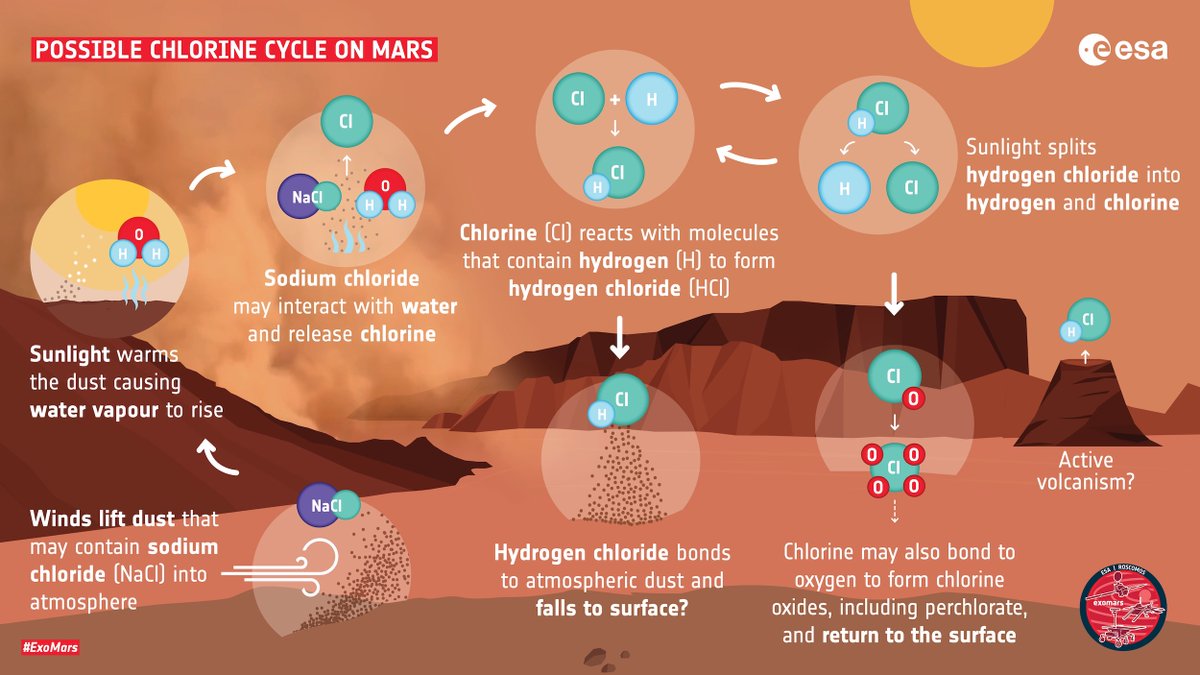
Although chlorine-based gases sometimes point to volcanic activity, I detected HCl in very distant locations at the same time (& didn’t find other volcanic gases) so I think it’s linked to an entirely new surface-atmosphere interaction driven by dust seasons instead

In a process similar to that on Earth, salts in the form of sodium chloride – remnants of evaporated oceans & embedded in the dusty surface of #Mars – are lifted into the atmosphere by winds….
https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2021/02/How_hydrogen_chloride_may_be_created_on_Mars
https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2021/02/How_hydrogen_chloride_may_be_created_on_Mars
…Sunlight warms the atmosphere causing dust, together with water vapour released from ice caps, to rise. The salty dust reacts with atmospheric water to release chlorine, which itself then reacts with molecules containing hydrogen to create hydrogen chloride!
I first spotted HCl in the global dust storm of 2018, observing it appear simultaneously in northern & southern hemispheres. It disappeared surprisingly quickly again at the end of the dust season. There’s hints of it coming back again the next year, too! https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Human_and_Robotic_Exploration/Exploration/ExoMars/ExoMars_discovers_new_gas_and_traces_water_loss_on_Mars
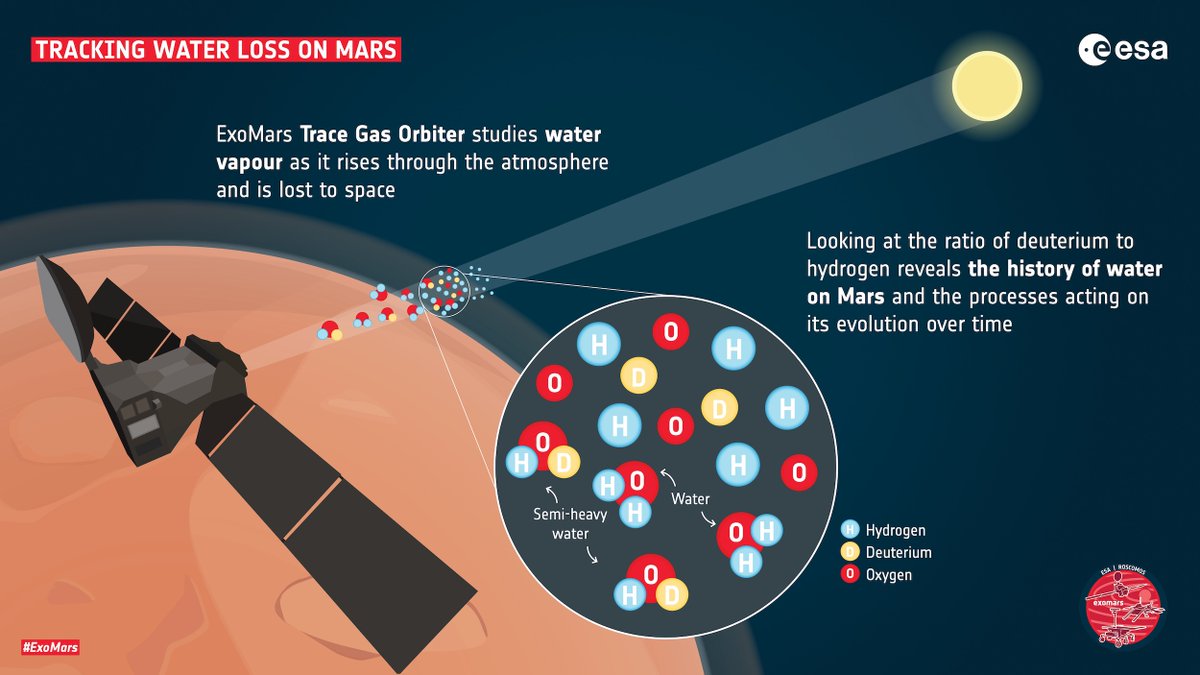
My second big revelation is that we need to refine the way we’re looking at how #Mars has lost its water over time – a process also linked to seasonal changes. Let me explain…


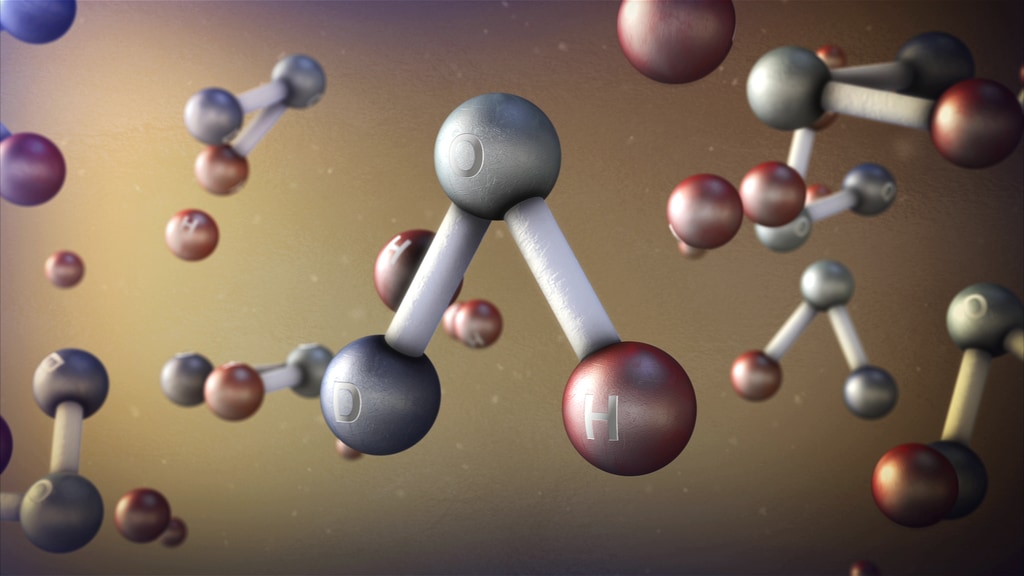
I’ve been studying water vapour and ‘semi-heavy’ water  (where one hydrogen atom is replaced by a deuterium atom, a form of hydrogen with an additional neutron)...
(where one hydrogen atom is replaced by a deuterium atom, a form of hydrogen with an additional neutron)...
https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2021/02/ExoMars_observing_water_in_the_martian_atmosphere2
 (where one hydrogen atom is replaced by a deuterium atom, a form of hydrogen with an additional neutron)...
(where one hydrogen atom is replaced by a deuterium atom, a form of hydrogen with an additional neutron)...https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2021/02/ExoMars_observing_water_in_the_martian_atmosphere2
The deuterium to hydrogen ratio, D/H, is our chronometer that tells us how water loss evolved over time. Thanks to my data, scientists can better calibrate this chronometer and test for potential new reservoirs of water on Mars…
( Credit: NASA/Goddard)
Credit: NASA/Goddard)
(
 Credit: NASA/Goddard)
Credit: NASA/Goddard)
… Previous measurements only provided the average over the depth of the whole atmosphere. My observations are like getting an upgrade from a 2D view to being able to explore the atmosphere in #3D 
https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2018/04/How_ExoMars_studies_the_atmosphere

https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2018/04/How_ExoMars_studies_the_atmosphere
The new measurements reveal dramatic variability in D/H with altitude and season as the water rises from its original location. Dust storms accelerate the water loss, and so does the intense southern summer 

My data also show that once water is fully vapourised, it has a large enrichment in semi-heavy water, and a D/H ratio six times greater than Earth’s, confirming that large amounts of water have been lost over time 
( @ExoMars_CaSSIS: https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2019/02/Eberswalde_crater_delta)
@ExoMars_CaSSIS: https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2019/02/Eberswalde_crater_delta)

(
 @ExoMars_CaSSIS: https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2019/02/Eberswalde_crater_delta)
@ExoMars_CaSSIS: https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2019/02/Eberswalde_crater_delta)
I’m very proud that my observations are enabling scientists to explore the martian atmosphere like never before! 
Full story : https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Human_and_Robotic_Exploration/Exploration/ExoMars/ExoMars_discovers_new_gas_and_traces_water_loss_on_Mars
#ExploreFarther

Full story : https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Human_and_Robotic_Exploration/Exploration/ExoMars/ExoMars_discovers_new_gas_and_traces_water_loss_on_Mars
#ExploreFarther

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter