Most of us are familiar with major salivary gland tumors but are less familiar with minor salivary gland carcinomas (MSGCs). Let’s take a closer look. 1/12
#RGphx
Imaging of Malignant Minor Salivary Gland Tumors of the Head and Neck
https://bit.ly/3nySJWG
#RGphx
Imaging of Malignant Minor Salivary Gland Tumors of the Head and Neck
https://bit.ly/3nySJWG
Unlike major salivary gland tumors which are often benign, 60% of minor salivary gland tumors are malignant. According to WHO, adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) and mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC) comprise 70% of MSGCs. 2/12
#RGphx
#RGphx
What is the most common mucosal site for minor salivary gland carcinomas? 3/12 #RGphx @cookyscan1 @RadioGraphics
The most common site for MSGC is in oral cavity subsites: palate > lingual > buccal > retromolar > labial. They also occur in the sinonasal passages, nasopharynx, lacrimal gland, ceruminous glands along the EAC, larynx, and trachea. 4/12
#RGPhx
#RGPhx
Though often hard to distinguish, the role of imaging is useful in diagnosing extent of disease into a local or invasive type. Invasive type shows deep submucosal invasion, bone marrow infiltration, or perineural spread. 5/12
#RGphx
#RGphx
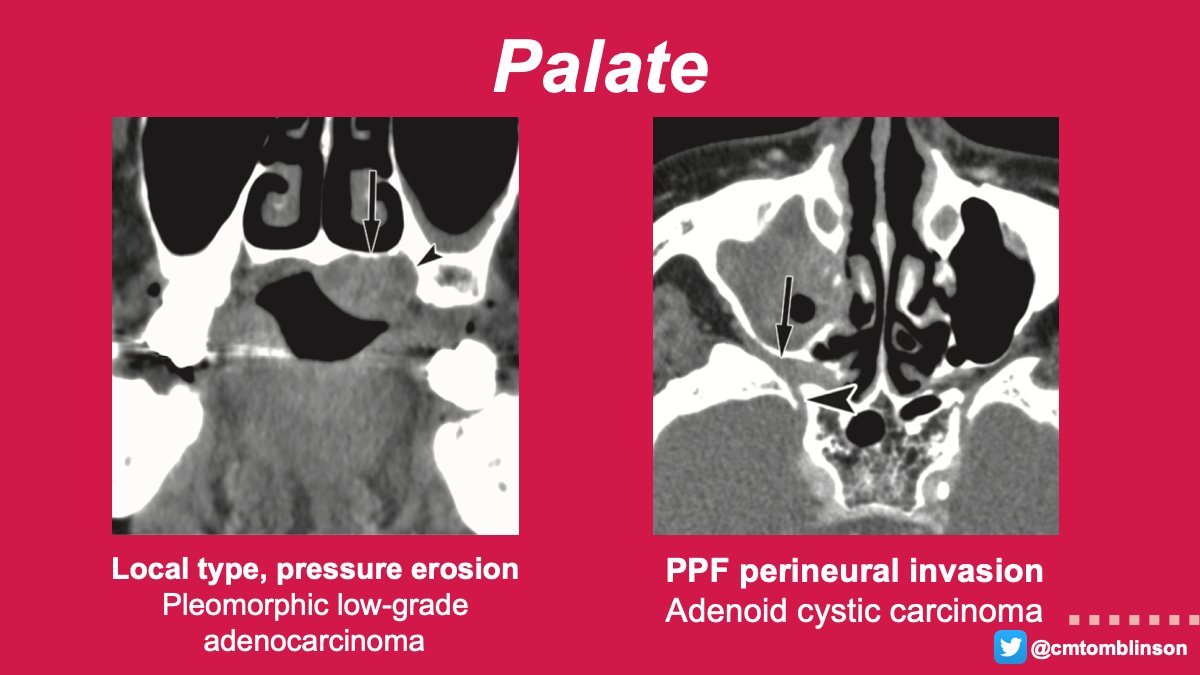
The hard-soft palate junction is most common site & MEC > ACC. These may cause pressure erosion (localized) or destruction of hard palate or pterygoid plate (invasive). PNS can extend to pterygopalatine fossa (PPF), foramen rotundum, cavernous sinus, & Meckel’s cave. 6/12
#RGphx
#RGphx
Buccal glands are located posteriorly > anteriorly to the parotid duct and outside the buccinator muscle. MEC and ACC are most common histopathologic types. Remember to check buccal fat pats for symmetry! 7/12
#RGphx
#RGphx
The paranasal sinuses are more commonly affected (76.7%) compared to the nasal cavity, with the maxillary sinus being the most common site. PNS is found in 44% of ACC originating from the maxillary sinus. 8/12
#RGphx
#RGphx
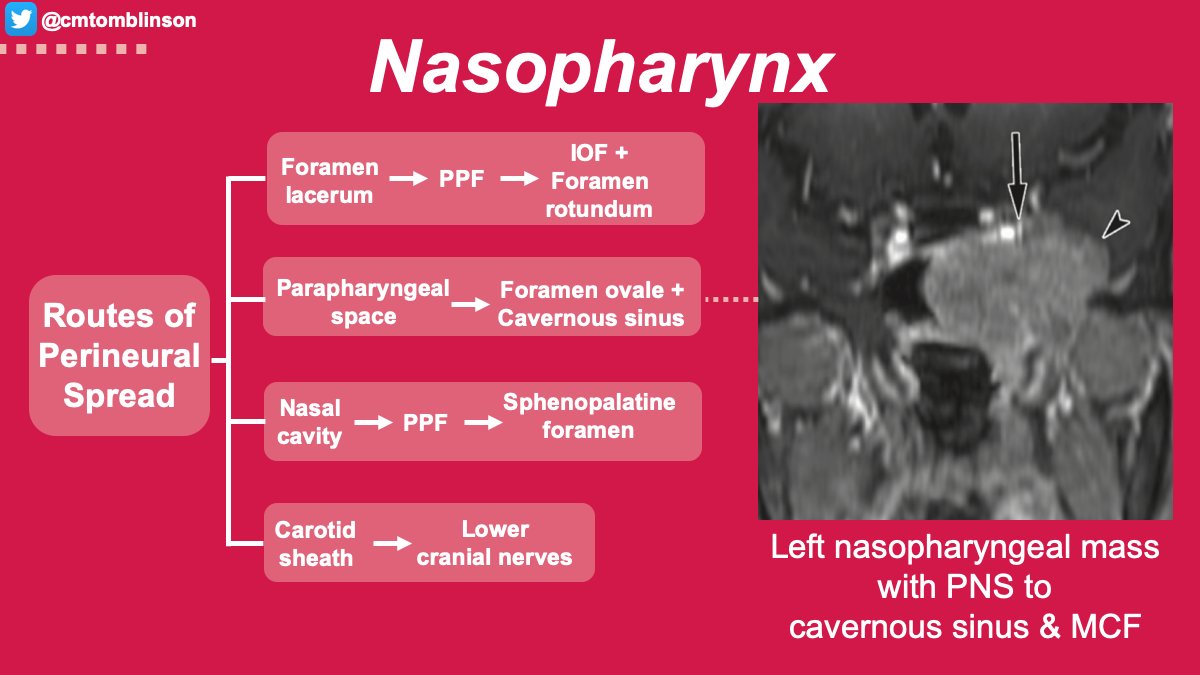
Most nasopharyngeal MSGCs present at advanced stages with concerning rates of invasion to the parapharyngeal space (77.8%), skull base (66.7%), and cavernous sinus (33.3%). 9/12
#RGphx
#RGphx
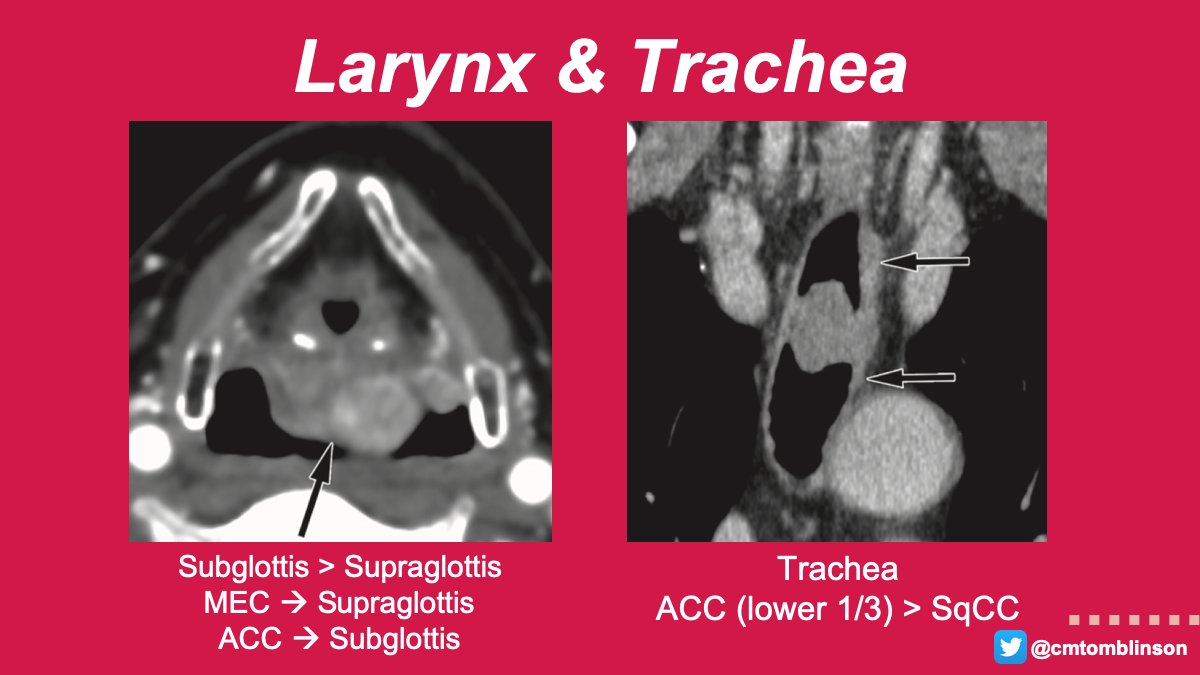
In the larynx, glands are absent along the free edge of the membranous vocal fold, which can be helpful in distinguishing from SqCC.
In the trachea, patients can be asymptomatic until the lumen is narrowed by 50%, then present with symptoms of airway obstruction. 10/12
#RGphx
In the trachea, patients can be asymptomatic until the lumen is narrowed by 50%, then present with symptoms of airway obstruction. 10/12
#RGphx
In summary, understanding the distribution, histopathologies, and epidemiology of MSGCs can help facilitate speedy diagnosis. Imaging plays a large role in evaluating extent of disease at the time of diagnosis and post-treatment surveillance imaging. 11/12
#RGphx
#RGphx
Thanks for tuning in! What’s your experience with diagnosing and treating these lesions? 12/12
https://bit.ly/3nySJWG
#RGphx
https://bit.ly/3nySJWG
#RGphx
@TopfHNS @KyleMannionHN @langermology @NettervilleJim
Any clinical insights into minor salivary gland carcinomas from the #OTOHNS world?
How can #Rads help you in our reports on these?
Any clinical insights into minor salivary gland carcinomas from the #OTOHNS world?
How can #Rads help you in our reports on these?

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter