Pleased to present @geolsoc climate change statement, written with wonderful colleagues including @anandpallavijha @theFosterlab @maryhgagen @oceans_O2 @rdlarter @ClimateSamwell @ErinMcClimate @rpancost @EloquentScience @charliejrwill
https://jgs.lyellcollection.org/content/178/1/jgs2020-239
A thread (1/12)
https://jgs.lyellcollection.org/content/178/1/jgs2020-239
A thread (1/12)
This statement written by @paleoclimatesoc committee and other climate experts shows how the geosciences have helped scientists better understand the climate system.
Looking forward to @seismatters explain more in tonight’s @Ri_Science Xmas lecture
(2/12)
Looking forward to @seismatters explain more in tonight’s @Ri_Science Xmas lecture
(2/12)
We centred the statement around the nine questions below, including geology’s future role in climate mitigation – pls read open access article for more detail https://jgs.lyellcollection.org/content/178/1/jgs2020-239
(3/12)
(3/12)
1. What does the geological record of climate change look like?
4 billion years of climate variations confirm importance of greenhouse gases in determining climate state & habitability of our planet, and provide evidence for feedbacks & tipping points in climate system
4/12
4 billion years of climate variations confirm importance of greenhouse gases in determining climate state & habitability of our planet, and provide evidence for feedbacks & tipping points in climate system
4/12
2. Why has climate changed in the past?
Throughout Earth history, CO2 acted as both driver of – & feedback to – global climate change. E.g. Pleistocene glacial–interglacial cycles paced by orbital changes, but magnitude of transitions sensitive to CO2 concentrations.
5/12
Throughout Earth history, CO2 acted as both driver of – & feedback to – global climate change. E.g. Pleistocene glacial–interglacial cycles paced by orbital changes, but magnitude of transitions sensitive to CO2 concentrations.
5/12
3. Is our current warming unusual?
CO2 conc at highest level for at least past 3 million years. As far as we know, only instantaneous Cretaceous–Paleogene meteorite impact event caused global climate change more rapid than the current human-induced global warming.
6/12
CO2 conc at highest level for at least past 3 million years. As far as we know, only instantaneous Cretaceous–Paleogene meteorite impact event caused global climate change more rapid than the current human-induced global warming.
6/12
4. What does geological record indicate about global v. regional change?
Climate changes at the poles will be larger than elsewhere, and summer sea ice is predicted to eventually disappear from most of the Arctic, as was the case during the Pliocene c. 3 million years ago
7/12
Climate changes at the poles will be larger than elsewhere, and summer sea ice is predicted to eventually disappear from most of the Arctic, as was the case during the Pliocene c. 3 million years ago
7/12
5. When Earth’s temp changed in the past, what were impacts?
Changes in temperature & CO2 impact: sea-level, water cycle, ecosystems, ocean acidification & O2 depletion. ENSO & monsoons, affecting food & water for billions of people, also varied with past climate change.
8/12
Changes in temperature & CO2 impact: sea-level, water cycle, ecosystems, ocean acidification & O2 depletion. ENSO & monsoons, affecting food & water for billions of people, also varied with past climate change.
8/12
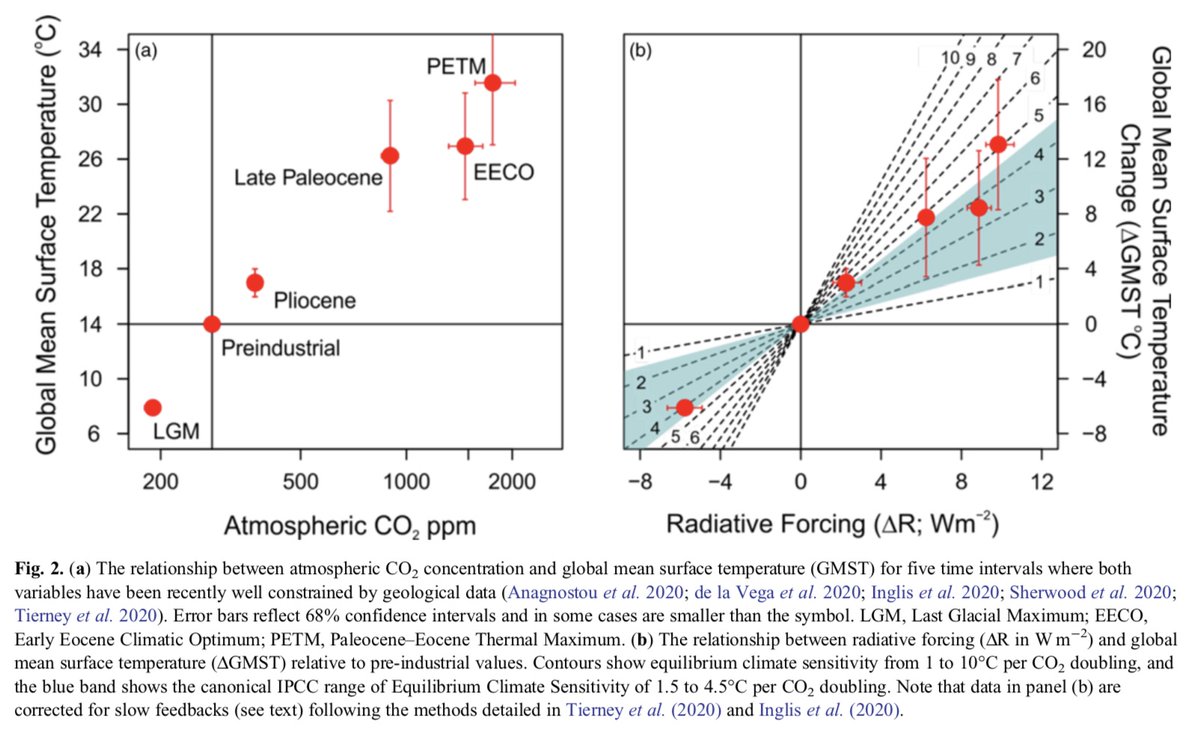
6. How does geological record inform our quantification of climate sensitivity?
With estimates of past radiative forcing & equilibrium climate sensitivity values of 2.6 - 3.9°C, we can explain majority of the warming/cooling in geological record, fig by @theFosterlab
9/12
With estimates of past radiative forcing & equilibrium climate sensitivity values of 2.6 - 3.9°C, we can explain majority of the warming/cooling in geological record, fig by @theFosterlab
9/12
7. Are there past climate analogues for the future?
There is no perfect analogue but geological record provides us with useful windows through which we can explore possible future climates and it informs us how the Earth works in different climate states.
10/12
There is no perfect analogue but geological record provides us with useful windows through which we can explore possible future climates and it informs us how the Earth works in different climate states.
10/12
8. How can the geological record be used to evaluate climate models?
Recent successes in model evaluation using the geological record increase our confidence of future climate predictions from models.
11/12
Recent successes in model evaluation using the geological record increase our confidence of future climate predictions from models.
11/12
9. Geology’s role in dealing with the climate emergency?
Geoscientists will play an important role in transition to low carbon, green economy, from discovering metal resources critical for renewable energy, to geothermal technologies, and carbon capture & sequestration.
12/12
Geoscientists will play an important role in transition to low carbon, green economy, from discovering metal resources critical for renewable energy, to geothermal technologies, and carbon capture & sequestration.
12/12

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter