Great news—MOTHER TO INFANT ANTIBODY TRANSFER!
Great news—MOTHER TO INFANT ANTIBODY TRANSFER! New study demonstrates #SARSCoV2 IgG antibodies were transferred across the placenta to infant cord blood in 87% of pregnant women with antibodies.
 Potential for moms’ antibodies to provide infant protection from #COVID19!
Potential for moms’ antibodies to provide infant protection from #COVID19! 
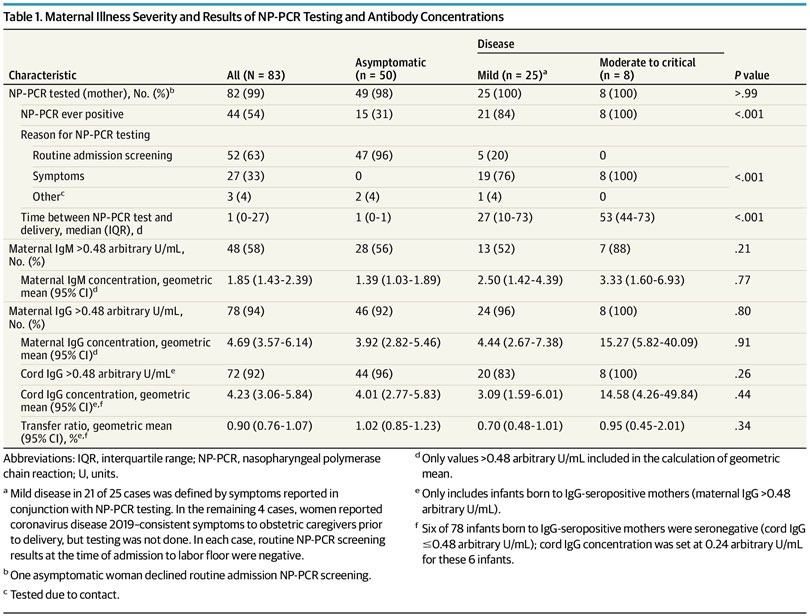
2) Moreover, IgG antibodies were transferred across the placenta *regardless of the severity* of mother’s previous #COVID19.
(Placental transfer ratios more than 1.0 were observed among women with asymptomatic #SARSCoV2, or mild, moderate, & severe COVID)
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/2775945
(Placental transfer ratios more than 1.0 were observed among women with asymptomatic #SARSCoV2, or mild, moderate, & severe COVID)
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/2775945
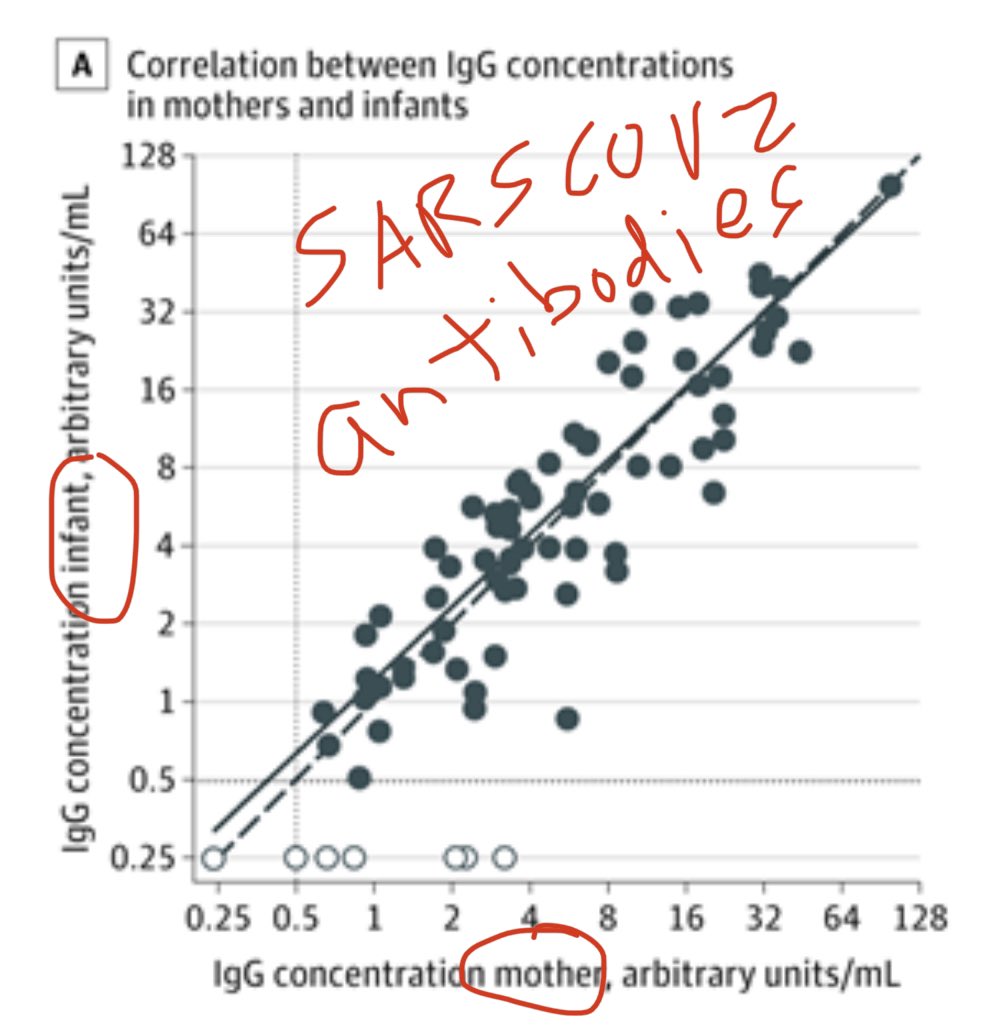
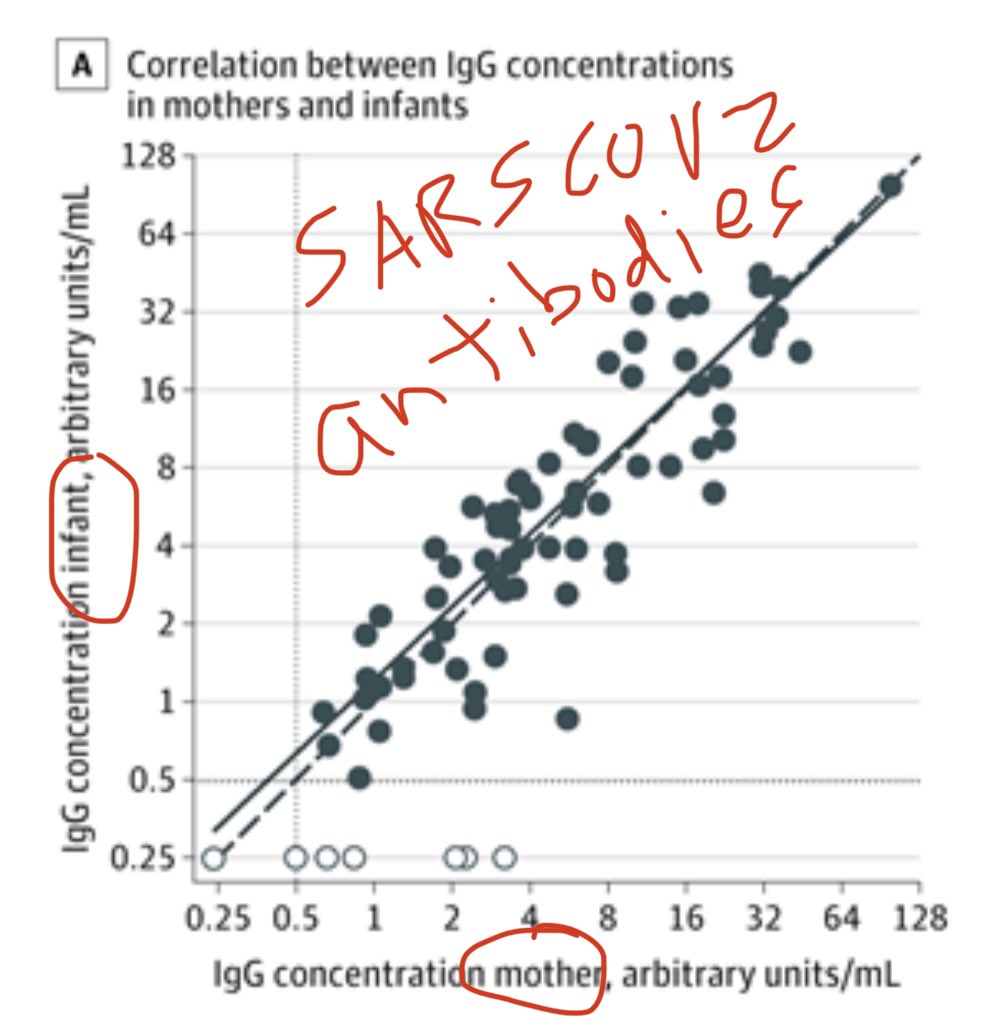
3) How tight is the correlation between maternal blood antibody levels and infant umbilical cord blood antibody levels? A whopping r=0.89! That’s incredibly high!
Cord blood IgG concentrations were positively correlated with maternal IgG concentrations (r = 0.886; P < .001).
Cord blood IgG concentrations were positively correlated with maternal IgG concentrations (r = 0.886; P < .001).
4) So 72 of 83 antibody positive mothers (87%) transferred IgG antibodies. What about the other 11?
Of 11 moms who were seropositive with infants who were seronegative:
5 moms were seropositive with IgM.
other 6 moms had really low IgG.
So explainable excerptions.
Of 11 moms who were seropositive with infants who were seronegative:
5 moms were seropositive with IgM.
other 6 moms had really low IgG.
So explainable excerptions.
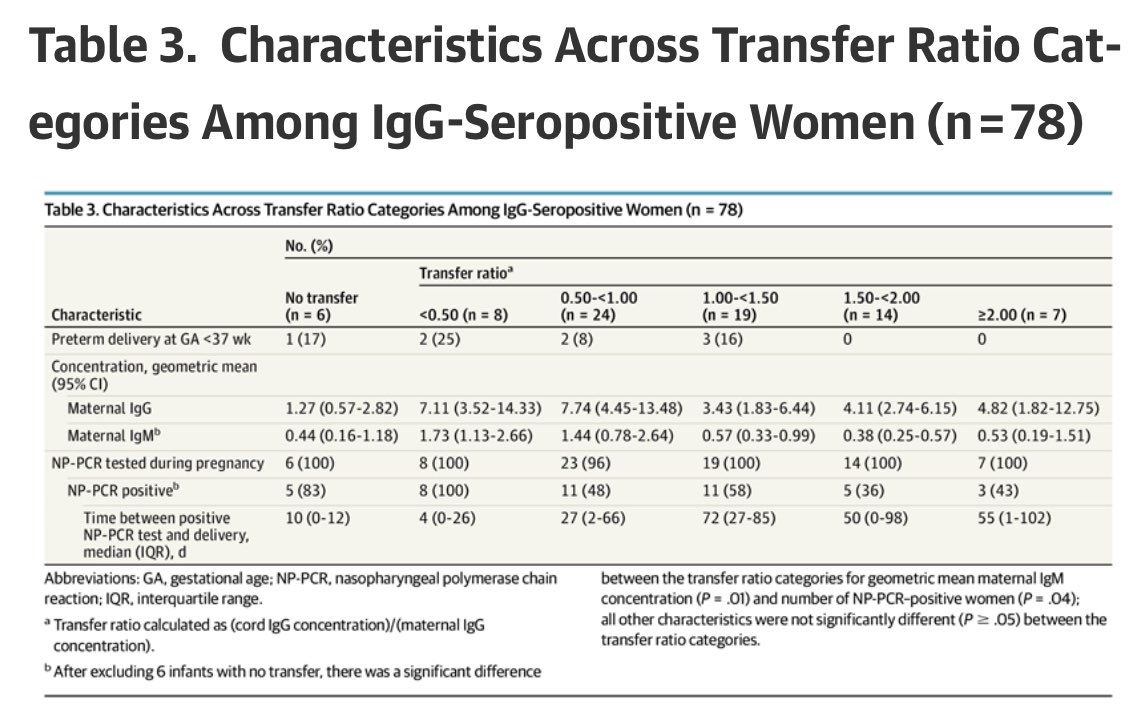
5) Transfer ratios (how much relative antibody transferred from mom to infant) were not different among infants born to mothers with asymptomatic or symptomatic illness (or severity)
This is huge too.
This is huge too.
6) also, among 26 women with mild, moderate, or critical #COVID19, with term delivery and positive PCR test result prior to delivery— the **longer time the PCR test was before delivery (longer ago illness), the more antibodies** mom transferred to infant. (r = 0.620; P < .001).
7) the “findings are aligned with studies of vaccine-elicited antibodies to pertussis, rubella, hepatitis B, and influenza, where cord sera/maternal sera transfer ratios ranging from 0.8 to 1.7 have been observed.”
8) “We did not observe a significant difference in transfer efficiency comparing infants born preterm, but this finding was likely affected by small numbers (n = 9) of preterm infants, with the earliest born at 31 weeks’ gestation. Further studies will be needed for preterm”
9) “When vaccines are widely available, the optimal timing of maternal vaccination during pregnancy will need to consider maternal and fetal factors including the time needed to ensure neonatal protection.”
 Potentially maybe vaccinate moms earlier for maybe more protection.
Potentially maybe vaccinate moms earlier for maybe more protection.
 Potentially maybe vaccinate moms earlier for maybe more protection.
Potentially maybe vaccinate moms earlier for maybe more protection.
10) that said—“Further studies are needed to determine if SARS-CoV-2 antibodies are protective against newborn infection; if so, at what concentration; and whether the transplacental kinetics of vaccine-elicited antibodies are similar to naturally acquired antibodies.”
11) An accompanying editorial notes that “While there is a potential for some protection from breast milk antibodies in lactating infants, this might be limited and less effective than protection from transplacental antibodies.” https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/2775944?utm_source=silverchair&utm_campaign=jama_network&utm_content=covid_weekly_highlights&utm_medium=email
12) oped writer notes that in “neonatal varicella infection, higher likelihood of infection and more severe neonatal disease in infants born to mothers infected perinatally who are unable to provide passive protection to their newborns.”
Thus — antibody transfer is key.
Thus — antibody transfer is key.
13) Although more study needed, Dr Muñoz notes: “However, the timing of maternal vaccination to protect the infant, as opposed to the mother alone, would necessitate an adequate interval from vaccination to delivery (of at least 4 weeks)...”
14) “When considering that up to 2 weeks from complete vaccination (2-dose series with 21 or 28 days or more between doses with current COVID-19 vaccines) is necessary for higher efficacy of the vaccine and that transplacental transfer begins around 17 weeks (before birth)
15) “...increasing exponentially as gestation advances and the placenta grows, maternal vaccination starting in the early second trimester of gestation might be optimal to achieve the highest levels of antibodies in the newborn.”
16) “If what we know about other important vaccine-preventable diseases in infants for which maternal vaccination is recommended (tetanus, pertussis, influenza) or under investigation (respiratory syncytial virus) holds true...”
17) ...”transplacentally acquired antibody rapidly decays by the 2nd month of life & continues to drop so that by 6-12 months, protective efficacy is reduced. Available data on the effect of COVID-19 in newborns and infants suggests that severe disease may occur in early life.”
18) Bottomline: It is promising that mother to infant transfer of IgG antibodies to #SARSCoV2 occurs in high frequency, and could maybe yield protection in future studies if what we know from other studies is true. And while not forever, might protect in critical early infancy.
19) Lots of questions about kids vaccines—they are doing more trials in kids. Results likely late spring or summer—doing more precise dosing studies for kids because of variable body sizes. Some vaccines in China may have pediatric vaccine data by March.
20) two other key studies on convalescent plasma therapy — of transfusing plasma with high antibody concentrations - for prevention of severe #COVID19. Read thread  below. https://twitter.com/drericding/status/1356173085989285893
below. https://twitter.com/drericding/status/1356173085989285893
 below. https://twitter.com/drericding/status/1356173085989285893
below. https://twitter.com/drericding/status/1356173085989285893

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter