In this thread, we will discuss the basics of electrification and the different stages of electrification.
/1
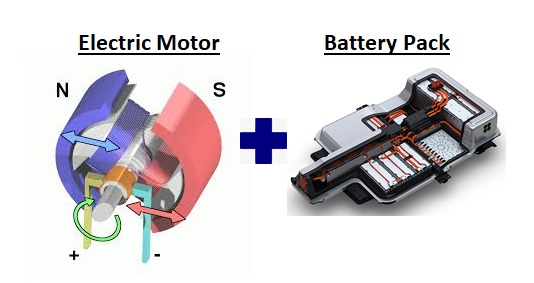
Electrification: Introduction of Electric motor and Higher capacity Battery to assist or replace the engine in a vehicle forms the basis of electrification. Electrification is often used to improve fuel efficiency and reduce pollution
Electrification: Introduction of Electric motor and Higher capacity Battery to assist or replace the engine in a vehicle forms the basis of electrification. Electrification is often used to improve fuel efficiency and reduce pollution
/2
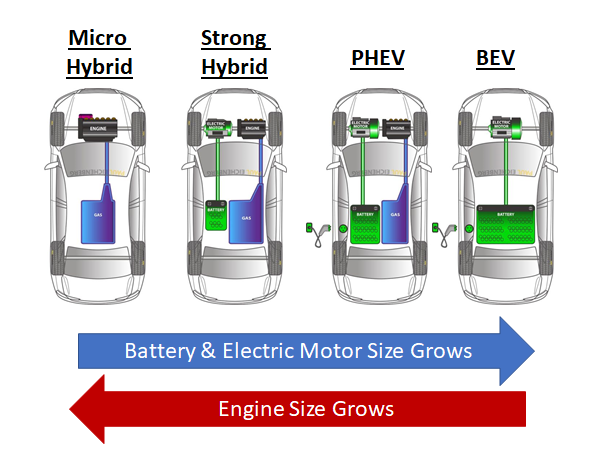
Different Stages: Depending on the size of the battery and motor, electrification can be achieved in different stages.
Micro Hybrid → Mild Hybrid → Strong Hybrid → Plug-in-Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) → Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
Different Stages: Depending on the size of the battery and motor, electrification can be achieved in different stages.
Micro Hybrid → Mild Hybrid → Strong Hybrid → Plug-in-Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) → Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
/3a
Micro Hybrid
Micro hybrid is the simplest form of electrification. The most common feature is the "Start-Stop system", wherein the engine stops whenever the car is idling at a traffic light and restarts whenever the driver presses the accelerator or clutch.
Micro Hybrid
Micro hybrid is the simplest form of electrification. The most common feature is the "Start-Stop system", wherein the engine stops whenever the car is idling at a traffic light and restarts whenever the driver presses the accelerator or clutch.
/3b
That way the vehicle saves fuel when stationary. It does not have an electric motor nor a huge battery
Today more than 50% of the vehicle produced in the world have this simple stop/start feature.
That way the vehicle saves fuel when stationary. It does not have an electric motor nor a huge battery
Today more than 50% of the vehicle produced in the world have this simple stop/start feature.
/4a
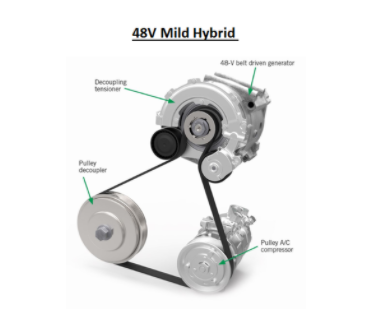
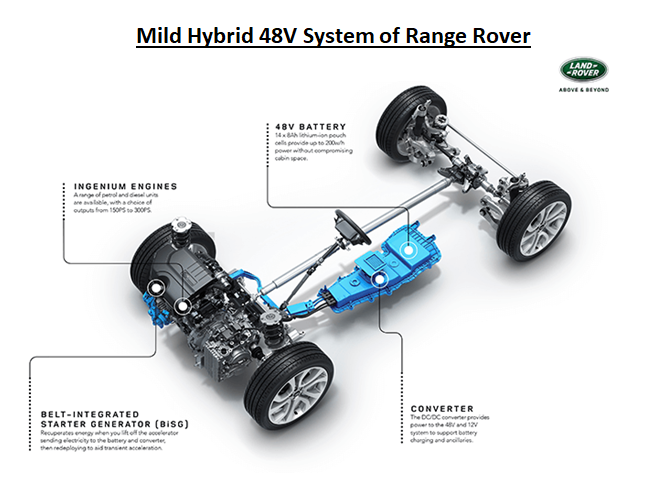
Mild Hybrid - This technology is also called "Passive boost". Here starter motor and alternator are merged to create a starter generator which helps assist the vehicle speed in the event of Acceleration and thereby reducing the higher fuel requirement during acceleration.
Mild Hybrid - This technology is also called "Passive boost". Here starter motor and alternator are merged to create a starter generator which helps assist the vehicle speed in the event of Acceleration and thereby reducing the higher fuel requirement during acceleration.
/4b
The component used to perform this function is BISG - Belt Integrated starter generator and this is placed in the belt system of the ICE engine as an auxiliary. This can generate up to 10kw motor power.
The component used to perform this function is BISG - Belt Integrated starter generator and this is placed in the belt system of the ICE engine as an auxiliary. This can generate up to 10kw motor power.
/4c
The battery capacity required is slightly higher than the micro-hybrid and usually operates in a 48V system
The battery capacity required is slightly higher than the micro-hybrid and usually operates in a 48V system
/5a
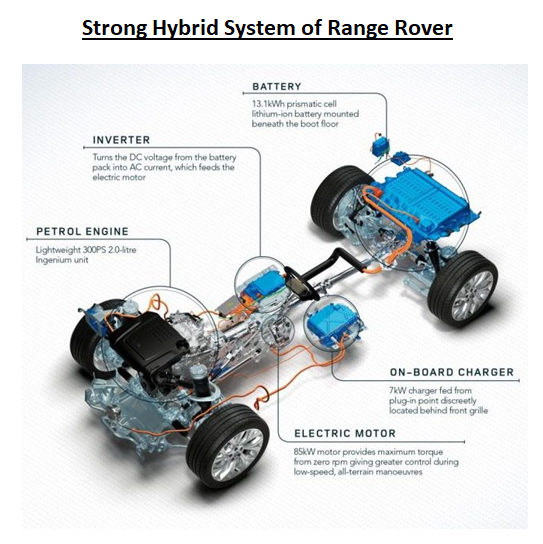
Strong Hybrid - This features a higher power starter generator and higher capacity battery to operate the vehicle in stand-alone electric mode for several kilometers.
Strong Hybrid - This features a higher power starter generator and higher capacity battery to operate the vehicle in stand-alone electric mode for several kilometers.
/5b
It has an additional clutch between engine and gearbox to help disconnect the engine from the motor system and thereby enabling the vehicle to operate only with an electric motor.
It has an additional clutch between engine and gearbox to help disconnect the engine from the motor system and thereby enabling the vehicle to operate only with an electric motor.
/5c
The motor capacity in this would be in excess of 20kw and can go up to 100kw depending on how big is the vehicle. Here ICE is used to both run the vehicle as well as to charge the battery, which in turn powers the motor.
The motor capacity in this would be in excess of 20kw and can go up to 100kw depending on how big is the vehicle. Here ICE is used to both run the vehicle as well as to charge the battery, which in turn powers the motor.
/6a
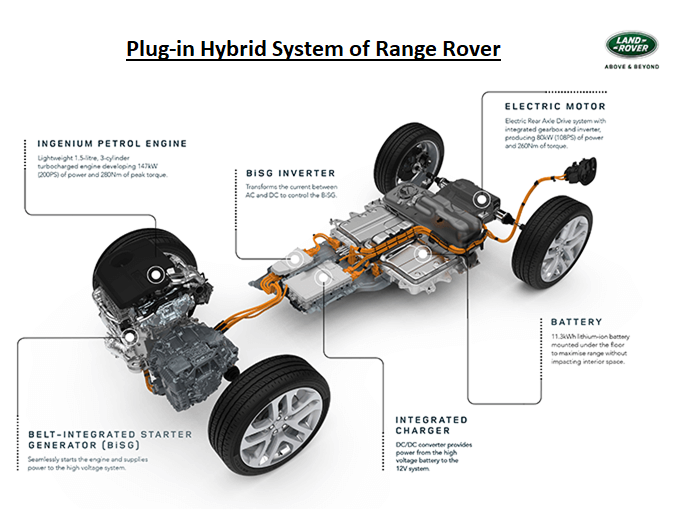
Plug-in-Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) - It is the highest form of a hybrid system. PHEVs are very similar to strong hybrids but they have a plug-in option to charge the battery from the external charging stations.
Plug-in-Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) - It is the highest form of a hybrid system. PHEVs are very similar to strong hybrids but they have a plug-in option to charge the battery from the external charging stations.
/6b
It has a much bigger motor and battery capacity as it can run up to 100km with an electric drive. Because of the increased motor and battery capacity of PHEV, the size of the engine is usually reduced to improve fuel efficiency.
It has a much bigger motor and battery capacity as it can run up to 100km with an electric drive. Because of the increased motor and battery capacity of PHEV, the size of the engine is usually reduced to improve fuel efficiency.
/7
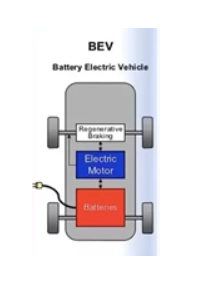
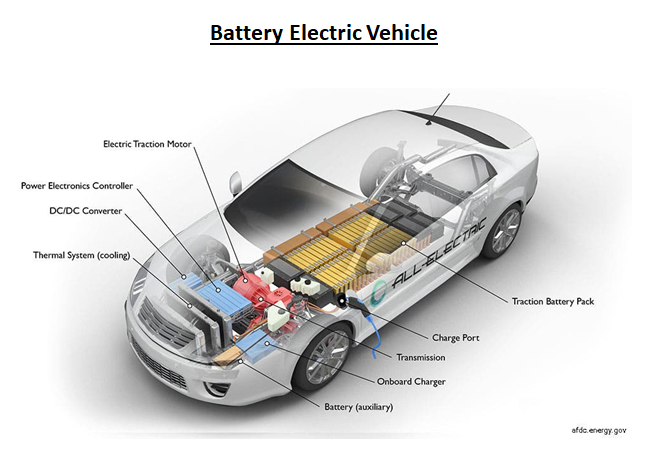
Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) - It's the ultimate form of electrification with 100% electric drive. This does not feature an IC engine and the vehicle operates solely on Motor and Battery combination.
Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) - It's the ultimate form of electrification with 100% electric drive. This does not feature an IC engine and the vehicle operates solely on Motor and Battery combination.
Hope you found this useful, will be back next week with another interesting thread. Until then please like and share it with your friends. Also, don't forget to provide your feedback by replying to this tweet.
Here is the start of the thread: https://twitter.com/EvQuotient/status/1334806603539738625

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter