Been waiting for 

Important story on what a “tariff-free” deal means in practice and why it’s not enough for two economies as closely integrated.
Tariffs are removed on goods that meet rules of origin. This is a complex and nuanced area of customs.
/1 https://twitter.com/pmdfoster/status/1346746239874953217


Important story on what a “tariff-free” deal means in practice and why it’s not enough for two economies as closely integrated.
Tariffs are removed on goods that meet rules of origin. This is a complex and nuanced area of customs.
/1 https://twitter.com/pmdfoster/status/1346746239874953217
Important to remember that trade deals (FTAs) weren't designed with such a high degree of economic integration in mind.
So some of the standard RoO provisions will seem incredibly restrictive under the UK-EU deal.
/2
So some of the standard RoO provisions will seem incredibly restrictive under the UK-EU deal.
/2
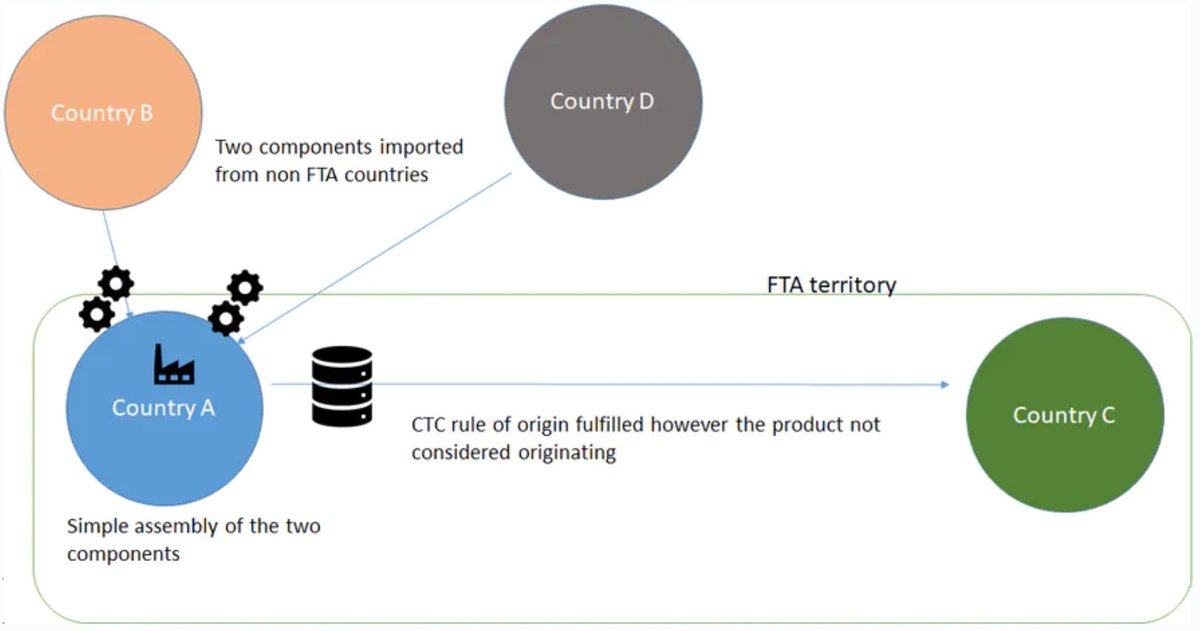
Minimal operations or insufficient processing is a standard part of an FTA. Most, if not all FTAs, include a provision on minimal processing – processing not considered sufficient to confer originating status even if rules of origin have been met.
/3
/3
It is standard procedure not to apply cumulation when goods have only been subject to minimal processing.
To be able to cumulate origin and consider the final product of UK origin, the processing carried out in the UK needs to exceed minimal operations.
/4
To be able to cumulate origin and consider the final product of UK origin, the processing carried out in the UK needs to exceed minimal operations.
/4
The level of integration between the UK and the EU means that this will have significant consequences for a number of industries.
For example, in supply chains where goods are brought into the UK from the EU and reassembled, sorted or repackaged and re-exported to ROI.
/5
For example, in supply chains where goods are brought into the UK from the EU and reassembled, sorted or repackaged and re-exported to ROI.
/5
The @Foodanddrinkfed raised this issue and the impact it will have on UK food and drink businesses (same goes for a number of other industries)
Some practical examples of how it works were covered in a brilliant by @faisalislam
by @faisalislam 
/6 https://twitter.com/faisalislam/status/1344018202301444096?s=20
Some practical examples of how it works were covered in a brilliant
 by @faisalislam
by @faisalislam 
/6 https://twitter.com/faisalislam/status/1344018202301444096?s=20
Again, important to remember that it's a common provision. Just not a common scenario because the goods don't normally go straight back to where they came from.
This is how it's usually used:
/7
This is how it's usually used:
/7
Solution?
For goods that originate in the EU and meet the rules of origin on the way in, it would be quite simple.
The EU Commission already has a number of origin-related derogations. Some examples here
/8 https://ec.europa.eu/taxation_customs/business/calculation-customs-duties/rules-origin/general-aspects-preferential-origin/arrangements-list/overseas-countries-territories-oct_en
For goods that originate in the EU and meet the rules of origin on the way in, it would be quite simple.
The EU Commission already has a number of origin-related derogations. Some examples here

/8 https://ec.europa.eu/taxation_customs/business/calculation-customs-duties/rules-origin/general-aspects-preferential-origin/arrangements-list/overseas-countries-territories-oct_en
But the question is whether or not the EU will have any incentive to do that...
This provision impacts the UK supply chains much more than EU ones...
/ends
This provision impacts the UK supply chains much more than EU ones...
/ends

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter