The great dome of Heaven rises above, and no man knows its limitations.
The broad Earth is spread wide, and no man knows its boundaries.
Man cannot fathom it all; O God who is great, have compassion on my littleness.
The broad Earth is spread wide, and no man knows its boundaries.
Man cannot fathom it all; O God who is great, have compassion on my littleness.
Bear patiently with my blunderings, and overlook my ignorance.
Your reach is so great, and mine is so small; help me to know You for myself.
I am helpless and lost.
I am helpless and lost.
Hail to The Supreme Power and Spirit!
early 16th century (in dome (sense 3)): from Latin domus ; other senses are via French dôme, from Italian duomo ‘cathedral, dome’.
Shaped like a dome?
Shaped like a dome?
What does this tell you exactly?
They have lied about everything.
We all live inside a dome.
All an illusion.
An optical illusion (also called a visual illusion) is an illusion caused by the visual system and characterized by a visual percept that arguably appears to differ from reality
An optical cavity, resonating cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors that forms a standing wave cavity resonator for light waves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, surrounding the gain medium and providing feedback of the laser light.
What is meant by optical resonator?
A part of a laser, consisting of two mirrors, one highly reflective and one partly reflective, placed on either side of a laser pump.
A part of a laser, consisting of two mirrors, one highly reflective and one partly reflective, placed on either side of a laser pump.
An optical resonator is needed to build up the light energy in the beam. The resonator is formed by placing a pair of mirrors facing each other so that light emitted along the line between the mirrors is reflected back and forth.
a resonator?
: something that resounds or resonates: such as. a : a hollow metallic container for producing microwaves or a piezoelectric crystal put into oscillation by the oscillations of an outside source. b : a device for increasing the resonance of a musical instrument.
: something that resounds or resonates: such as. a : a hollow metallic container for producing microwaves or a piezoelectric crystal put into oscillation by the oscillations of an outside source. b : a device for increasing the resonance of a musical instrument.
Piezoelectricity is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials in response to applied mechanical stress. The word piezoelectricity means electricity resulting from pressure and latent heat.
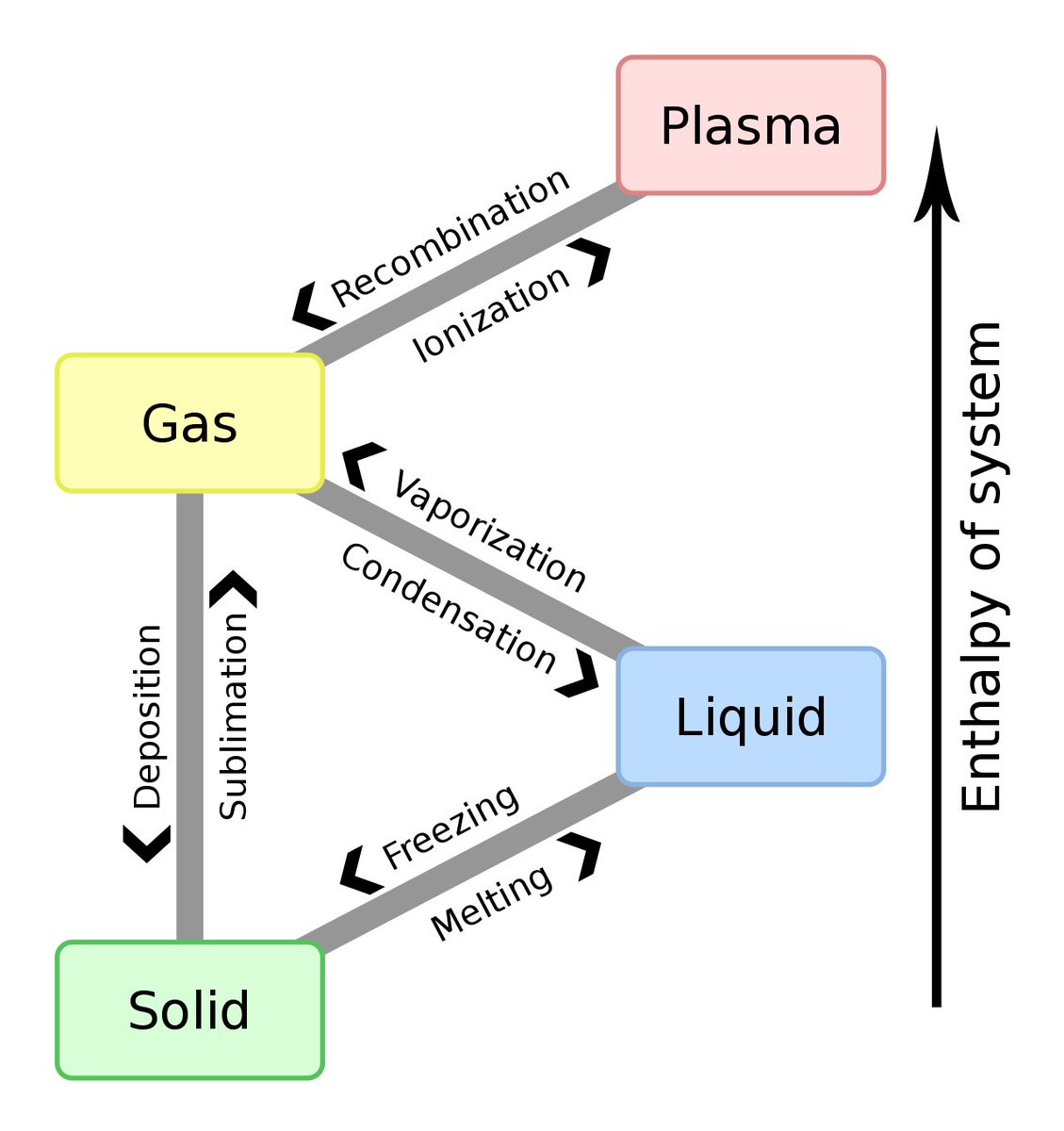
Latent heat is energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature process — usually a first-order phase transition.
Latent heat can be understood as energy in hidden form which is supplied or extracted to change the state of a substance without changing its temperature.
Examples are latent heat of fusion and latent heat of vaporization involved in phase changes, i.e. a substance condensing or vaporizing at a specified temperature and pressure.
The term was introduced around 1762 by British chemist Joseph Black. It is derived from the Latin latere (to lie hidden).
″Latent heat″ is energy transferred in a process without change of the body's temperature, for example, in a phase change (solid/liquid/gas).
Two common forms of latent heat are latent heat of fusion (melting) and latent heat of vaporization (boiling). These names describe the direction of energy flow when changing from one phase to the next: from solid to liquid, and liquid to gas.
In chemistry, thermodynamics, and many other related fields, phase transitions (or phase changes) are the physical processes of transition between the basic states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas, as well as plasma in rare cases
In physics, a plasmon is a quantum of plasma oscillation. Just as light (an optical oscillation) consists of photons, the plasma oscillation consists of plasmons.
The plasmon can be considered as a quasiparticle since it arises from the quantization of plasma oscillations, just like phonons are quantizations of mechanical vibrations. Thus, plasmons are collective (a discrete number) oscillations of the free electron gas density.
For example, at optical frequencies, plasmons can couple with a photon to create another quasiparticle called a plasmon polariton.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plasmon
Optical surface plasmons are being investigated with a view to improve makeup by L'Oréal and others.
Optical surface plasmons are being investigated with a view to improve makeup by L'Oréal and others.
Plasmons are collective electron oscillations usually excited at metal surfaces by a light source. Doped graphene layers have also shown the similar surface plasmon effects to that of metallic thin films.
Through the engineering of metallic substrates or nanoparticles (e.g., gold, silver and copper) with graphene, the plasmonic properties of the hybrid structures could be tuned for improving the optoelectronic device performances.
It is worth noting that the electrons at the metallic structure could transfer to the graphene conduction band. This is attributed to the zero bandgap property of graphene nanosheet.
Graphene plasmons can also be decoupled from their environment and give rise to genuine Dirac plasmon at low-energy range where the wavelengths exceed the damping length. These graphene plasma resonances have been observed in the GHz–THz electronic domain.

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter