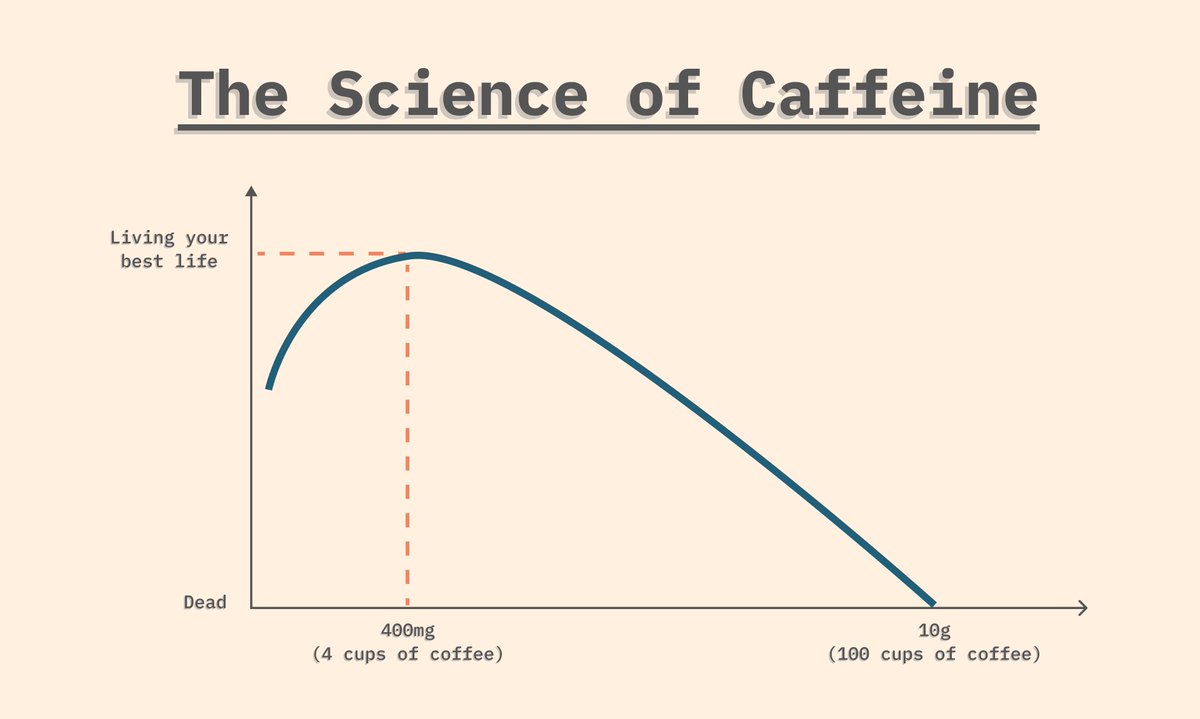
2/7
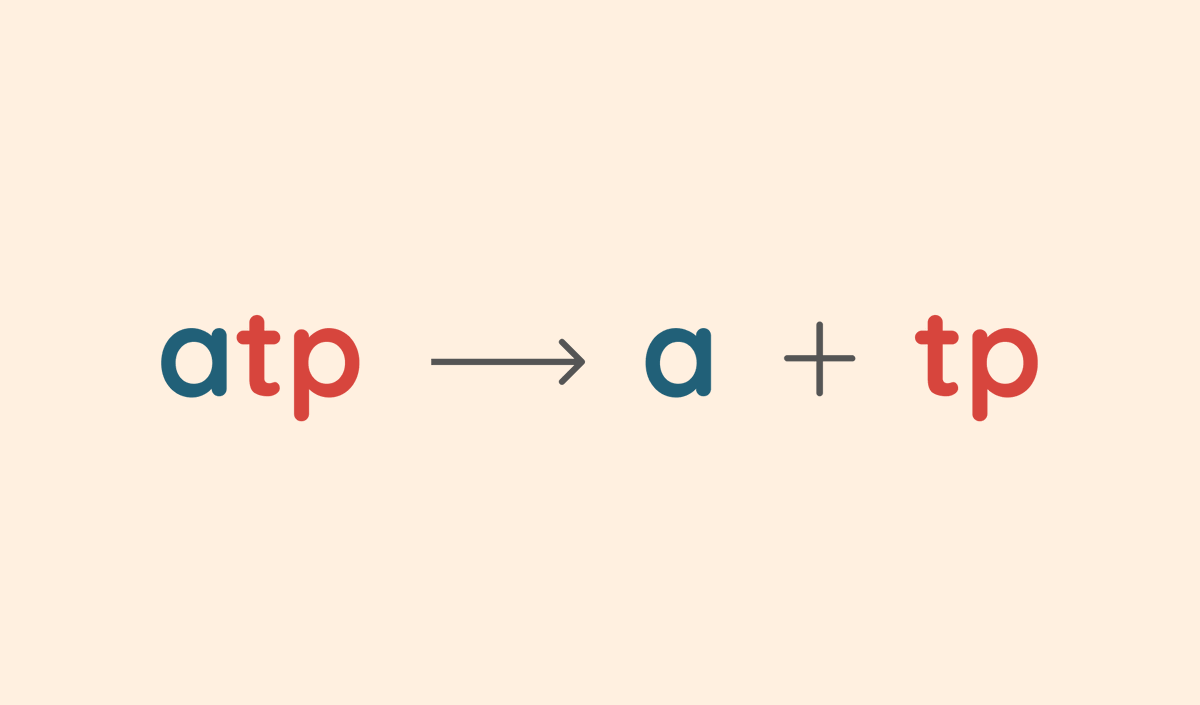
Your body gets energy by breaking down a molecule called ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate).
As is obvious, one of the things it breaks it down into is the ‘A’ in ATP – Adenosine.
Your body gets energy by breaking down a molecule called ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate).
As is obvious, one of the things it breaks it down into is the ‘A’ in ATP – Adenosine.
3/7
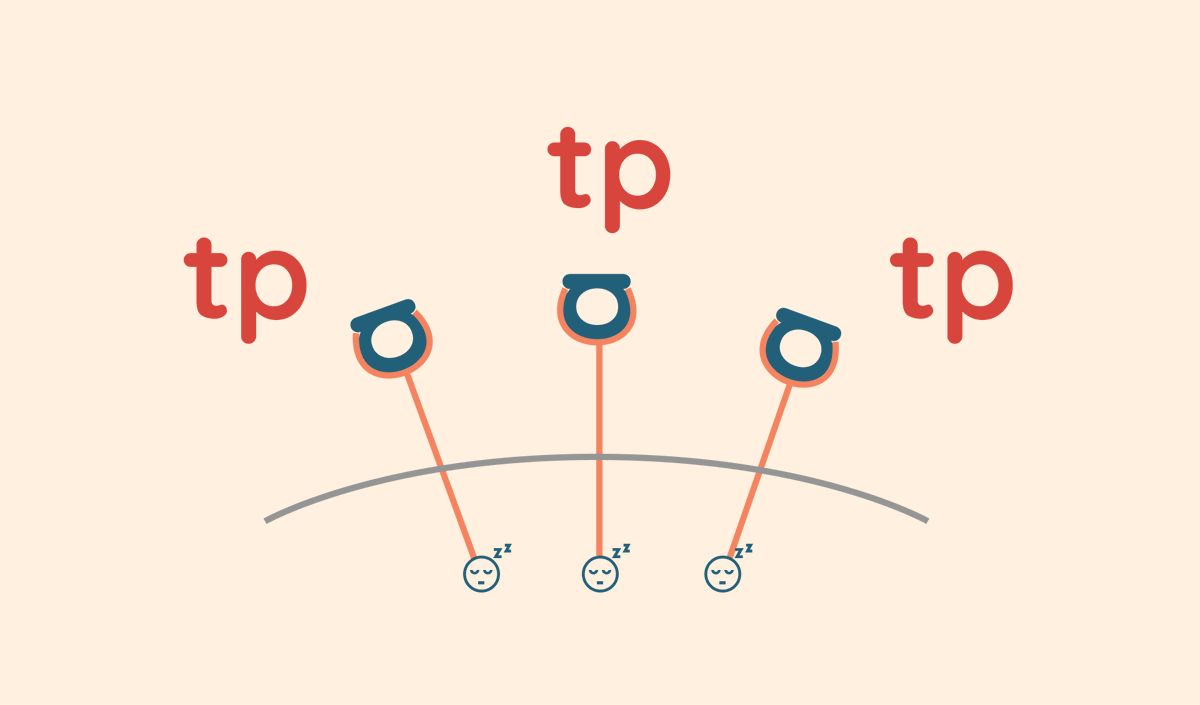
The cells in your body have receptors for adenosine.
When adenosine lodges into these receptors, it triggers a reaction that makes you sleepy.
Your heartbeat slows down, your muscles become calmer, and you feel more at ease.
The cells in your body have receptors for adenosine.
When adenosine lodges into these receptors, it triggers a reaction that makes you sleepy.
Your heartbeat slows down, your muscles become calmer, and you feel more at ease.
4/7
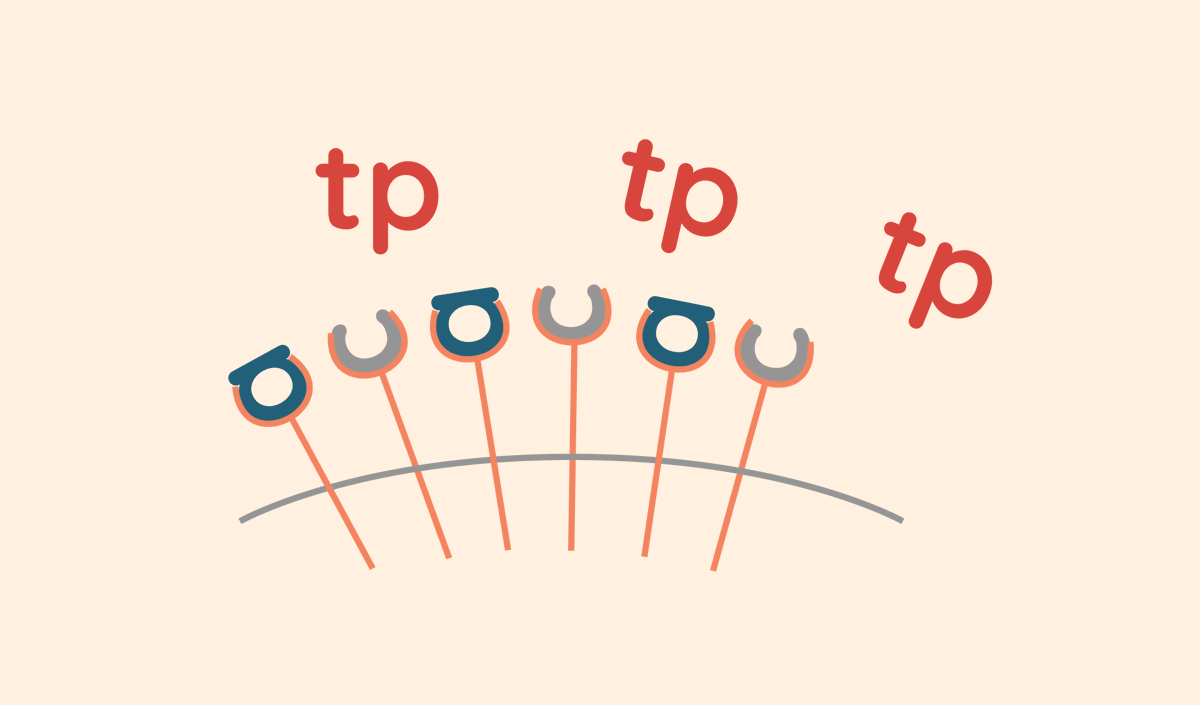
Now for the interesting bit.
You see, caffeine’s molecular structure is similar to that of adenosine.
It’s so similar, that when you consume caffeine, adenosine receptors confuse it for adenosine itself.
Now for the interesting bit.
You see, caffeine’s molecular structure is similar to that of adenosine.
It’s so similar, that when you consume caffeine, adenosine receptors confuse it for adenosine itself.
5/7
However, since caffeine isn’t identical to adenosine, it doesn’t trigger the same sleep-inducing reaction that adenosine would’ve.
This is why you feel more awake after a cup of coffee.
However, since caffeine isn’t identical to adenosine, it doesn’t trigger the same sleep-inducing reaction that adenosine would’ve.
This is why you feel more awake after a cup of coffee.
6/7
If you consistently consume too much caffeine, eventually, your body catches up.
It creates more adenosine receptors for the adenosine that’s feeling left out.
If you consistently consume too much caffeine, eventually, your body catches up.
It creates more adenosine receptors for the adenosine that’s feeling left out.

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter