Role of Stents in Dialysis Vascular Access - Tweetorial
Role of Stents in Dialysis Vascular Access - Tweetorial  Indications for Stent Use
Indications for Stent Use  Recent Clinical Trials of Stents in Dialysis Vascular Access
Recent Clinical Trials of Stents in Dialysis Vascular Access Complications associated with Stent Use
Complications associated with Stent Use1/
@ASDINNews
#VascularAccessPearls
 Arterio-venous (AV) Access
Arterio-venous (AV) Access causes significant morbidity & mortality in patients on hemodialysis
 Most AV access associated complications are due to vascular stenosis
Most AV access associated complications are due to vascular stenosis
2/
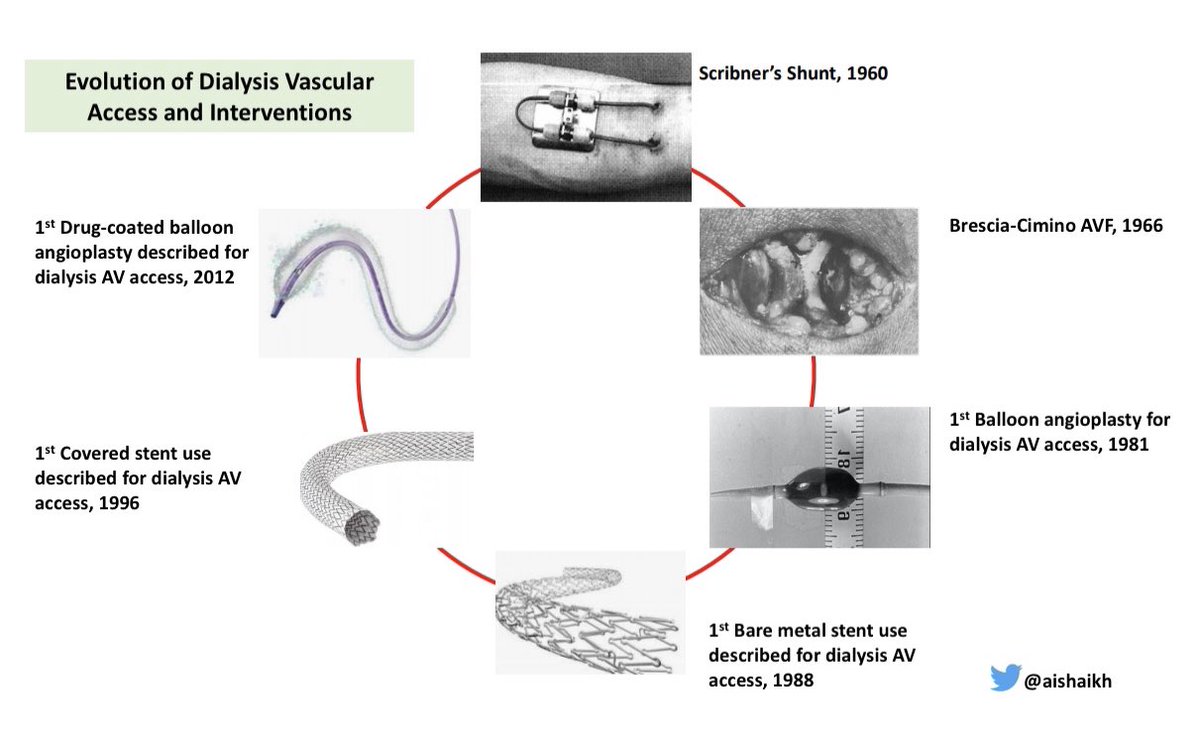
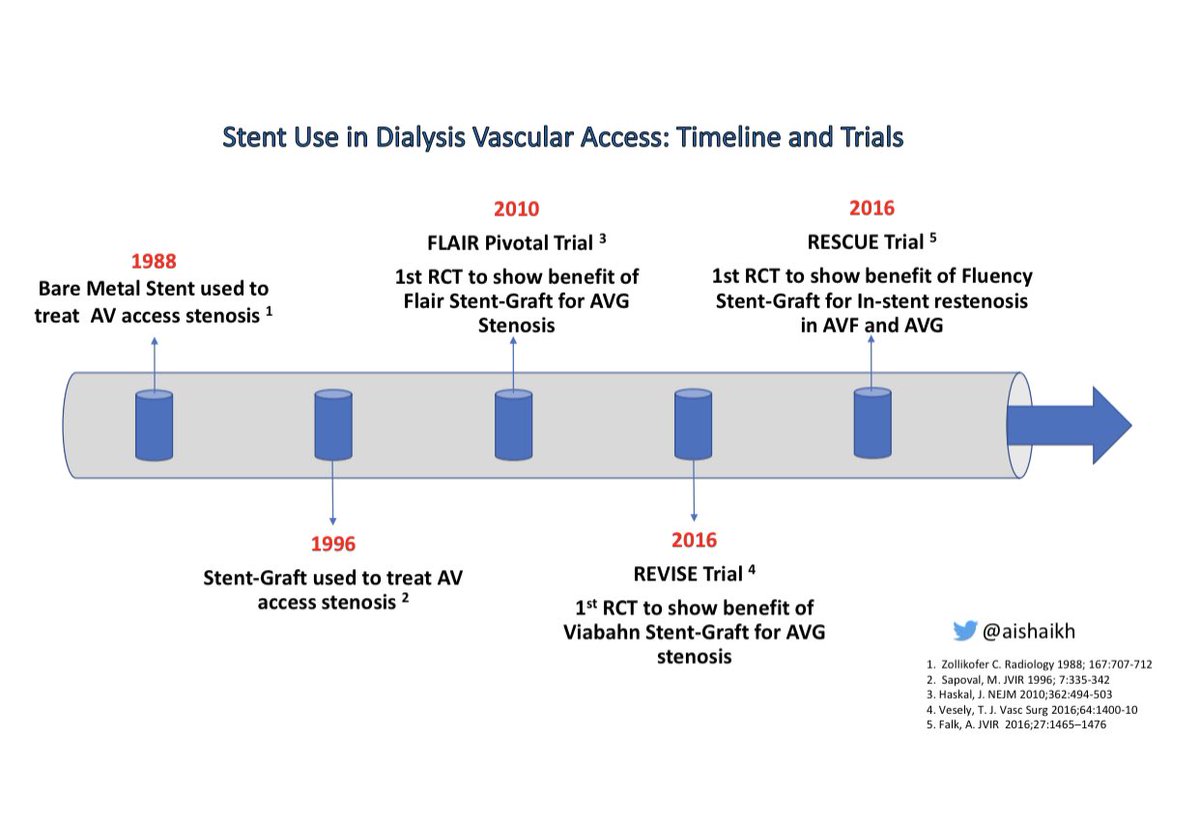
 Vascular Access care has evolved over the past 60 years:
Vascular Access care has evolved over the past 60 years: -Scribner’s Shunt in 1960

-Brescia-Cimino AVF in 1966

-1st Balloon Angioplasty in 1981

-1st Bare Metal Stent in 1988

-1st Covered Stent in 1996

-DCB use in 2012
3/
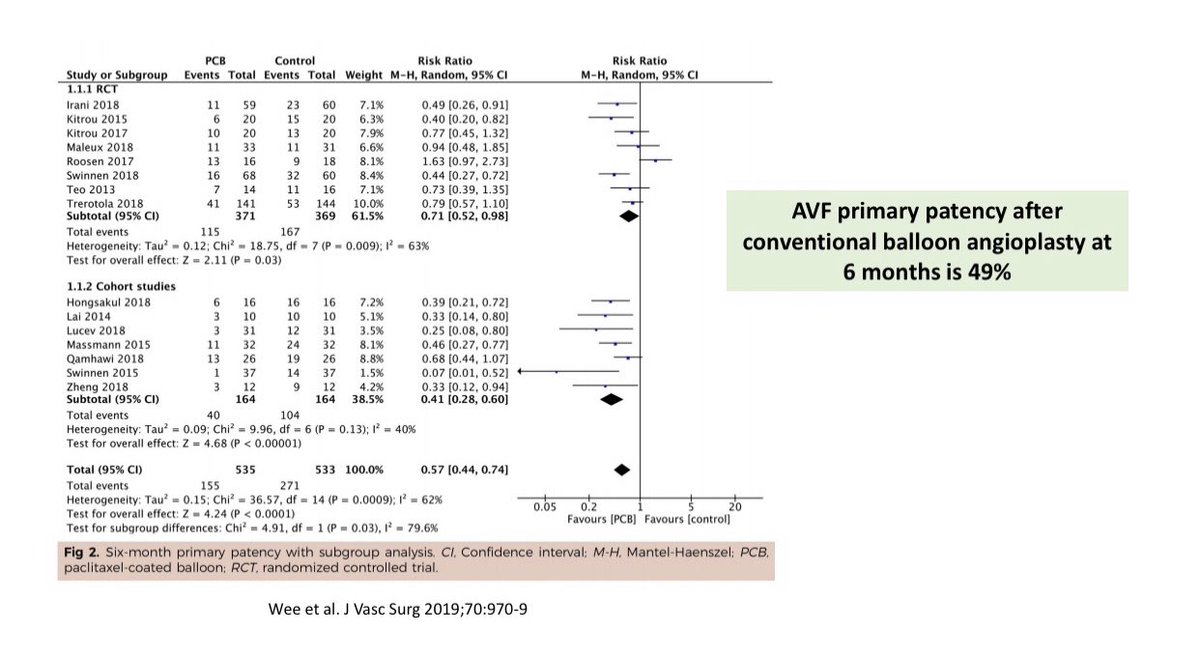
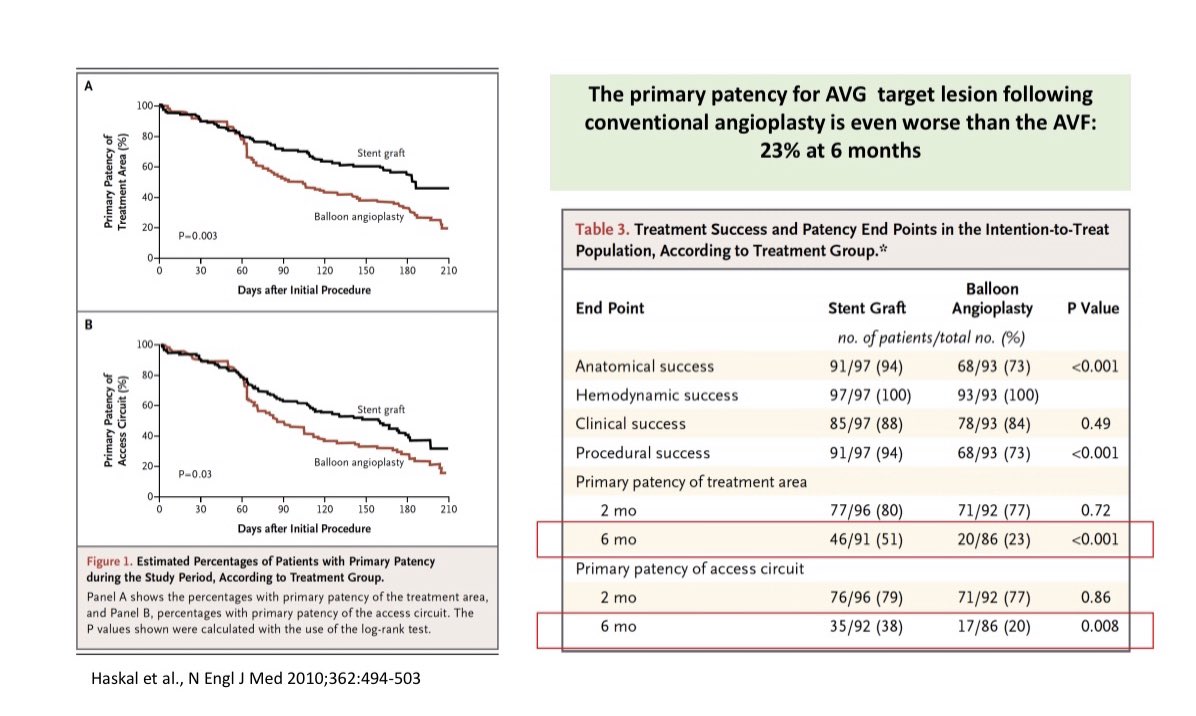
 Despite these innovations, AV access stenosis remains a big problem
Despite these innovations, AV access stenosis remains a big problem-Percutaneous Balloon Angioplasty (PTA) remains the 1st line therapy for stenosis but it is NOT very effective
-AVF patency after PTA is only 50% at 6-months & it is worse for AVGs

4/
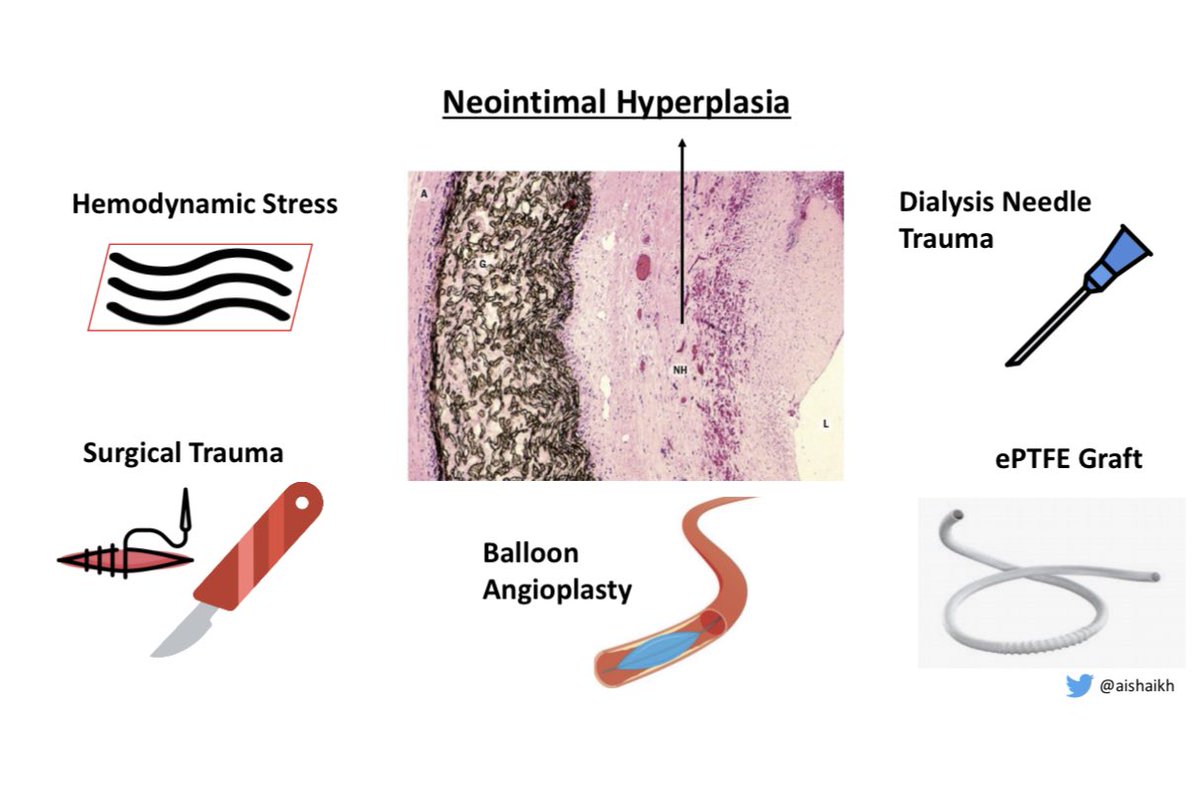
 Neointimal Hyperplasia (NIH) causes vascular stenosis & it is due to:
Neointimal Hyperplasia (NIH) causes vascular stenosis & it is due to: -Hemodynamic stress
-Surgical trauma
-Cannulation needle trauma
-AVG
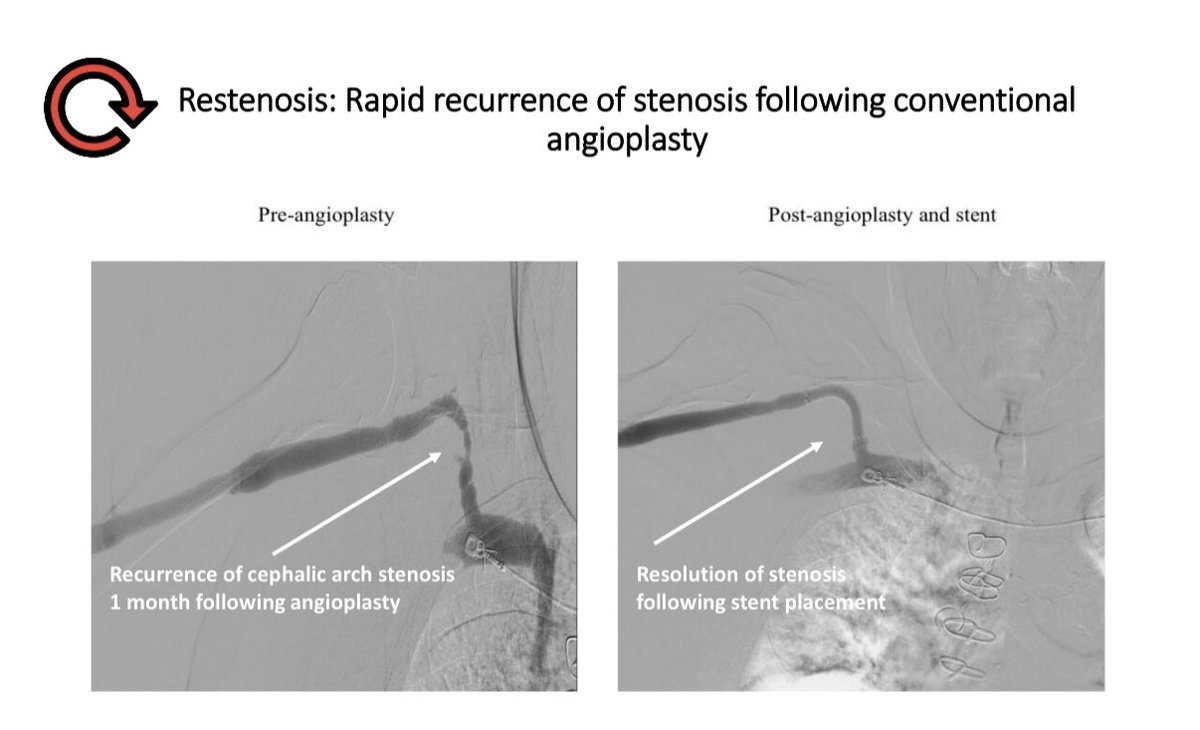
 But balloon angioplasty, the treatment for stenosis, can itself induce NIH & cause restenosis
But balloon angioplasty, the treatment for stenosis, can itself induce NIH & cause restenosis
5/
 Therefore, Endovascular Stents have been used to treat the vascular stenosis
Therefore, Endovascular Stents have been used to treat the vascular stenosis What are Endovascular Stents?
What are Endovascular Stents?They are scaffolds that provide mechanical endoluminal support to the vessel wall to maintain patency
6/
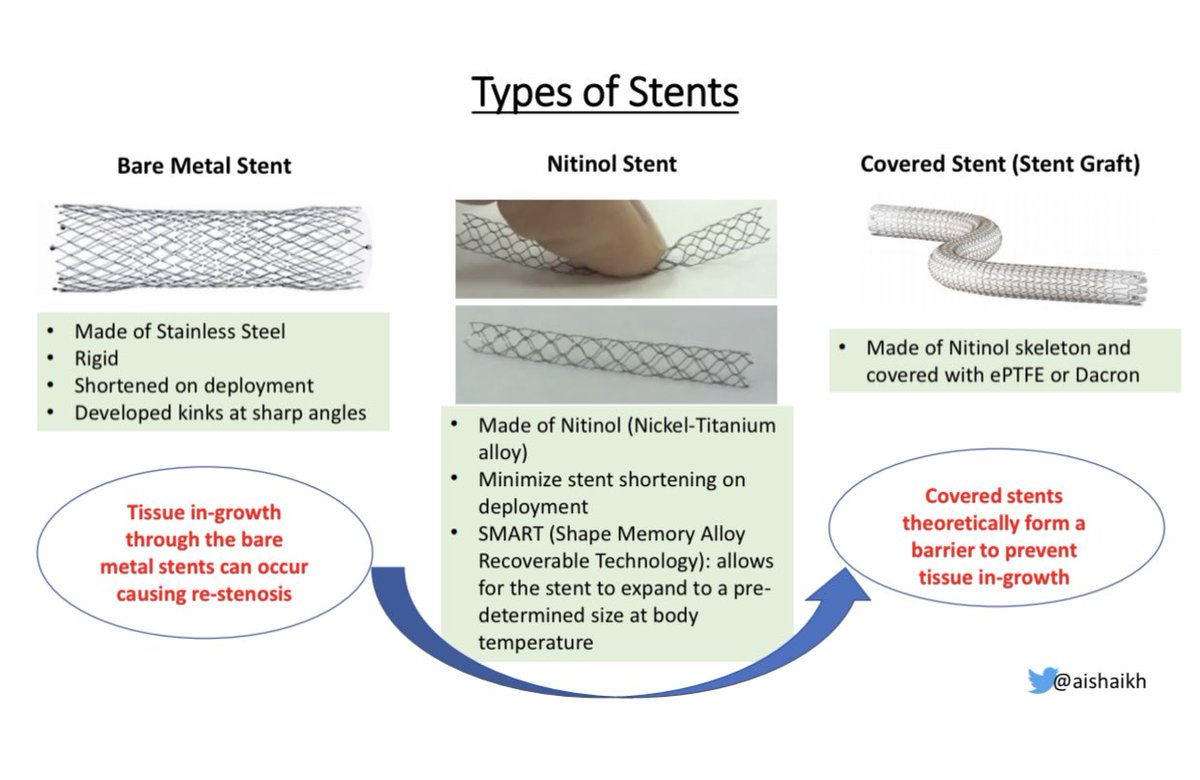
 Types of Stents:
Types of Stents:-1st generation stents were Bare-Metal Stents made of stainless steel
-Next generation of metal stents were Nitinol Stents made of nickel-titanium alloy
- Covered-Stents (Stent-Grafts) are Nitinol stents covered w/ ePTFE or Dacron
7/
 Bare Metal Stents & Nitinol Stents have problems because the tissue in-growth through the bare metal causes restenosis
Bare Metal Stents & Nitinol Stents have problems because the tissue in-growth through the bare metal causes restenosis Covered Stents (Stent-Grafts) theoretically form a barrier, & prevent tissue in-growth through the stent & cause less restenosis
Covered Stents (Stent-Grafts) theoretically form a barrier, & prevent tissue in-growth through the stent & cause less restenosis
8/
 Recent clinical trials have tested the efficacy of Stent-Grafts for AV access stenosis
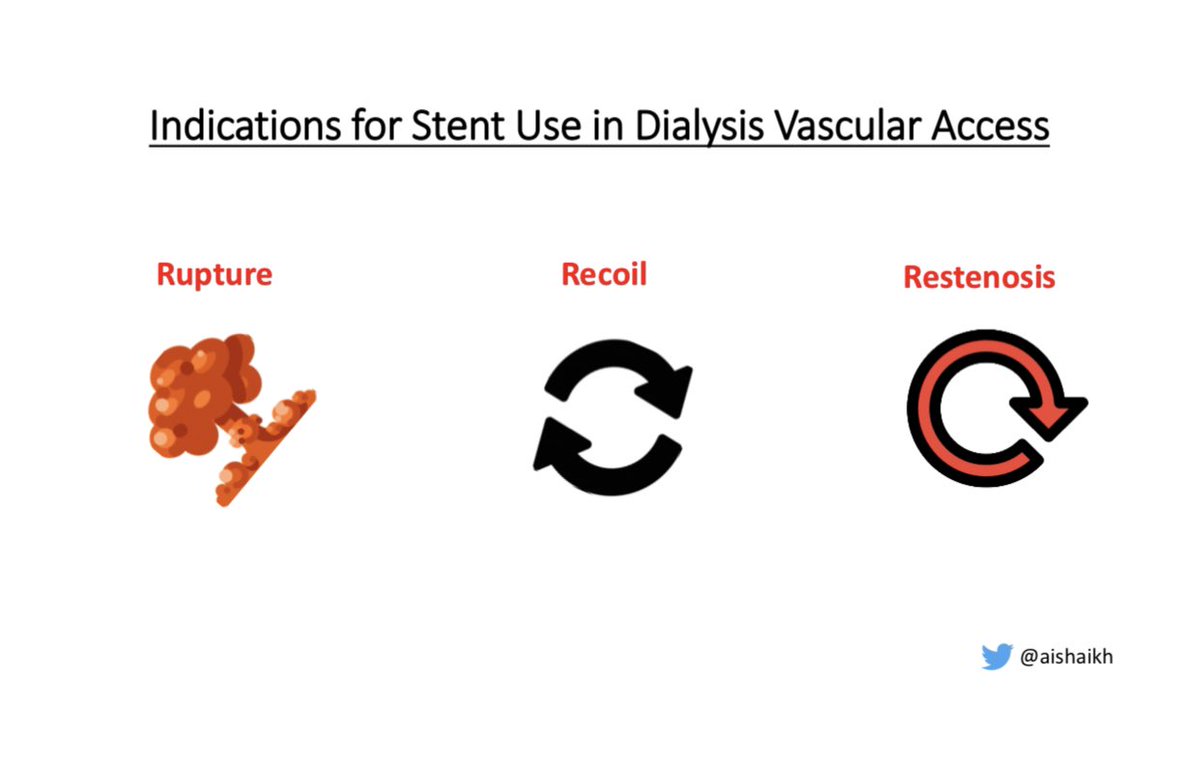
Recent clinical trials have tested the efficacy of Stent-Grafts for AV access stenosis  But before we get to the trials, let’s discuss the basic indications for Stent use:
But before we get to the trials, let’s discuss the basic indications for Stent use: Rupture of the vessel
Rupture of the vessel  Recoil (Residual stenosis)
Recoil (Residual stenosis) Restenosis
Restenosis 9/
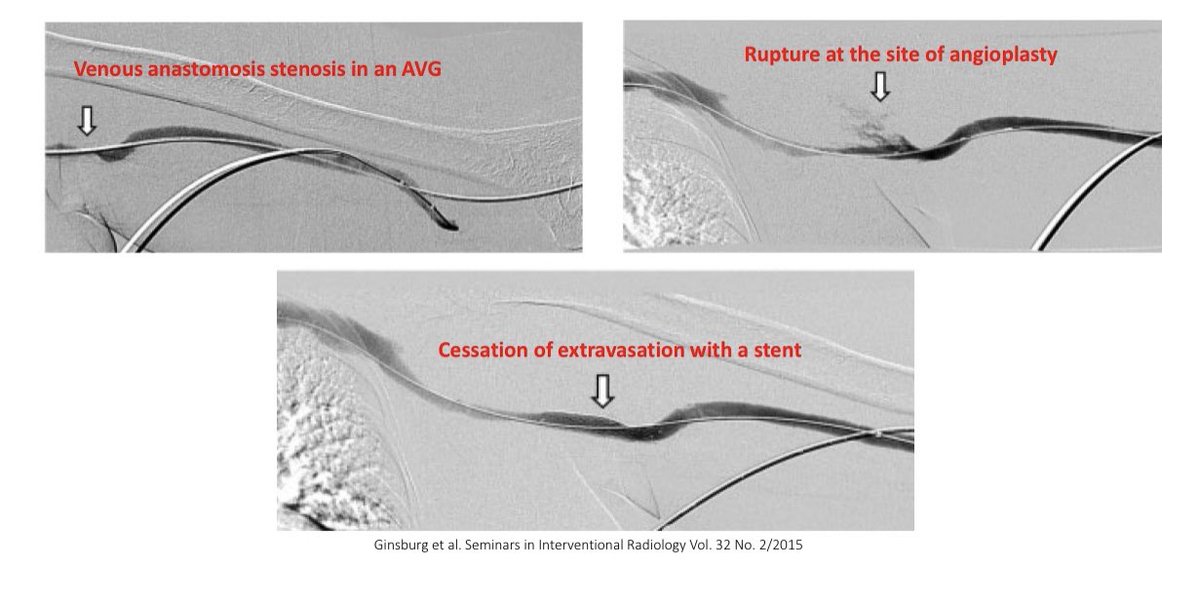
 Rupture of the vessel can occur during angioplasty of a severely stenotic lesion
Rupture of the vessel can occur during angioplasty of a severely stenotic lesion In most cases, extravasation can be controlled w/ manual compression or balloon tamponade but if bleeding persists then stents can be used to control the bleeding
In most cases, extravasation can be controlled w/ manual compression or balloon tamponade but if bleeding persists then stents can be used to control the bleeding
10/
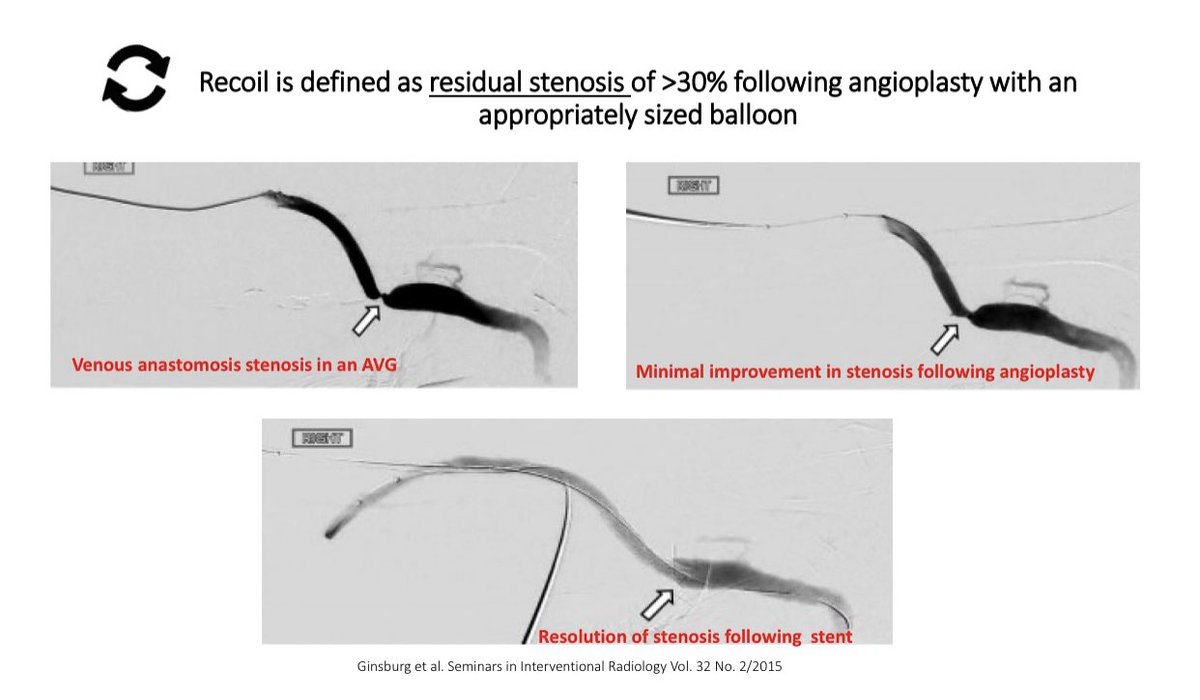
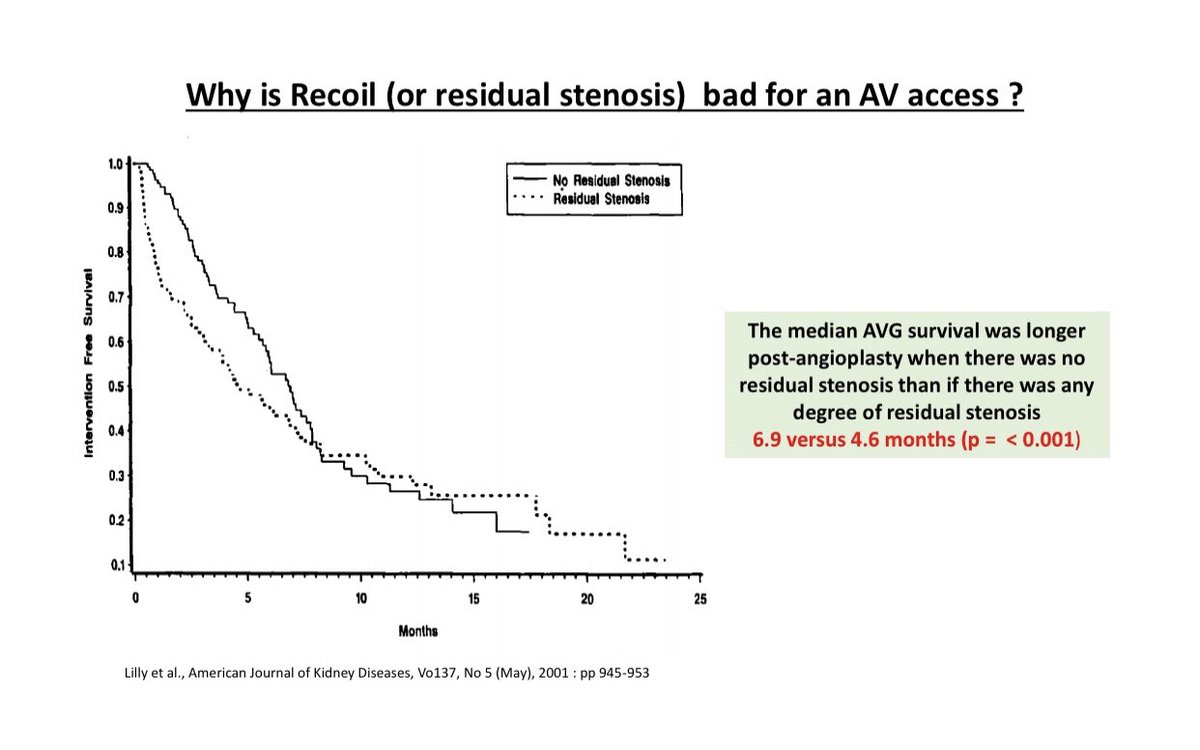
 Another indication for Stent use is Recoil
Another indication for Stent use is Recoil Recoil is defined as residual stenosis of > 30% following angioplasty & is thought to occur due to elastic recoil of the vessel wall
Recoil is defined as residual stenosis of > 30% following angioplasty & is thought to occur due to elastic recoil of the vessel wall Recoil is associated w/ poor AV access survival
Recoil is associated w/ poor AV access survival
11/
 Restenosis is the most common indication for stent use
Restenosis is the most common indication for stent use
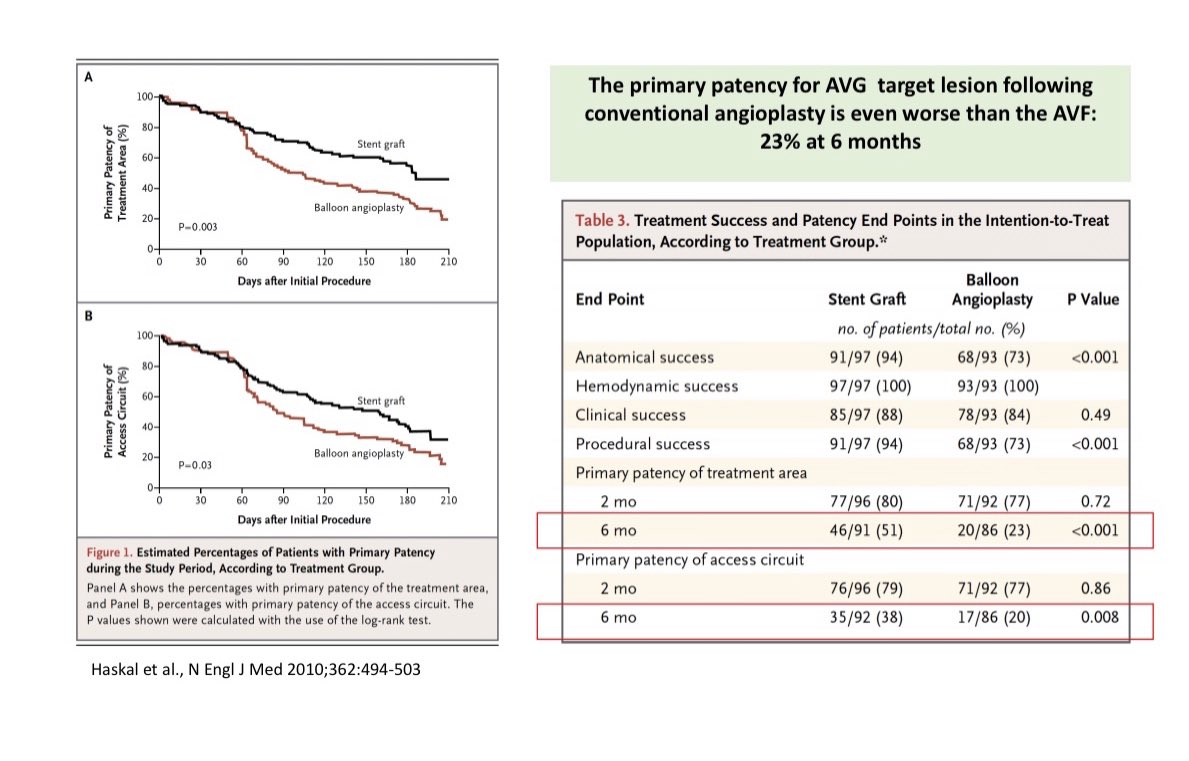
 AVG patency post-angioplasty is very poor
AVG patency post-angioplasty is very poor
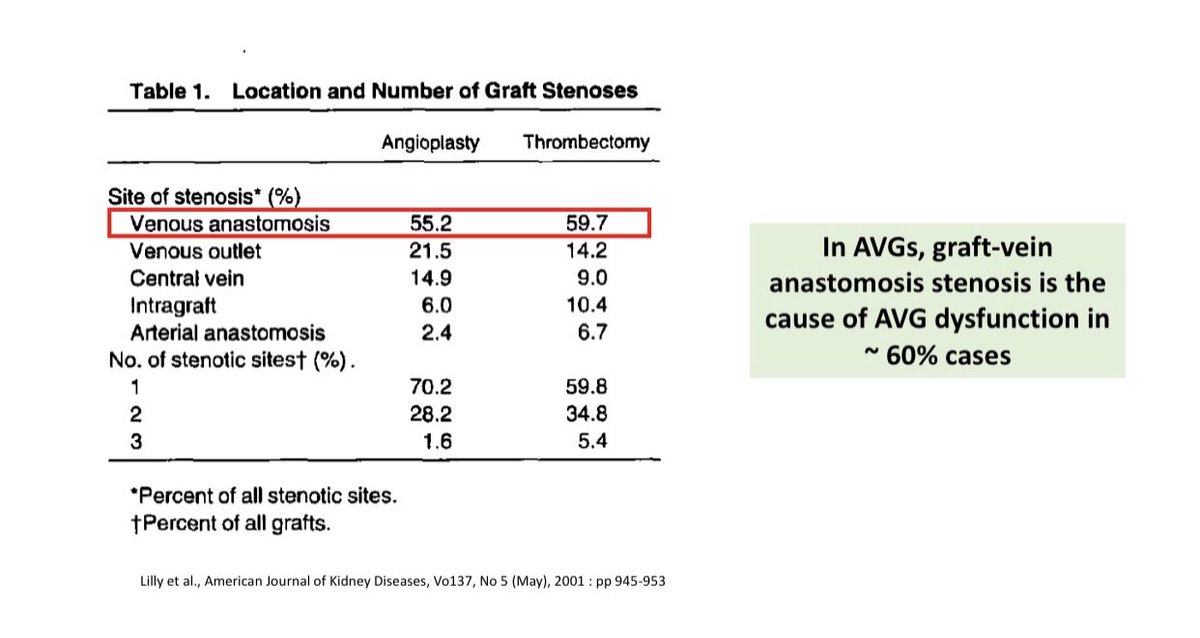
 Most common site for AVG stenosis is at the graft-vein anastomosis, therefore recent clinical trials have tested the Stent-grafts at this site
Most common site for AVG stenosis is at the graft-vein anastomosis, therefore recent clinical trials have tested the Stent-grafts at this site
12/
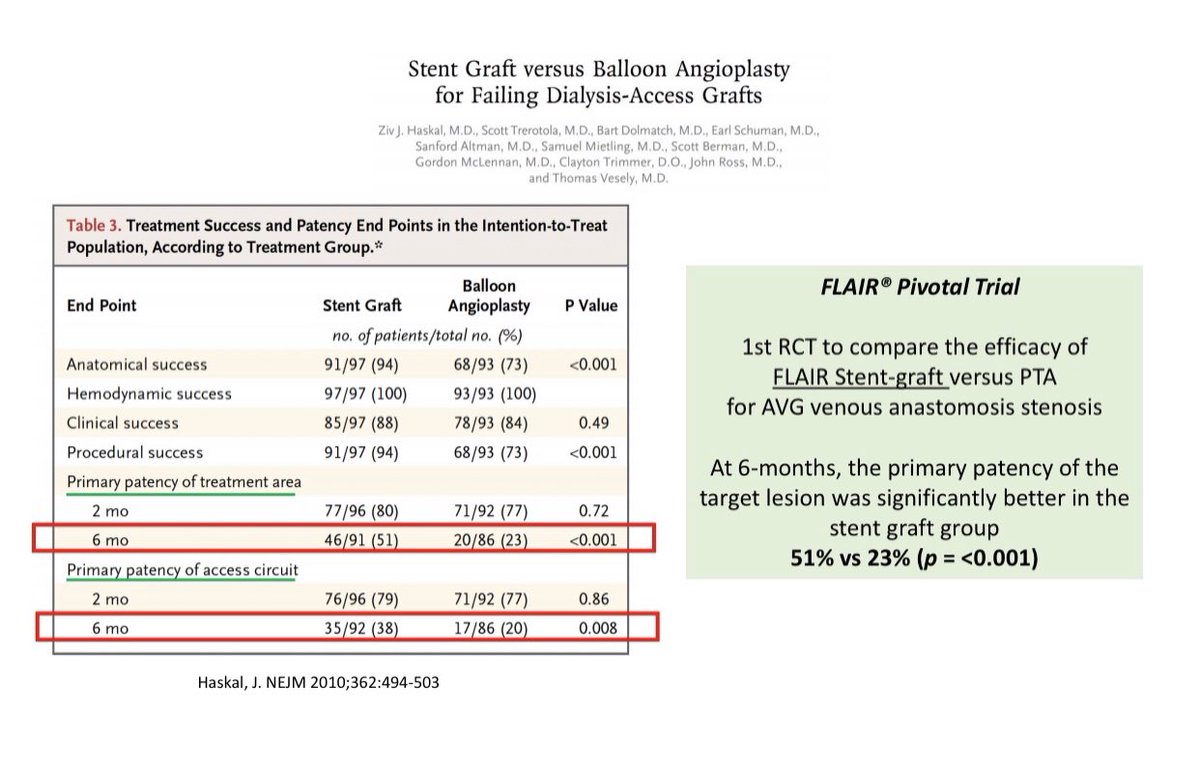
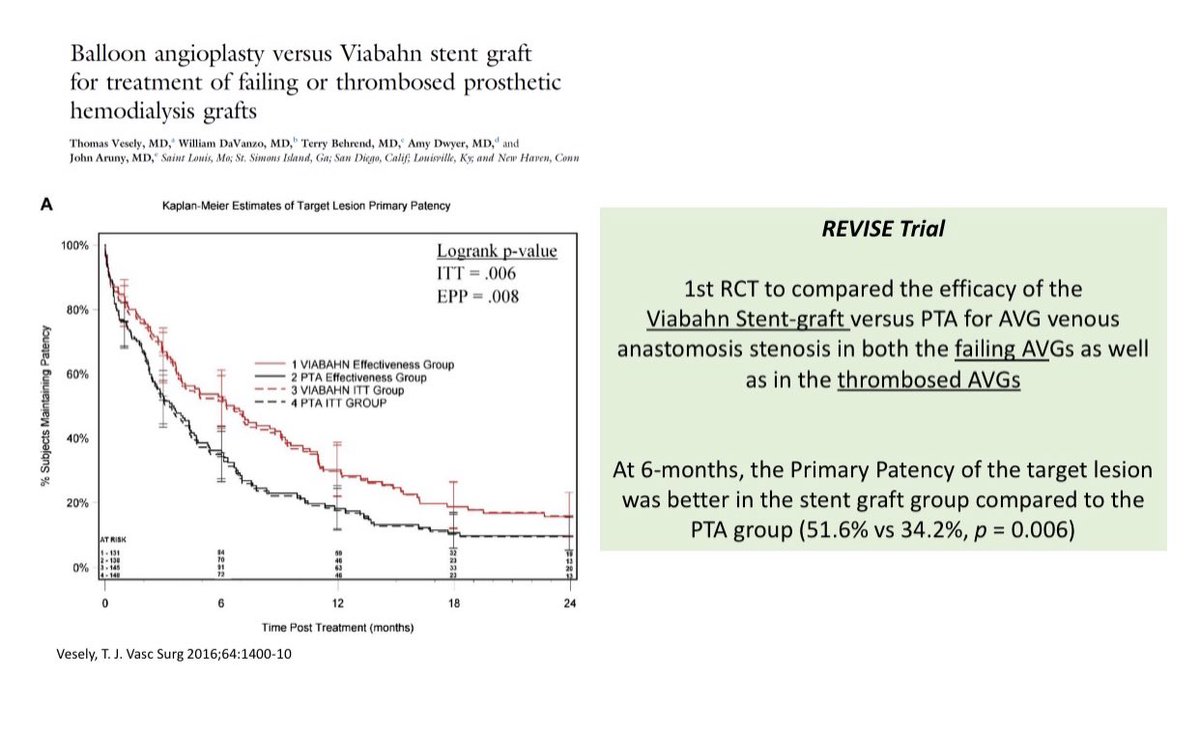
 Stent-Graft (SG)Trials in Dialysis Vascular Access
Stent-Graft (SG)Trials in Dialysis Vascular Access Flair PIVOTAL Trial: Flair SG vs. PTA for AVG
Flair PIVOTAL Trial: Flair SG vs. PTA for AVG  REVISE Trial: Viabahn SG vs PTA for AVG
REVISE Trial: Viabahn SG vs PTA for AVG Both trials showed better 6-month patency with SG use compared to PTA for graft-vein anastomosis stenosis
Both trials showed better 6-month patency with SG use compared to PTA for graft-vein anastomosis stenosis
13/
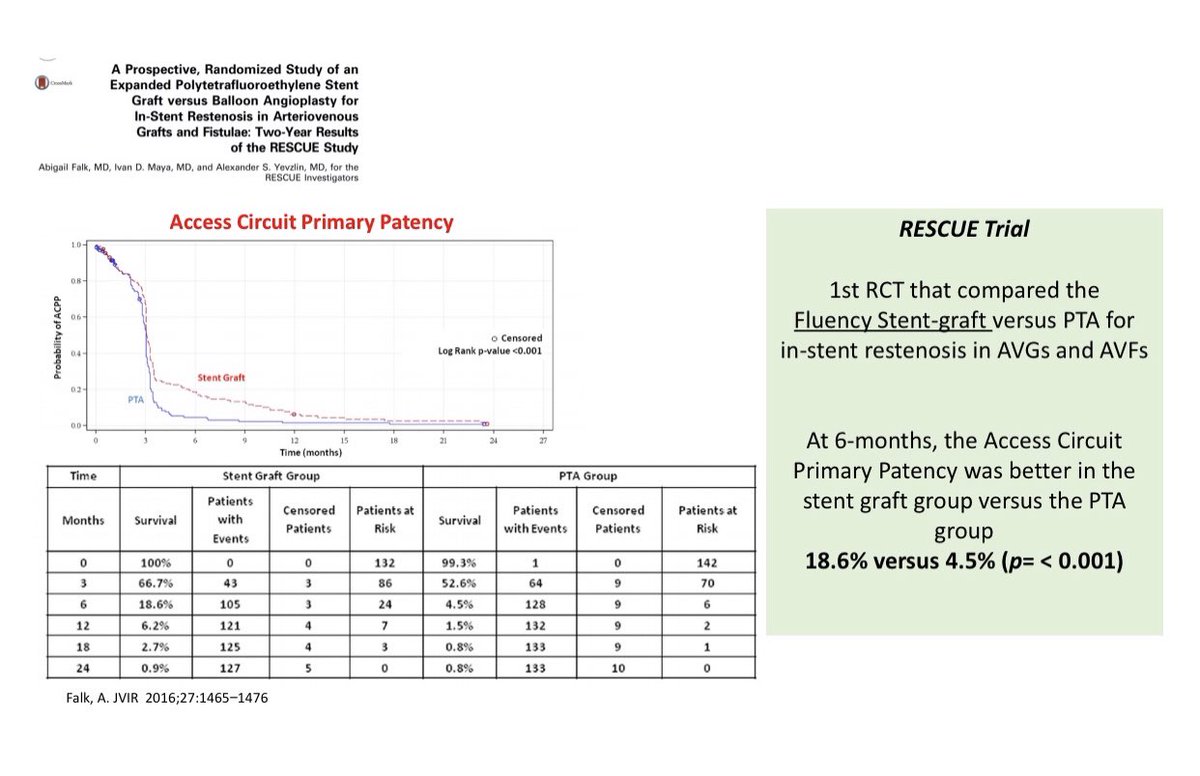
 Stent-Grafts (SG) have also been tested for In-stent restenosis
Stent-Grafts (SG) have also been tested for In-stent restenosis  RESCUE Trial: Fluency SG vs PTA for In-stent restenosis in both AVF & AVG
RESCUE Trial: Fluency SG vs PTA for In-stent restenosis in both AVF & AVG RESCUE Trial showed better 6-month patency with SG compared to PTA
RESCUE Trial showed better 6-month patency with SG compared to PTA
14/
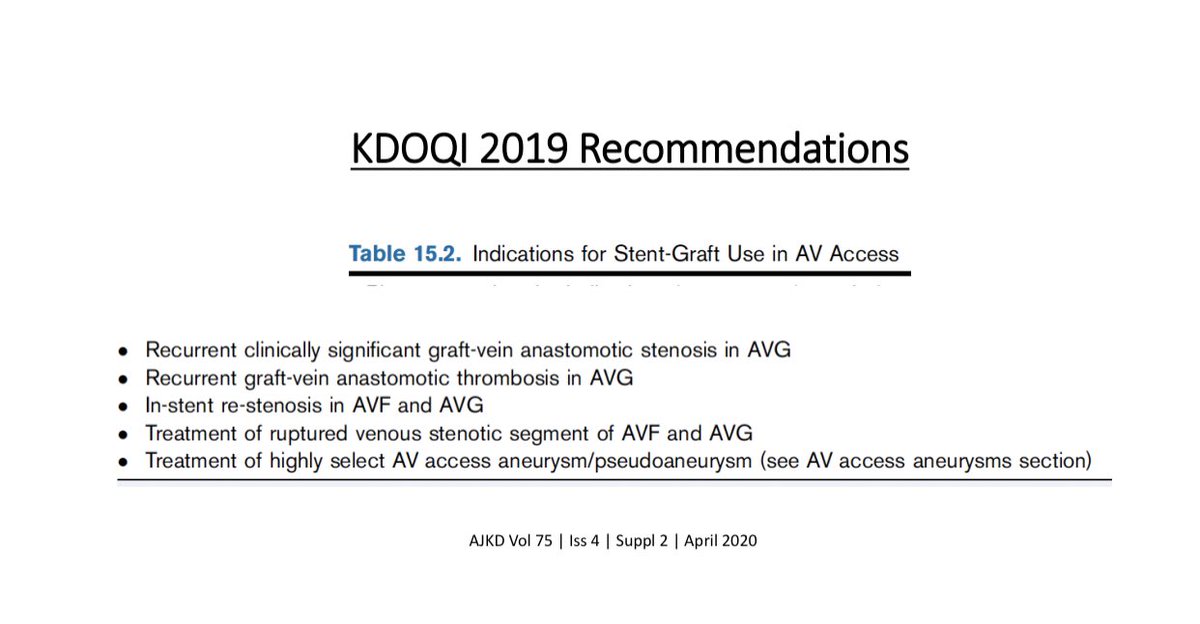
 Based on this data, KDOQI 2019 guidelines recommend Stent-Graft use for:
Based on this data, KDOQI 2019 guidelines recommend Stent-Graft use for: Recurrent graft-vein anastomosis stenosis in AVG
Recurrent graft-vein anastomosis stenosis in AVG  In-stent restenosis in AVF & AVG
In-stent restenosis in AVF & AVG
16/
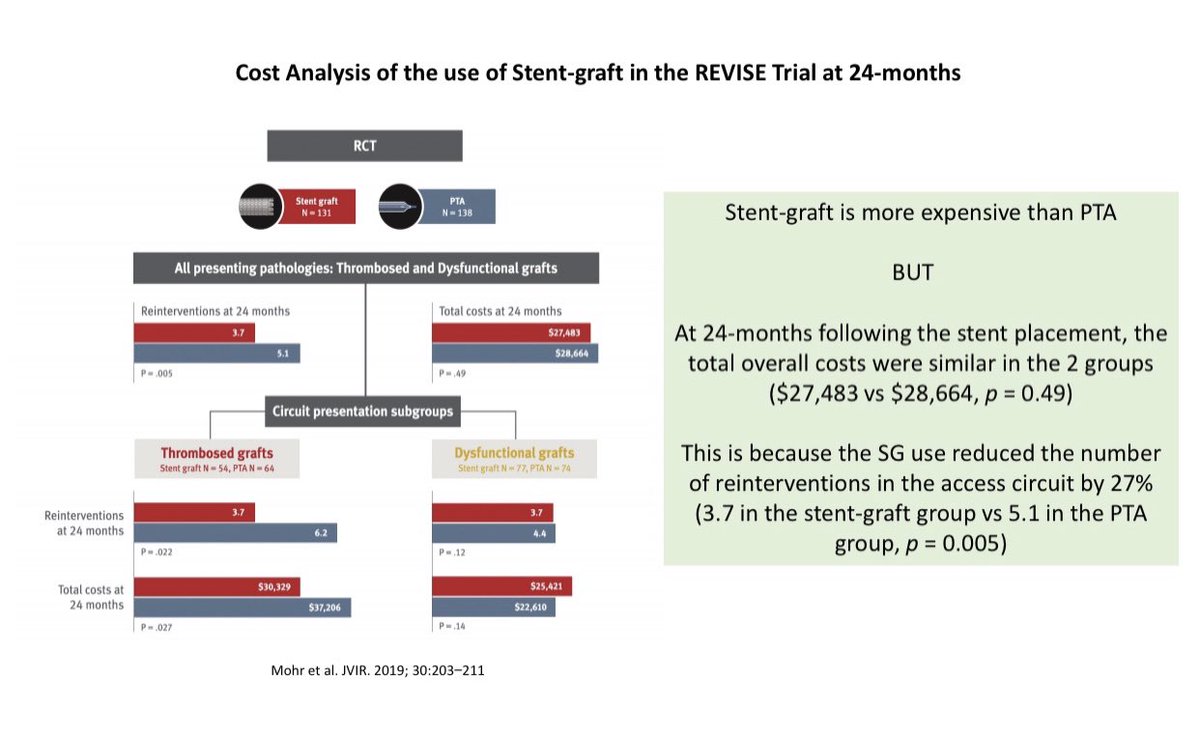
 Cost analysis of Stent-Grafts (SG) show that even though the initial cost of the SG is higher than the cost of balloon angioplasty, the overall cost was similar in the 2 groups at 24-months because the re-intervention rate was lower in the SG group
Cost analysis of Stent-Grafts (SG) show that even though the initial cost of the SG is higher than the cost of balloon angioplasty, the overall cost was similar in the 2 groups at 24-months because the re-intervention rate was lower in the SG group
17/
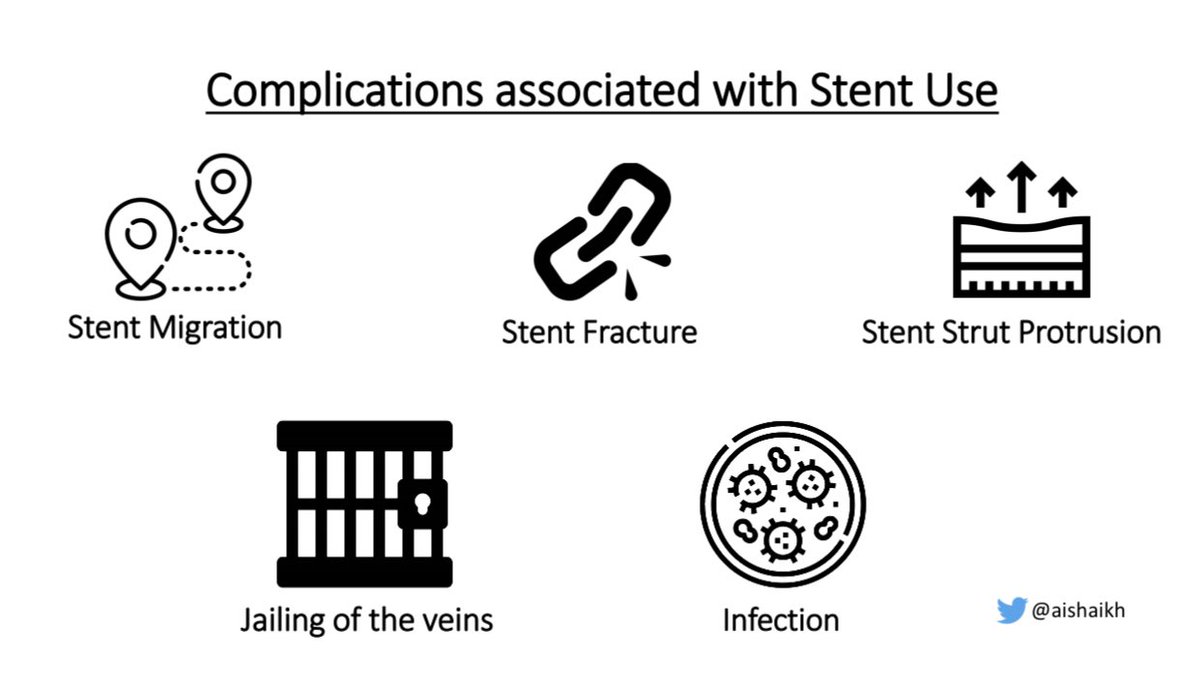
 Complications associated with Stent use:
Complications associated with Stent use: Stent Migration
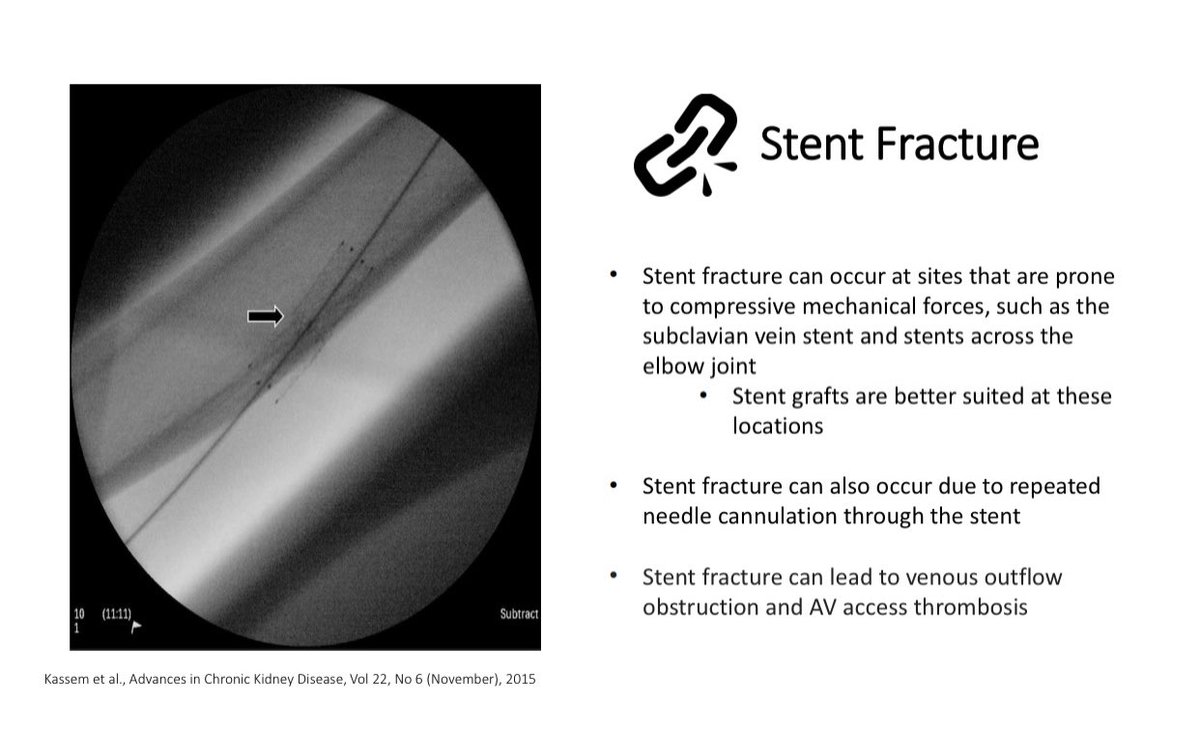
Stent Migration Stent Fracture
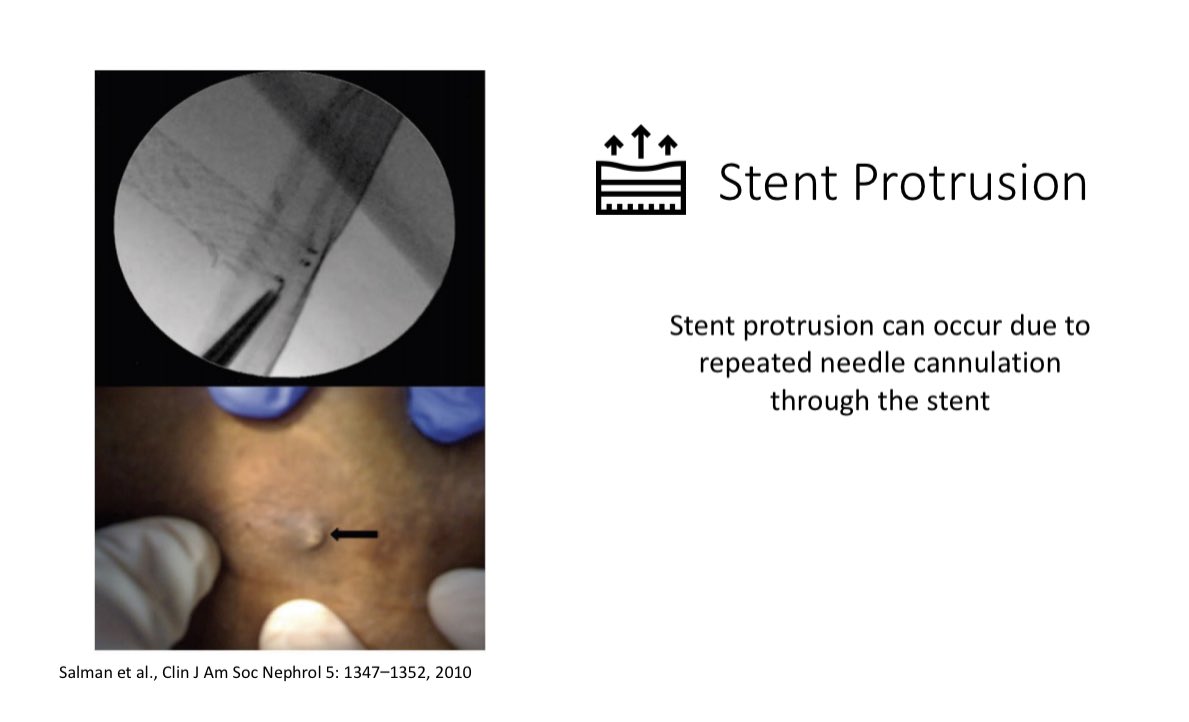
Stent Fracture Stent Strut Protrusion
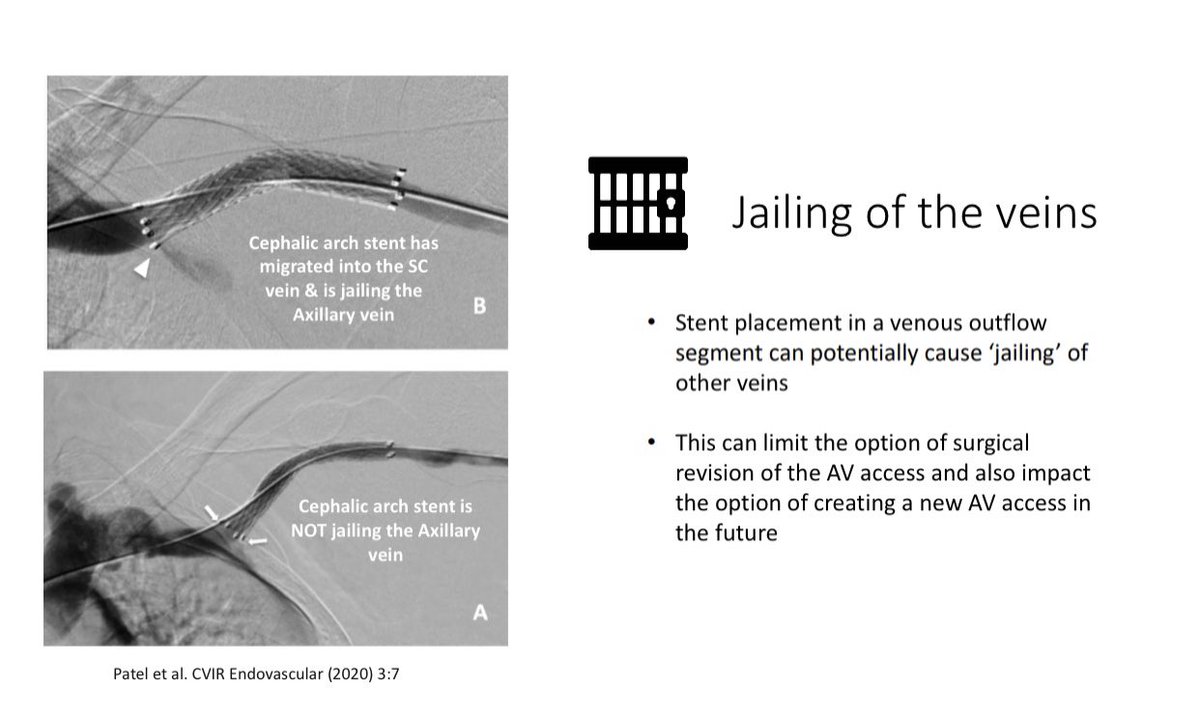
Stent Strut Protrusion Jailing of the veins
Jailing of the veins Infection
Infection 18/
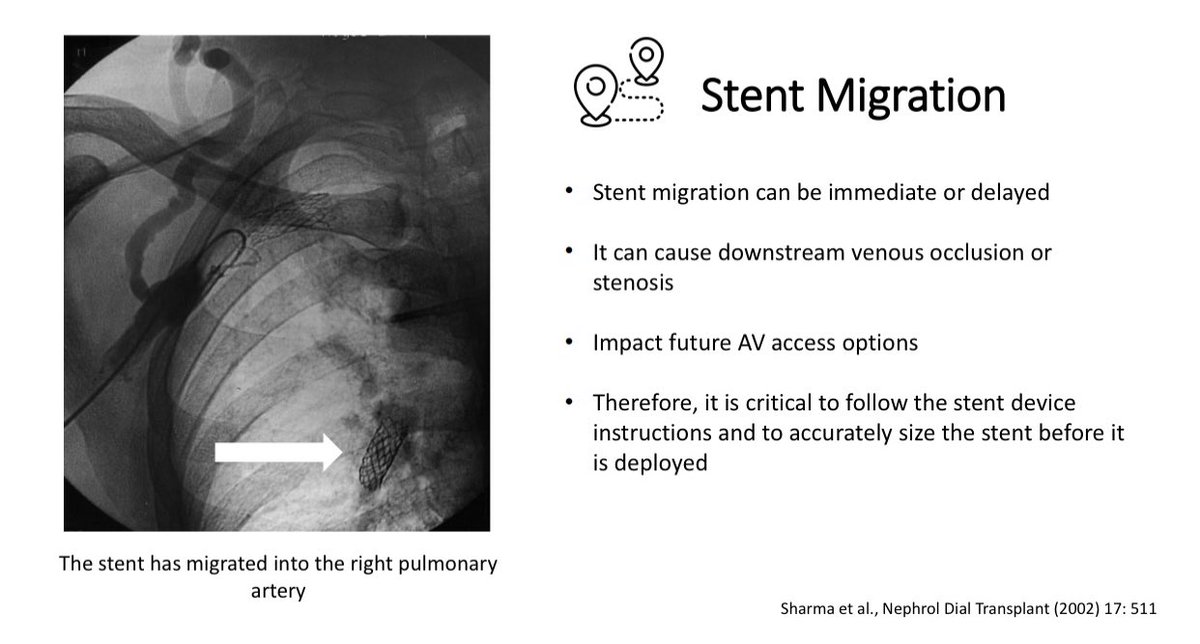
 Stent Migration can cause downstream vein occlusion/stenosis & can impact future AV access options
Stent Migration can cause downstream vein occlusion/stenosis & can impact future AV access options Stent fracture & protrusion can occur due to repeated cannulation thru the stent
Stent fracture & protrusion can occur due to repeated cannulation thru the stent
 Stent fracture can occur if stent is placed across a joint
Stent fracture can occur if stent is placed across a joint
19/
 Jailing of the Veins is a complication of stent placement & this can impact future AV access options
Jailing of the Veins is a complication of stent placement & this can impact future AV access options  Hence, the operator must be very careful during stent deployment in order to avoid this complication
Hence, the operator must be very careful during stent deployment in order to avoid this complication
20/
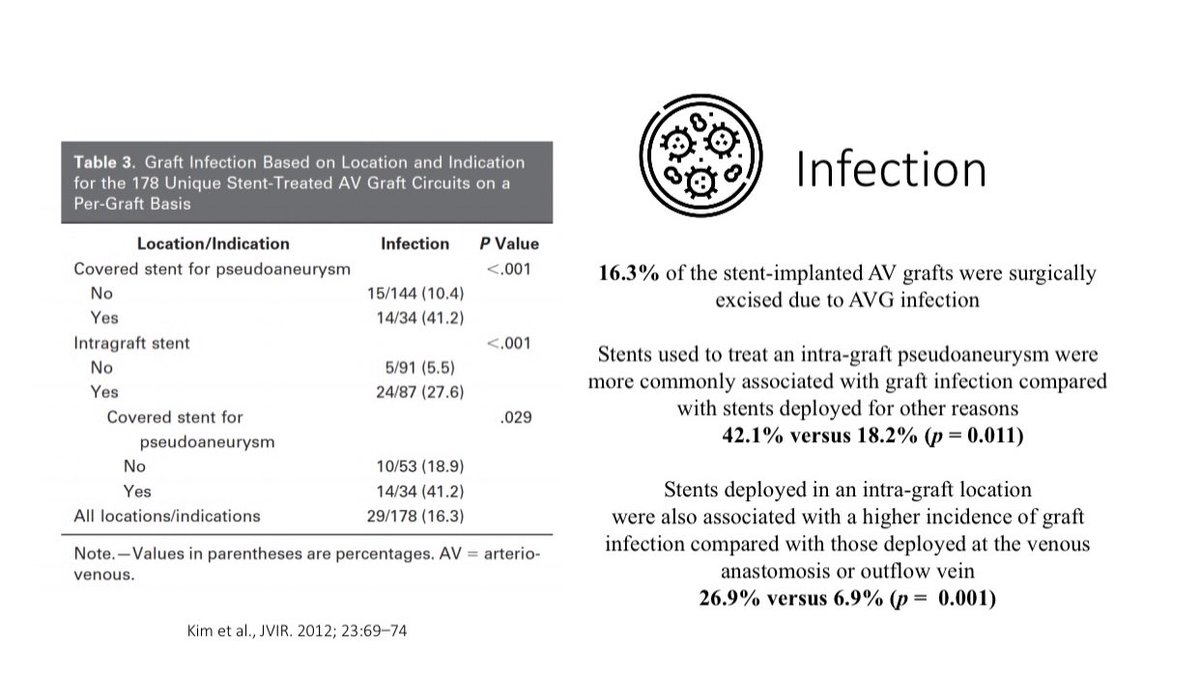
 Stent associated infection is a serious complication & may require AV access excision
Stent associated infection is a serious complication & may require AV access excision  Stent associated AV access infections are more common when the stents are placed in the Pseudo-aneurysms
Stent associated AV access infections are more common when the stents are placed in the Pseudo-aneurysms 
21/
 Stent placement must be avoided in pseudo-aneurysms & in the cannulation zone due to high risk of infection & risk of stent fracture from needle trauma
Stent placement must be avoided in pseudo-aneurysms & in the cannulation zone due to high risk of infection & risk of stent fracture from needle trauma KDOQI Guidelines state that stent placement for pseudo-aneurysm only be used as a ‘last resort’
KDOQI Guidelines state that stent placement for pseudo-aneurysm only be used as a ‘last resort’
22/
 Summary
Summary Stent-Grafts are a viable therapeutic option for AV access stenosis but it’s use must be guided by scientific evidence
Stent-Grafts are a viable therapeutic option for AV access stenosis but it’s use must be guided by scientific evidence  Balloon angioplasty remains the 1st line therapy for the majority of the AV access stenotic lesions
Balloon angioplasty remains the 1st line therapy for the majority of the AV access stenotic lesionsEnd/

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter