Like many people, I’ve assumed that the early Muslims were such successful conquerers because of the power of a new religion (Islam) to unify diverse peoples. But after doing some holiday reading, I’m struck by how important disease was in jumpstarting Muslim conquest. [thread]
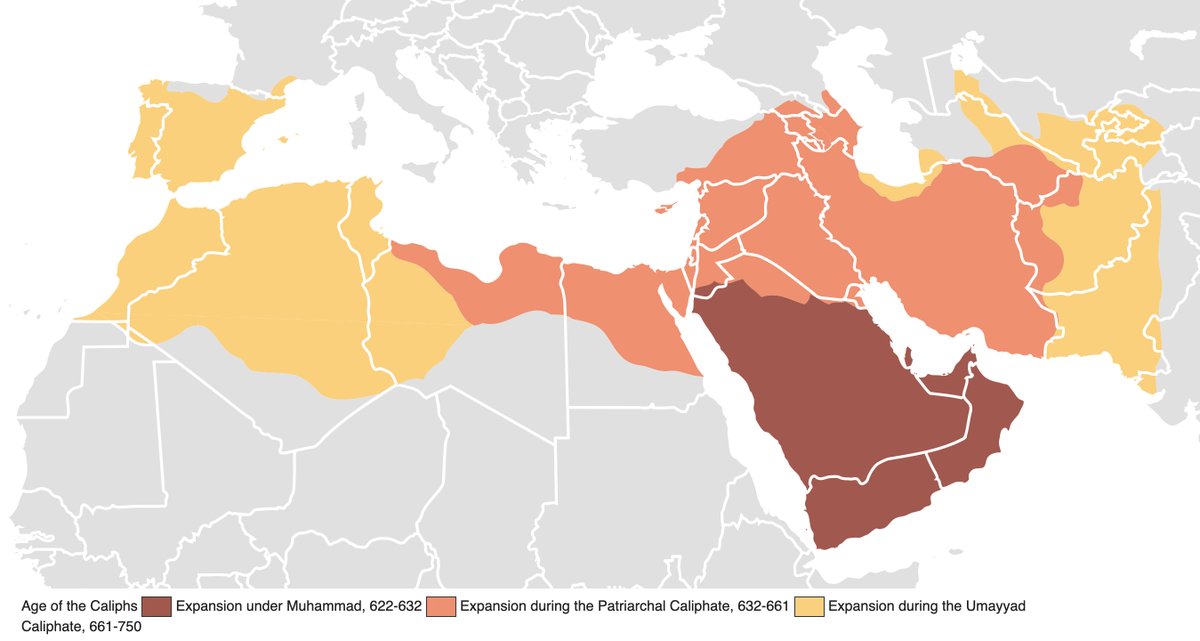
For context, the Muslim conquests were an awesome event in world history. Muhammad died in 642. Within decades, Arabian tribes, unified under Islam, conquered the Persians & large parts of the Byzantine Empire. Within ~a century, they built the largest empire ever (to that point)
What’s key is that Arabs tore through the Persians and Byzantines during a pandemic of bubonic plague, which started in the 540s and continued to recur for centuries. Plague targeted areas with high population density, such as core regions of Persia and Byzantium.
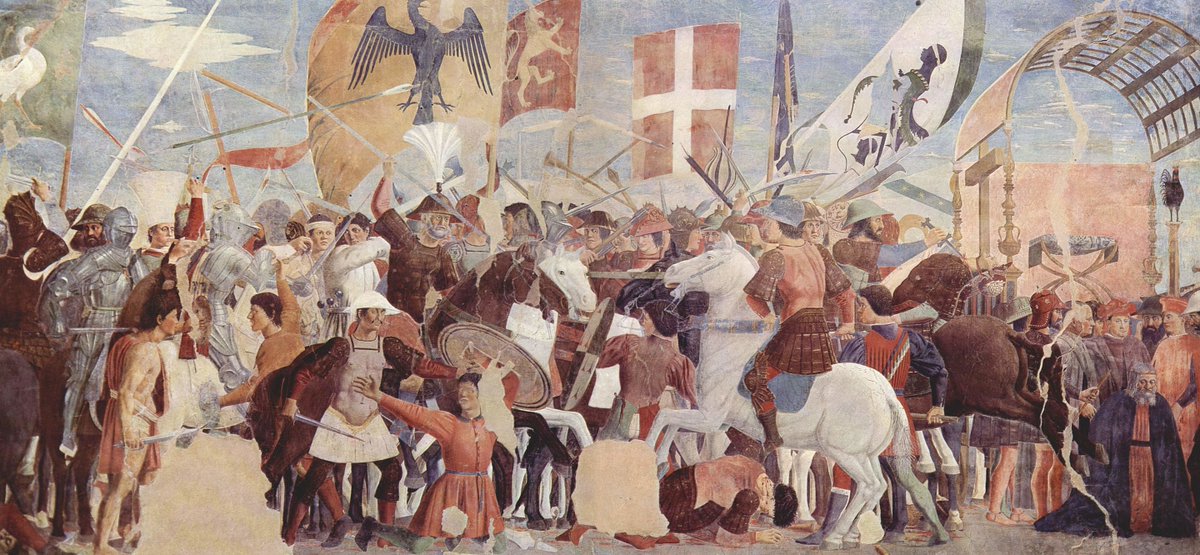
This had several effects. By annihilating population, plague likely hurt the economies of both empires. By creating weakness & anxiety, it contributed to the Persian-Byzantine Wars (pictured) and, after mass death in 628, to civil war in Persia, leaving both empires vulnerable.
The loss of life also meant limited manpower. According to Robert Hoyland (whose writings on this are excellent), chroniclers blamed the Byzantine defeat in the Battle of Yarmouk (arguably the most decisive battle in the Muslim conquests) partly on plague spreading through Syria.
Steppe peoples, whose sparse populations limited the spread of plague, penetrated Persia & Byzantium too. But coming from the north & east, they encountered societal & natural obstacles. Arabs—situated close to the empires' exposed underbellies—could strike much more easily.

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter![Like many people, I’ve assumed that the early Muslims were such successful conquerers because of the power of a new religion (Islam) to unify diverse peoples. But after doing some holiday reading, I’m struck by how important disease was in jumpstarting Muslim conquest. [thread] Like many people, I’ve assumed that the early Muslims were such successful conquerers because of the power of a new religion (Islam) to unify diverse peoples. But after doing some holiday reading, I’m struck by how important disease was in jumpstarting Muslim conquest. [thread]](https://pbs.twimg.com/media/Eq5LAjMVQAMAjAO.jpg)