(1/12) Where is fluconazole resistant yeast MOST difficult to treat?

(2/12) While each present unique issues  Fluconazole resistant fungal urinary tract infections (UTI) are particularly challenging. The rationale will require an adventure into antifungal PK…
Fluconazole resistant fungal urinary tract infections (UTI) are particularly challenging. The rationale will require an adventure into antifungal PK…
 Fluconazole resistant fungal urinary tract infections (UTI) are particularly challenging. The rationale will require an adventure into antifungal PK…
Fluconazole resistant fungal urinary tract infections (UTI) are particularly challenging. The rationale will require an adventure into antifungal PK…
(3/12) Let’s start with the basics  Most fungal UTIs are caused by C. albicans & other Candida spp.
Most fungal UTIs are caused by C. albicans & other Candida spp.
Yeast in urine usually non-pathogenic.
non-pathogenic.
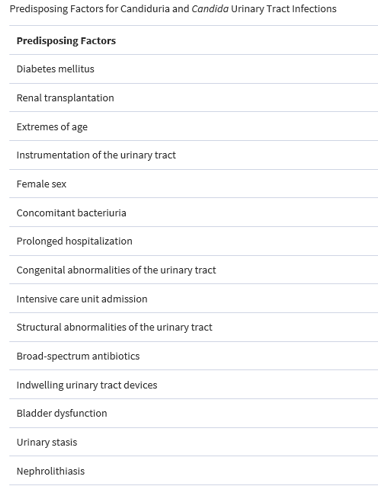
How do you know if it is pathogenic? ✓ for predisposing factors & for symptoms.
for symptoms.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21498839/
 Most fungal UTIs are caused by C. albicans & other Candida spp.
Most fungal UTIs are caused by C. albicans & other Candida spp.Yeast in urine usually
 non-pathogenic.
non-pathogenic. How do you know if it is pathogenic? ✓ for predisposing factors &
 for symptoms.
for symptoms. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21498839/
(4/12) Symptomatic  treat! Due to the PK profile, fluconazole = Candida spp. cystitis DOC if susceptible.
treat! Due to the PK profile, fluconazole = Candida spp. cystitis DOC if susceptible.
☟study: Fluconazole ↑↑ [tissue]/[plasma] ratio, Fluconazole [urine] >> [plasma]x 10!
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2543281/
 treat! Due to the PK profile, fluconazole = Candida spp. cystitis DOC if susceptible.
treat! Due to the PK profile, fluconazole = Candida spp. cystitis DOC if susceptible. ☟study: Fluconazole ↑↑ [tissue]/[plasma] ratio, Fluconazole [urine] >> [plasma]x 10!
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2543281/
(5/12) So what if fluconazole is resistant?
For most infections with C. glabrata or krusei itra, vori, and posa; BUT, these are
itra, vori, and posa; BUT, these are 

 suitable for cystitis!
suitable for cystitis!
For most infections with C. glabrata or krusei
 itra, vori, and posa; BUT, these are
itra, vori, and posa; BUT, these are 

 suitable for cystitis!
suitable for cystitis!
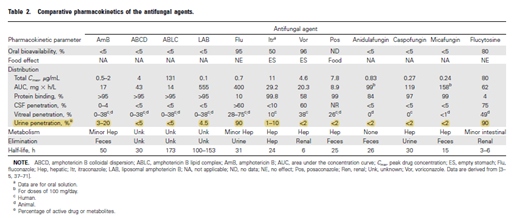
(6/12) Let’s review urinary penetration of different antifungals.  Only flucytosine and IV AmB are widely accepted to have adequate urinary penetration ☟
Only flucytosine and IV AmB are widely accepted to have adequate urinary penetration ☟
https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/43/Supplement_1/S28/318707
 Only flucytosine and IV AmB are widely accepted to have adequate urinary penetration ☟
Only flucytosine and IV AmB are widely accepted to have adequate urinary penetration ☟https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/43/Supplement_1/S28/318707
(7/12) What about Echinocandins? Despite minimal urinary penetration  Case reports have demonstrated successful
Case reports have demonstrated successful TX of Candida UTIs w/ mica & caspo… though the use of these agents for cystitis is
TX of Candida UTIs w/ mica & caspo… though the use of these agents for cystitis is  routinely recommended and more evidence is needed
routinely recommended and more evidence is needed 
https://dig.pharmacy.uic.edu/faqs/2019-2/august-2019-faqs/is-there-evidence-to-support-the-use-of-echinocandins-for-urinary-tract-infection/
 Case reports have demonstrated successful
Case reports have demonstrated successful TX of Candida UTIs w/ mica & caspo… though the use of these agents for cystitis is
TX of Candida UTIs w/ mica & caspo… though the use of these agents for cystitis is  routinely recommended and more evidence is needed
routinely recommended and more evidence is needed 
https://dig.pharmacy.uic.edu/faqs/2019-2/august-2019-faqs/is-there-evidence-to-support-the-use-of-echinocandins-for-urinary-tract-infection/
(8/12) Does the formulation of AmB matter? YES!
Lipid AmB << AmB deoxy for nephrotoxicity/infusion rxns but literature suggests liposomal has poor [kidney/urine] penetration… AND… Candida UTI treatment failure with liposomal AmB is reported.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10530471/
Lipid AmB << AmB deoxy for nephrotoxicity/infusion rxns but literature suggests liposomal has poor [kidney/urine] penetration… AND… Candida UTI treatment failure with liposomal AmB is reported.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10530471/
(9/12) Don’t forget about flucytosine! Not generally our first thought… but a viable option in some Candida cystitis.
Resistance develops quickly with monotherapy so TX for 7-10d only. Renally dosed and for hepatotoxicity
for hepatotoxicity 
Resistance develops quickly with monotherapy so TX for 7-10d only. Renally dosed and
 for hepatotoxicity
for hepatotoxicity 
(10/12) Looking for non-standard routes of admin? AmB deoxy can be administered as a bladder irrigation 
Irrigations can be done continuously [50mg/L] for 5-7d and may resolve Candida cystitis in > 90% of patients, however… relapse rates are high! https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7109077/
relapse rates are high! https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7109077/

Irrigations can be done continuously [50mg/L] for 5-7d and may resolve Candida cystitis in > 90% of patients, however…
 relapse rates are high! https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7109077/
relapse rates are high! https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7109077/
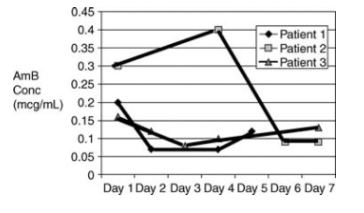
(11/12) Short courses of IV AmB deoxy can be considered for cystitis. In fact, single doses of AmB deoxy have produced fungicidal concentrations in urine for days-weeks after x1 IV dose! 
This graph shows AmB urine conc. following x1 IV dose in 3 patients.

This graph shows AmB urine conc. following x1 IV dose in 3 patients.
(12/12)
So… let’s recap!
 Fluconazole is DOC in susceptible Candida spp. UTIs
Fluconazole is DOC in susceptible Candida spp. UTIs
 Flucytosine & AmB are 1st line options w/strong evidence for fluconazole R isolates
Flucytosine & AmB are 1st line options w/strong evidence for fluconazole R isolates
 AmB formulation matters & don't forget to monitor for ADRs!
AmB formulation matters & don't forget to monitor for ADRs!
 Echinocandin PK is
Echinocandin PK is  and evidence is limited
and evidence is limited
So… let’s recap!
 Fluconazole is DOC in susceptible Candida spp. UTIs
Fluconazole is DOC in susceptible Candida spp. UTIs Flucytosine & AmB are 1st line options w/strong evidence for fluconazole R isolates
Flucytosine & AmB are 1st line options w/strong evidence for fluconazole R isolates AmB formulation matters & don't forget to monitor for ADRs!
AmB formulation matters & don't forget to monitor for ADRs! Echinocandin PK is
Echinocandin PK is  and evidence is limited
and evidence is limited

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter
![(4/12) Symptomatic treat! Due to the PK profile, fluconazole = Candida spp. cystitis DOC if susceptible. ☟study: Fluconazole ↑↑ [tissue]/[plasma] ratio, Fluconazole [urine] >> [plasma]x 10! https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2543281/ (4/12) Symptomatic treat! Due to the PK profile, fluconazole = Candida spp. cystitis DOC if susceptible. ☟study: Fluconazole ↑↑ [tissue]/[plasma] ratio, Fluconazole [urine] >> [plasma]x 10! https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2543281/](https://pbs.twimg.com/media/Eow6A9UW8AYIRAI.png)
![(8/12) Does the formulation of AmB matter? YES! Lipid AmB << AmB deoxy for nephrotoxicity/infusion rxns but literature suggests liposomal has poor [kidney/urine] penetration… AND… Candida UTI treatment failure with liposomal AmB is reported. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10530471/ (8/12) Does the formulation of AmB matter? YES! Lipid AmB << AmB deoxy for nephrotoxicity/infusion rxns but literature suggests liposomal has poor [kidney/urine] penetration… AND… Candida UTI treatment failure with liposomal AmB is reported. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10530471/](https://pbs.twimg.com/media/Eow67kgXYAAFw9y.png)