Internet Service providers (ISP) frequently use the terms “bandwidth” and “speed” interchangeably.
Guess its a sales trick. There is a subtle difference, although both are measured in 'Mbps'.
Guess its a sales trick. There is a subtle difference, although both are measured in 'Mbps'.
1. Bandwidth: the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over an Internet connection
2. Speed: the rate at which data can be downloaded (or uploaded) to a given device using that Internet connection
2. Speed: the rate at which data can be downloaded (or uploaded) to a given device using that Internet connection
Analogy:
Data is travelling over the Internet cable like water in a pipe. Bandwidth is the width of that pipe - essentially, the maximum volume of water (data) that can pass through at once. Speed, meanwhile, is the number of Mbps that can be downloaded by a given device.
Data is travelling over the Internet cable like water in a pipe. Bandwidth is the width of that pipe - essentially, the maximum volume of water (data) that can pass through at once. Speed, meanwhile, is the number of Mbps that can be downloaded by a given device.
So, even if your pipe size is big, if the water speed is slow then you will get slow delivery of water.
You might have installed a high capacity router but if ISP's speed is slow then it is slow.
BTW broadband as per FCC is minimum 25/3 Mbps.
You might have installed a high capacity router but if ISP's speed is slow then it is slow.
BTW broadband as per FCC is minimum 25/3 Mbps.
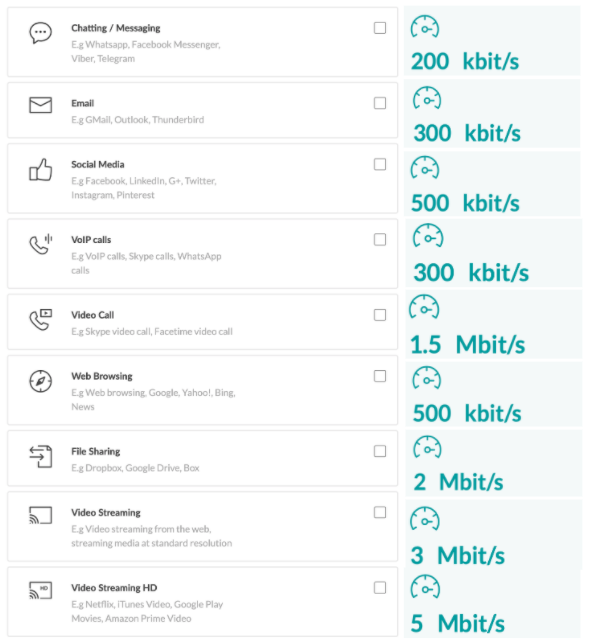
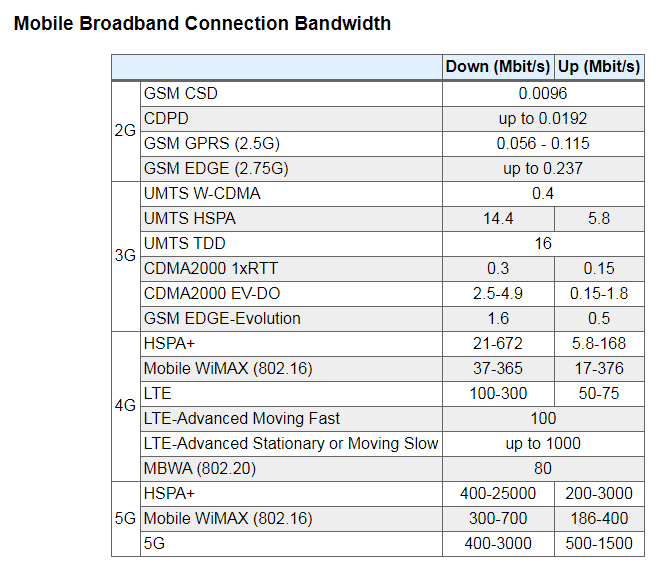
The amount of 'speed' or 'bandwidth' you need will vary widely depending on the size of your household, a number of concurrent users, intended activities, and etc.
Here's a ballpark:
Here's a ballpark:
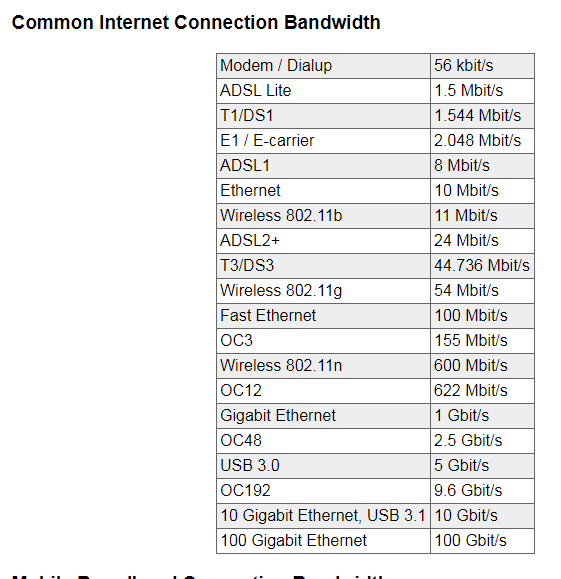
So based on the above, let's say you calculate your requirement at minimum 100 Mbps and you installed a 'Gigabit Ethernet' connection of XYZ company which has a capacity of 1 Gbits/s.
You have to ensure that the ISP has 'speed' at a minimum of 100 Mbps.

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter