/1a
Overview
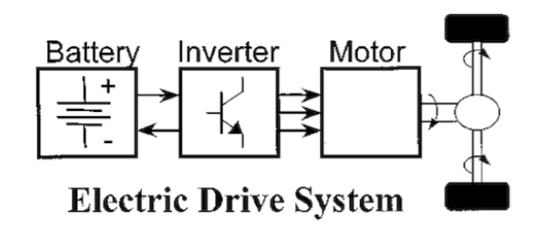
Instead of engines with petrol or diesel fuel, EVs use electric motors with electricity stored in the battery.
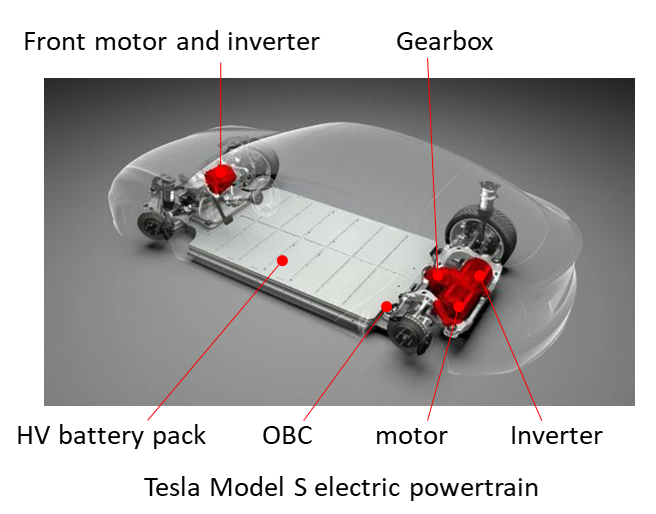
1. HV battery pack – for storing electric energy.
2. Charger – for Charging battery.
3. Motor – for converting electric energy to mechanical energy.
Overview
Instead of engines with petrol or diesel fuel, EVs use electric motors with electricity stored in the battery.
1. HV battery pack – for storing electric energy.
2. Charger – for Charging battery.
3. Motor – for converting electric energy to mechanical energy.
/1b
4. Gearbox – for boosting motor torque.
5. Inverter – for converting DC electric energy to AC electric energy.
4. Gearbox – for boosting motor torque.
5. Inverter – for converting DC electric energy to AC electric energy.
/2a
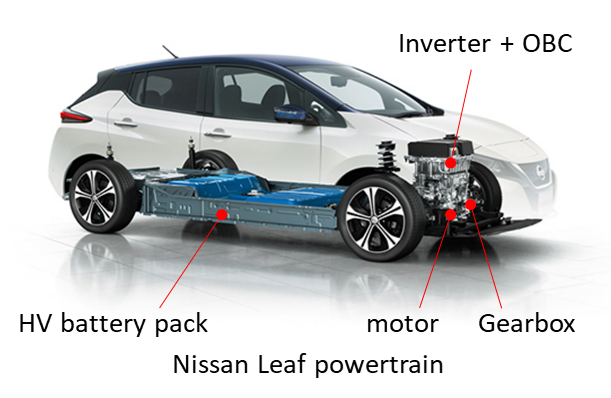
HV battery pack
1. HV battery pack is the energy source of EV, just like a fuel tank in a petrol or diesel vehicle.
2. They may use different cells (cylindrical or pouch), come with different voltage rating, energy rating, size, and shape.
HV battery pack
1. HV battery pack is the energy source of EV, just like a fuel tank in a petrol or diesel vehicle.
2. They may use different cells (cylindrical or pouch), come with different voltage rating, energy rating, size, and shape.
/2b
3. Higher energy rating (kWh) means more energy can be stored, hence a longer time to drive. But it also means EV has a bigger and heavier battery to carry around.
3. Higher energy rating (kWh) means more energy can be stored, hence a longer time to drive. But it also means EV has a bigger and heavier battery to carry around.
/2c
4. As electric energy needs to be passed onto traction motor through electric cables, HV system is adapted, so more power can be delivered through the same size of cable. Similar principle as HV power transmission on the national grid.
4. As electric energy needs to be passed onto traction motor through electric cables, HV system is adapted, so more power can be delivered through the same size of cable. Similar principle as HV power transmission on the national grid.
/3a
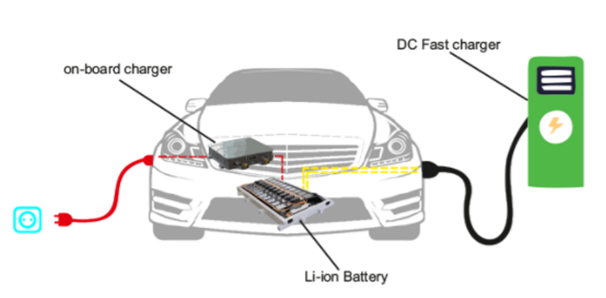
Battery charger
1. Before the drive, a petrol or diesel vehicle needs to be filled with fuel in the fuel tank. Same logic, the EV battery needs to be charged with electricity.
Battery charger
1. Before the drive, a petrol or diesel vehicle needs to be filled with fuel in the fuel tank. Same logic, the EV battery needs to be charged with electricity.
/3b
2. Most EVs come with an On-Board-Charger (OBC), so the battery can be charged using a wall socket at home.
2. Most EVs come with an On-Board-Charger (OBC), so the battery can be charged using a wall socket at home.
/3c
3. As the OBC power increases, the size and weight also increase, most modern EVs now offer Off-Board DC charging option, i.e. a more powerful (>50kW) Off-Board charger can be used to charge the battery quickly.
3. As the OBC power increases, the size and weight also increase, most modern EVs now offer Off-Board DC charging option, i.e. a more powerful (>50kW) Off-Board charger can be used to charge the battery quickly.
/4a
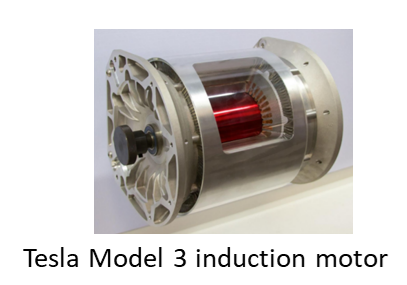
Motor
1. Electric motor is the moving source of the EV, just like the engine in petrol or diesel vehicle.
Motor
1. Electric motor is the moving source of the EV, just like the engine in petrol or diesel vehicle.
/4b
2. Different OEMs have their own preferred motor types, e.g. original Tesla Model S uses an induction motor, while in Model 3, a Permanent Magnet (PM) motor is used. Nissan Leaf uses a PM motor. While Renault Zoe uses a wound rotor motor.
2. Different OEMs have their own preferred motor types, e.g. original Tesla Model S uses an induction motor, while in Model 3, a Permanent Magnet (PM) motor is used. Nissan Leaf uses a PM motor. While Renault Zoe uses a wound rotor motor.
/4c
3. Same as petrol or diesel engine, the electric motor also comes with different power ratings, while a unit of kW is used instead of hp, e.g. Nissan leaf has a max power of 110kW, Tesla Model 3 D (Dual motor version) can have a max power of up to 350kW.
3. Same as petrol or diesel engine, the electric motor also comes with different power ratings, while a unit of kW is used instead of hp, e.g. Nissan leaf has a max power of 110kW, Tesla Model 3 D (Dual motor version) can have a max power of up to 350kW.
/5a
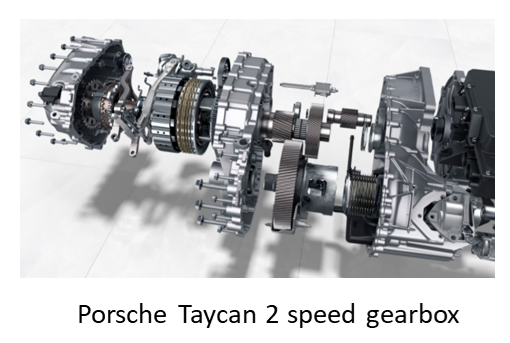
Gearbox
1. With the unique torque-speed characteristics of an electric motor (which will be covered in a later section), EV can have NO gearbox at all. Lohner-Porsche Mixte used 4 motors mounted directly in wheels.
Gearbox
1. With the unique torque-speed characteristics of an electric motor (which will be covered in a later section), EV can have NO gearbox at all. Lohner-Porsche Mixte used 4 motors mounted directly in wheels.
/5b
2. While in modern EVs, in order to balance the weight and performance, 1 speed (two-stage) gearbox with around 9:1 reduction ratio is commonly used.
2. While in modern EVs, in order to balance the weight and performance, 1 speed (two-stage) gearbox with around 9:1 reduction ratio is commonly used.
/5c
3. For some high-performance vehicles, even 2 speed gearbox is still used, i.e. high reduction ratio for faster acceleration, and low reduction ratio for a high-speed drive.
3. For some high-performance vehicles, even 2 speed gearbox is still used, i.e. high reduction ratio for faster acceleration, and low reduction ratio for a high-speed drive.
/6a
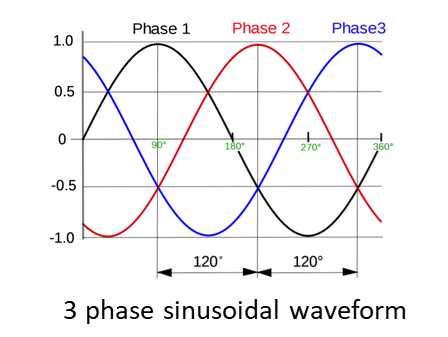
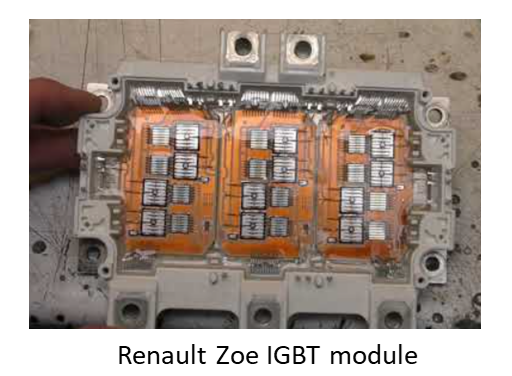
Inverter
1. As battery can only provide DC electric power while most modern EVs use 3 phase AC motor, an inverter (also called Motor Control Unit) is needed, so a proper 3 phase voltage/current can be created for driving the motor.
Inverter
1. As battery can only provide DC electric power while most modern EVs use 3 phase AC motor, an inverter (also called Motor Control Unit) is needed, so a proper 3 phase voltage/current can be created for driving the motor.
/6b
2. Thanks to a power electronics device so-called IGBT (Isolated Gate Bipolar Transistor), DC voltage/current can be “inverted” in very high frequency (around 10kHz) PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) format.
2. Thanks to a power electronics device so-called IGBT (Isolated Gate Bipolar Transistor), DC voltage/current can be “inverted” in very high frequency (around 10kHz) PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) format.
Hope you found this useful, will be back next week with another interesting thread. Until then please like and share it with your friends. Also, don't forget to provide your feedback by replying to this tweet.
Here is the start of the thread https://twitter.com/EvQuotient/status/1337421941745958912

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter