#GunsofFebruary On 8 Feb '45 the Reichswald area of Germany was subjected to the largest @CanadianArmy artillery barrage in #WW2 Over 1000 guns fired in support of First Canadian Army's Operation VERITABLE. Here are some #artillery facts about the operation.
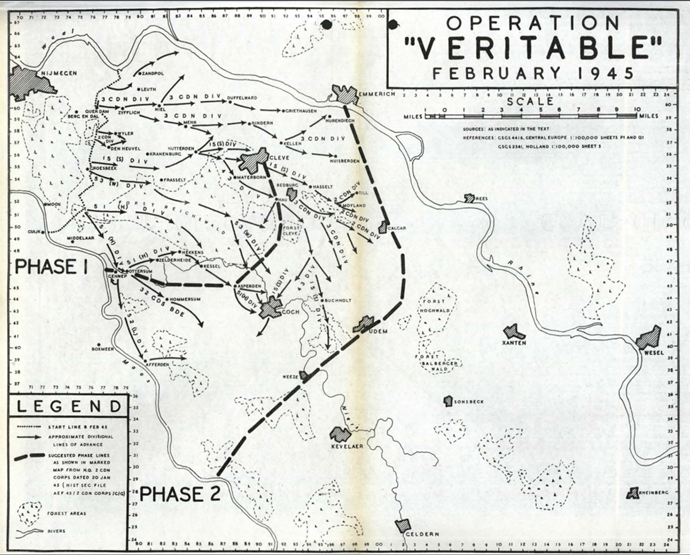
First Canadian Army’s drive to clear the enemy from between the Maas and Rhine Rivers and thus establish the jumping off point for the Allied crossing of the Rhine. First Canadian Army was commanded by General Harry Crerar, a Gunner.
First Canadian Army was bolstered by XXX British Corps commanded by LGen Brian Horrocks. XXX Corps was the tip of the spear. The manouvre plan was to assault on a 5-division frontage:
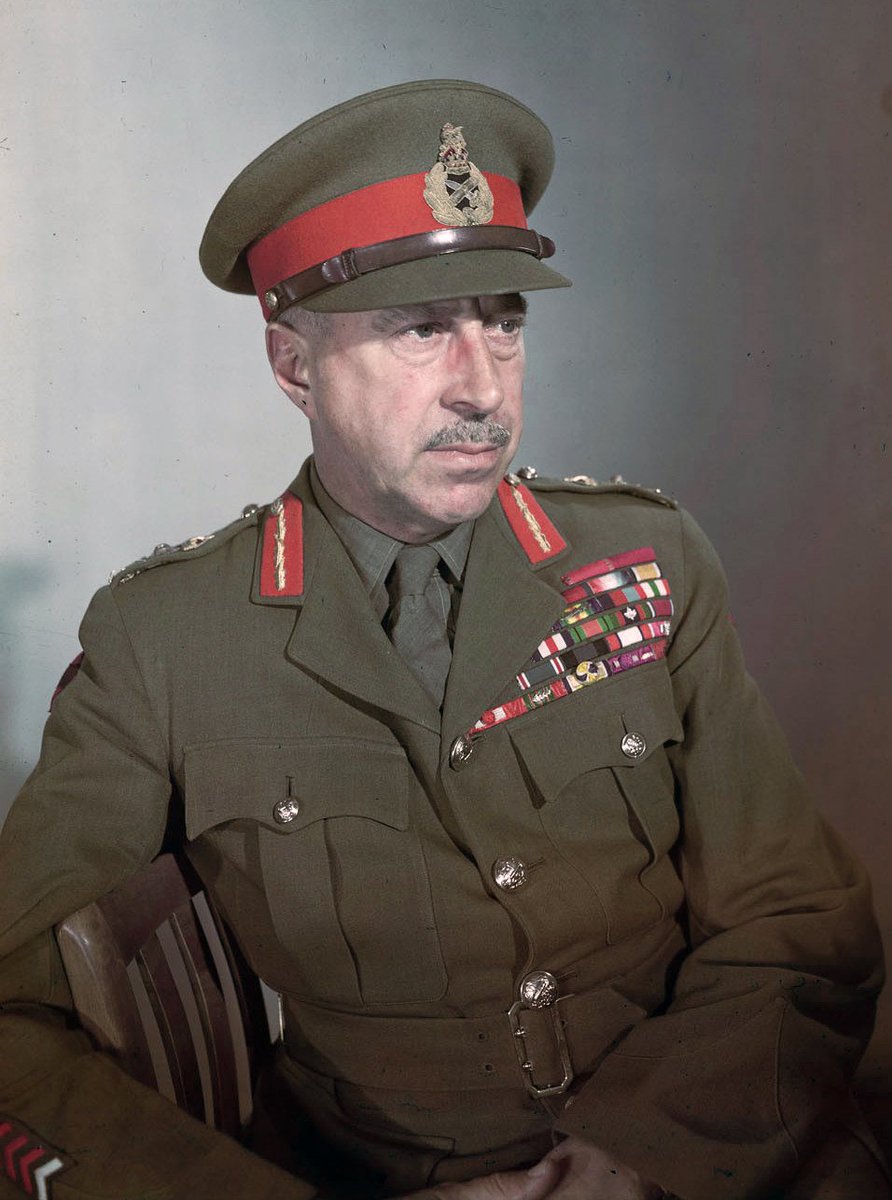
The senior gunner in FCA, the Brigadier Royal Artillery (BRA), was Brigadier EC Plow (pictured). Plow had at his disposal a total of 938 field, medium, heavy and super-heavy guns augmented with 96 heavy anti-aircraft guns employed in a ground role. http://gunner.ca/English/Great%20Gunners/plow.htm
The majority of the fire support came from the Divisional Artilleries. By February 1945 a Canadian Divisional Artillery was organized as follows:
The DAs were reinforced by Med Regts, from Army Groups Royal Artillery (AGRA) which were assigned to FCA. An AGRA consisted of, typically, one heavy regt of 7.2- or 8-inch howitzers or 155-mm guns, three medium regts of 4.5- or 5.5-inch guns, and one or two regts of 25-pounders.
Five AGRAs: 3rd, 4th, 5th and 9th British AGRAs as well as the 2nd Canadian AGRA. To give an idea of what an AGRA brought to the fight, here's how 2nd Cdn AGRA was organized:
The Fire Plan had three objectives: firstly, to neutralize all known enemy batteries, secondly to destroy all known headquarters and communications nodes, and finally to neutralize enemy in the line of advance of the infantry.
The fire plan consisted of three elements: first, a five-hour period of artillery preparation that included a deceptive smoke screen “to stupefy the enemy defences prior to H Hr and .... to blind the form up and move to the start line from the possible enemy OPs.”
Secondly, a standing barrage of smoke and high explosive of an hour’s duration to allow the infantry to form up on the start line, and finally, the protective barrage that supported the attacking forces during their advance.
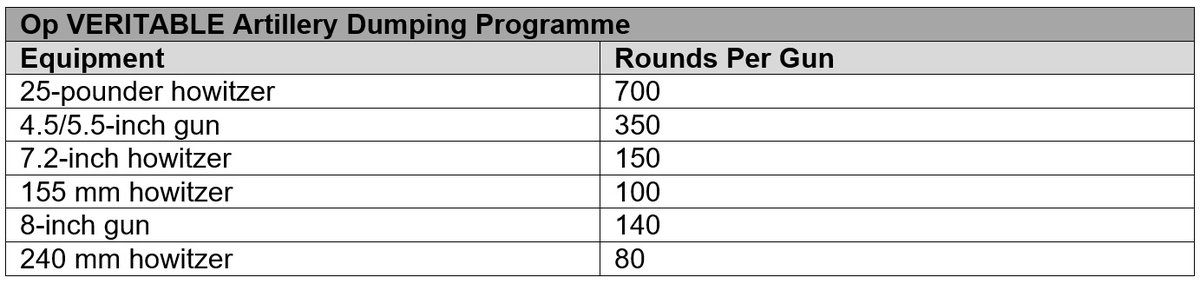
Naturally, the ammunition required was massive: it totalled 500,000 rounds and weighed a total of 11,000 tons. Here's the dumping programme that was required by rounds-per-gun.
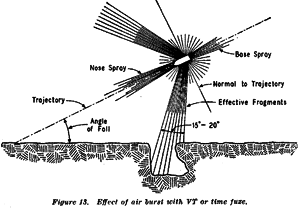
Included in the ammunition was a new fuze, known as "Variable Time." It was first used by the US Artillery during the Battle of the Bulge and was included in the FCA ammunition for VERITABLE. The fuze used a radar emitter in the nose to determine the perfect height of burst....
...for effective air burst. After its first use at St. Vith , 23 Dec 44, US Artillery report stated: “it is hard to believe, but the cumulative figures indicate 2,000 enemy dead, which could be observed and counted…VT ammunition is most deadly.”
Also in the arsenal was the 1st Canadian Rocket Battery: The battery consisted of twelve “projectors” which were two-wheel trailers mounting 32 light-gauge tubes. Each tube fired a three-inch rocket with a 29-pound high explosive warhead to ranges between 4,000 and 8,000 yards.
The rockets were fired using a ripple effect with a quarter second between launches, so that the rockets did not hit each other in flight. In one salvo, the twelve projectors fired an impressive total of 384 rockets that produced an impact area of approximately 700 square yards
By D-3, guns began deploying into the area. Like the ammunition dumping programme, the occupation of new gun positions occurred at night. Some of the routes available were mere cart tracks cutting through the numerous tree plantations that had turned soft and muddy.
In one instance, the Gun Position Officer of a heavy battery had to guide each gun to its position individually, proceeding it on foot along a narrow path, guiding the driver of the gun tractor by a flashlight with two layers of heavy paper wrapped around it to dim the light.
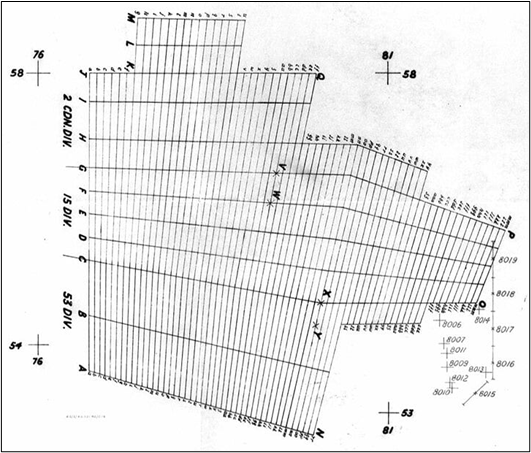
On D-2, 6 February, graphical descriptions of each battery’s targets and fire tasks, known as traces, were delivered to the batteries partaking in VERITABLE. The various command posts thereafter spent a busy 48 hours making the necessary calculations to engage their targets.
This is what the trace looked like. You'll note there are no lanes for 51 Highland Division, whose commander decided to opt for a series of concentrations rather than a barrage.
D-day, 8 February, dawned grey and rainy. At 0500 hrs the fire plan began. Horrocks was perched in an observation post constructed for him by the Royal Engineers consisting of a platform half-way up a tree and recalled “the noise was unbelievable.”
The German artillery, although much depleted, still posed a threat to troops exposed during the advance. The German 84th Division had 114 howitzers at its disposal. Thus a key objective of the fire plan was the neutralization of the German artillery and mortar threat.
In the days leading up to the operation, the First Canadian Army identified 45 hostile battery locations. During the preliminary bombardment, a concentration was scheduled to engage each of the identified German batteries with an average Allied-to-German gun ratio of 40:1.
The overwhelming fire superiority of the First Canadian Army is reflected in the following observation by XXX British Corps: “At 0900 hrs a single medium gun which had been located by Sound Rangers was bombarded by four Medium [Regiments].”
Counter Mortar fire was equally important. The 2nd Canadian Division CMO had at his disposal 20 Observation Posts, two radars and two Mortar Locators to locate German mortars. The fire of ten 7.2-inch howitzer batteries of four guns each was dedicated to the CMO.
A total of 5,953 tons of munitions were fired during VERITABLE consisting of 450,997 shells. the destructive effect of the artillery during VERITABLE was minor; only about 2-3% of German casualties resulted from artillery and of the 28 German guns that were engaged....
....during counter-battery fire, it was determined 5 were probably hit and 7 were withdrawn. The VERITABLE fire plan demonstrated the true value of artillery lay not in its destructive effects as much as in its morale effects...
namely its ability to suppress the enemy and prevent their movement and retaliatory firing. A post war analysis of the barrage found: “His troops, particularly those of the 84th Division, appeared to find the moral effects of our artillery fire devastating....
Suffering from the nervous strain of the prolonged bombardment, prisoners stated that they had the impression of being opposed by overwhelming forces which it was useless to resist…during the barrage it was impossible to send runners or to move local reserves.”
What the VERITABLE fire plan demonstrates is that after five years of war, the fire support system of the First Canadian Army had achieved a level of efficiency and effectiveness that allowed it to literally blast its way through German defences.

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter