It’s time for a Twitter #creatine update.
The recent @TheIOPN @laurent_bannock podcast with @ScottForbes14 provides a great outline.
Let’s try a link-based and visual podcast notes. https://www.wedoscience.com/creatine-myths-and-common-questions-with-dr-scott-forbes-phd/
The recent @TheIOPN @laurent_bannock podcast with @ScottForbes14 provides a great outline.
Let’s try a link-based and visual podcast notes. https://www.wedoscience.com/creatine-myths-and-common-questions-with-dr-scott-forbes-phd/
00:13:36
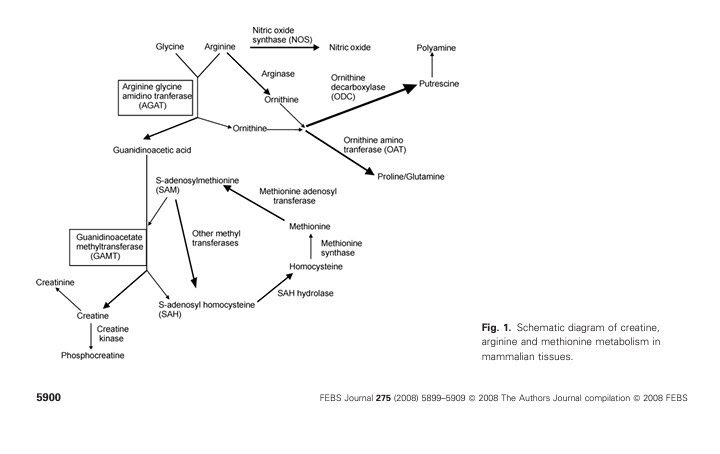
Creatine is formed from three amino acids; arginine, glycine and methionine. In your kidneys and liver, it's put together in a two-step process and it forms creatine.
Creatine is formed from three amino acids; arginine, glycine and methionine. In your kidneys and liver, it's put together in a two-step process and it forms creatine.
00:16:21
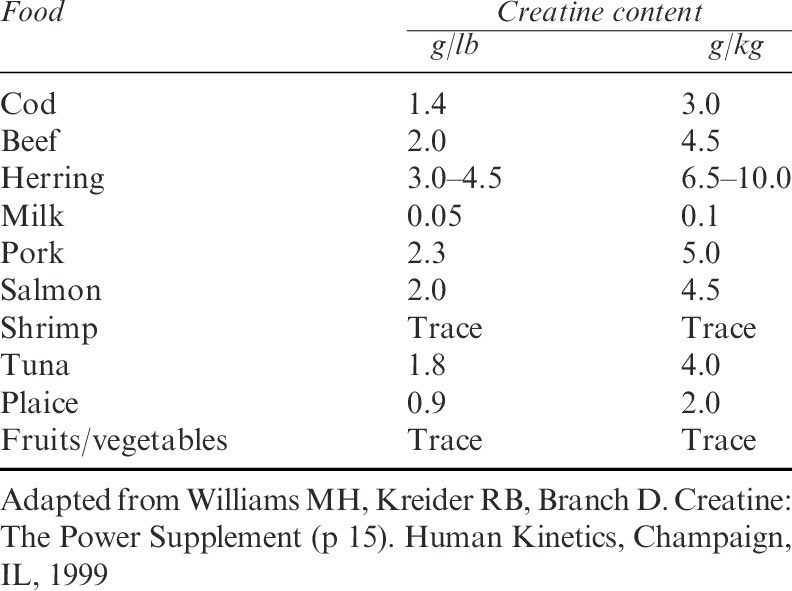
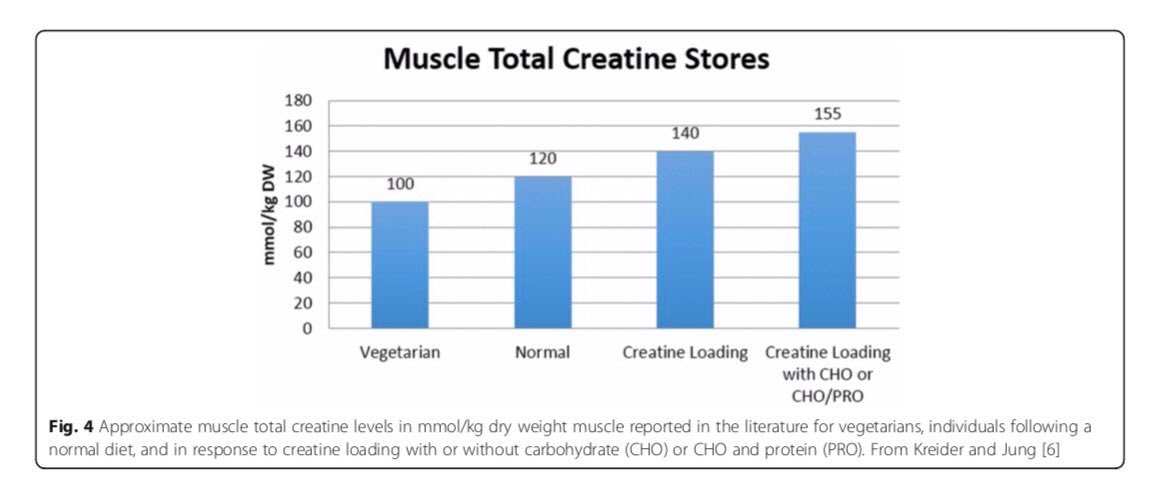
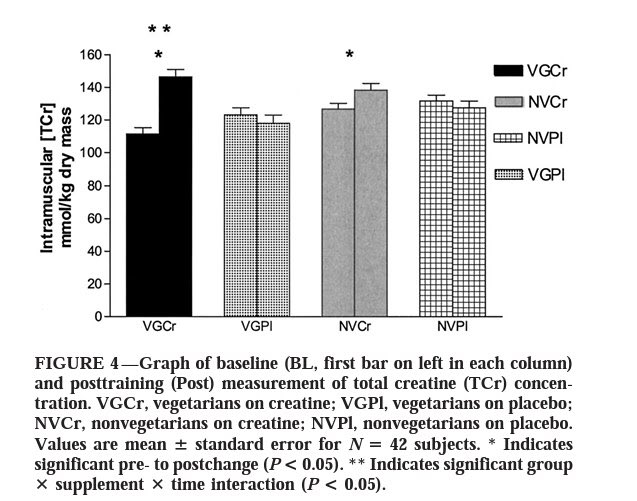
“First of all, yeah, so if you don't consume meat in your diet as you're a vegetarian or vegan, typically, you have lower creatine levels within your muscle. Typically, respond better to creatine supplementation. Vegetarians seem to respond better.”
“First of all, yeah, so if you don't consume meat in your diet as you're a vegetarian or vegan, typically, you have lower creatine levels within your muscle. Typically, respond better to creatine supplementation. Vegetarians seem to respond better.”
“Gordon Bell, did a study looking at responders and non-responders to creatine.”
https://journals.lww.com/nsca-jscr/fulltext/2004/08000/acute_creatine_monohydrate_supplementation__a.39.aspx
https://journals.lww.com/nsca-jscr/fulltext/2004/08000/acute_creatine_monohydrate_supplementation__a.39.aspx
00:20:16
“Common question is do you have to cycle creatine..?There's actually been no research to examine the effectiveness of creatine when you cycle...It's a difficult question to answer...with creatine, what you need to do is you need to load the muscle.”
“Common question is do you have to cycle creatine..?There's actually been no research to examine the effectiveness of creatine when you cycle...It's a difficult question to answer...with creatine, what you need to do is you need to load the muscle.”
“if you take a lower dose of creatine by just a little bit longer period of time, you can also saturate the muscle with creatine”
https://journals.physiology.org/doi/pdf/10.1152/jappl.1996.81.1.232
https://journals.physiology.org/doi/pdf/10.1152/jappl.1996.81.1.232
00:26:15
“Creapure. That's what we use in most of our studies. independently tested and seems to be the purest form of creatine out there.”
“Creapure. That's what we use in most of our studies. independently tested and seems to be the purest form of creatine out there.”
00:27:16
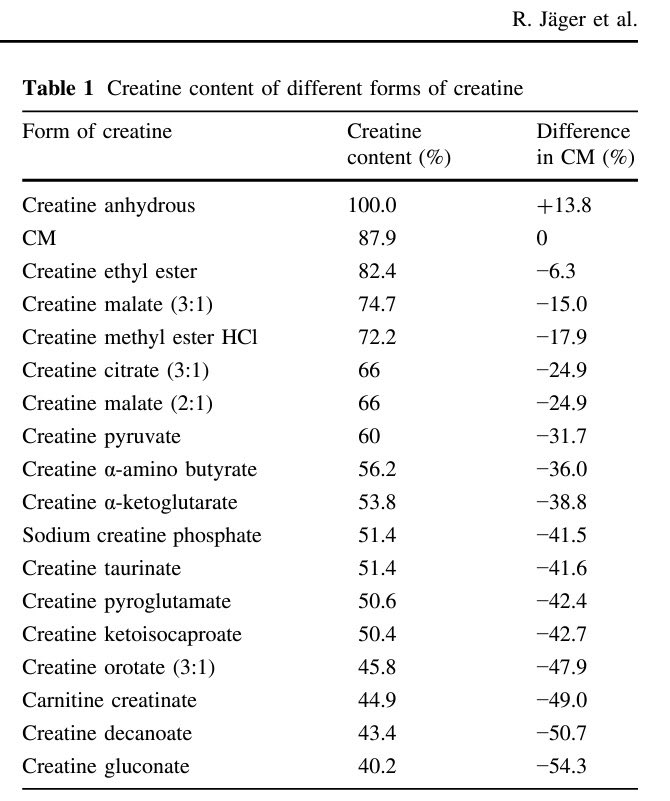
“The different types of creatine might have different levels of creatine in them. We know creatine monohydrate has been the most studied form of creatine.”
“The different types of creatine might have different levels of creatine in them. We know creatine monohydrate has been the most studied form of creatine.”
00:36:31
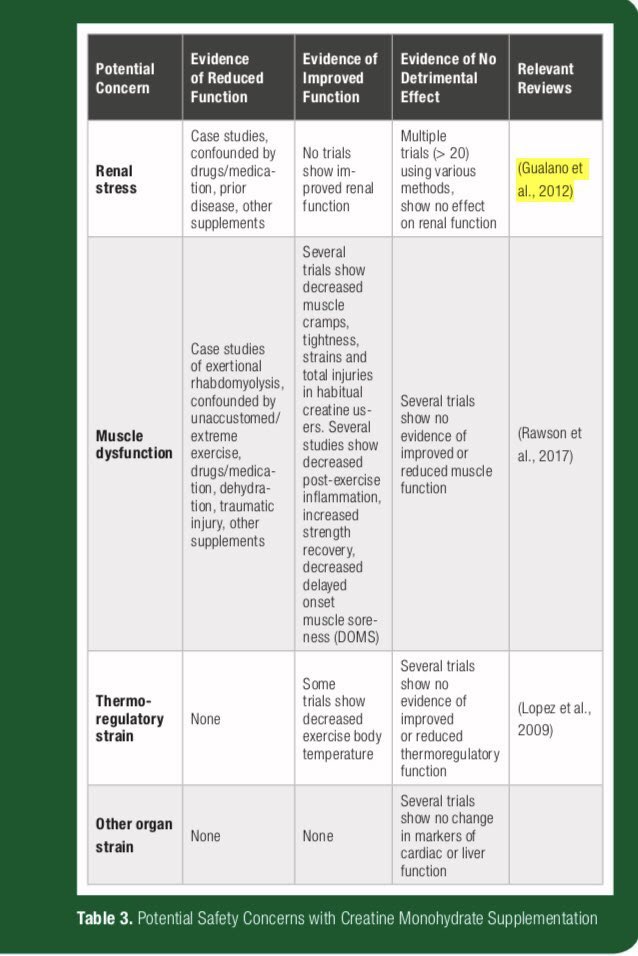
“Some people think that it's going to be damaging to your kidneys and liver, but the evidence for that is pretty strong that it does not do any damage to your kidneys and liver,”
“Some people think that it's going to be damaging to your kidneys and liver, but the evidence for that is pretty strong that it does not do any damage to your kidneys and liver,”
00:39:12
“The way that it actually transports into the muscle is through a sodium-dependent transporter.
If you bring sodium into the muscle cell, it actually brings water with it...that's one of the mechanisms, whereby creatine functions and how it actually works.”
“The way that it actually transports into the muscle is through a sodium-dependent transporter.
If you bring sodium into the muscle cell, it actually brings water with it...that's one of the mechanisms, whereby creatine functions and how it actually works.”
00:42:06
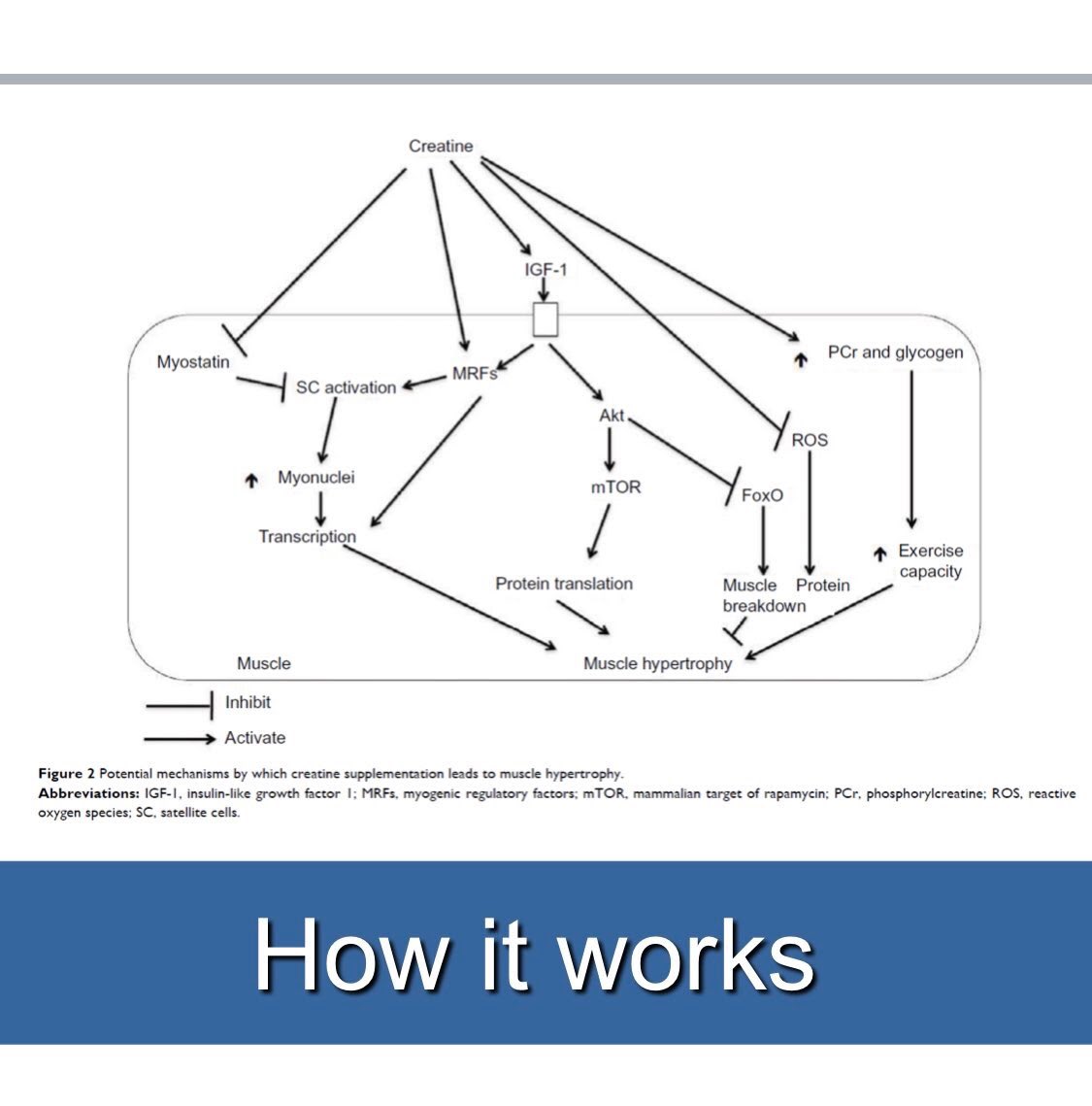
“creatine works is through – there's a whole bunch of different mechanisms. It's not just by increasing the amount of phosphocreatine within the muscle.”
“creatine works is through – there's a whole bunch of different mechanisms. It's not just by increasing the amount of phosphocreatine within the muscle.”
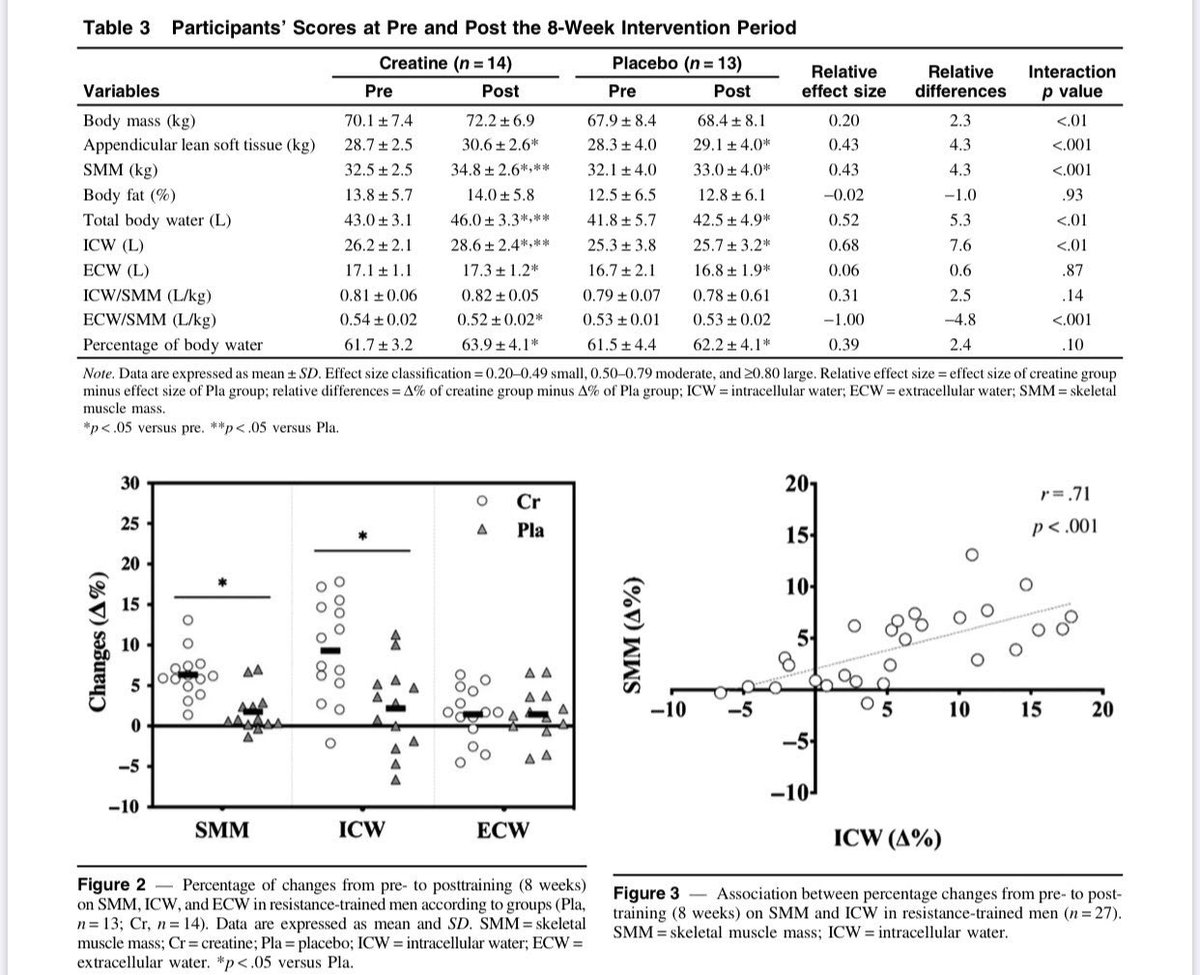
“If you combine it with resistance exercise, they get bigger and stronger muscles compared to if they just performed resistance training with a placebo.”
https://journals.lww.com/acsm-msse/Fulltext/2014/06000/Creatine_Supplementation_during_Resistance.16.aspx
https://journals.lww.com/acsm-msse/Fulltext/2014/06000/Creatine_Supplementation_during_Resistance.16.aspx
0:46:24
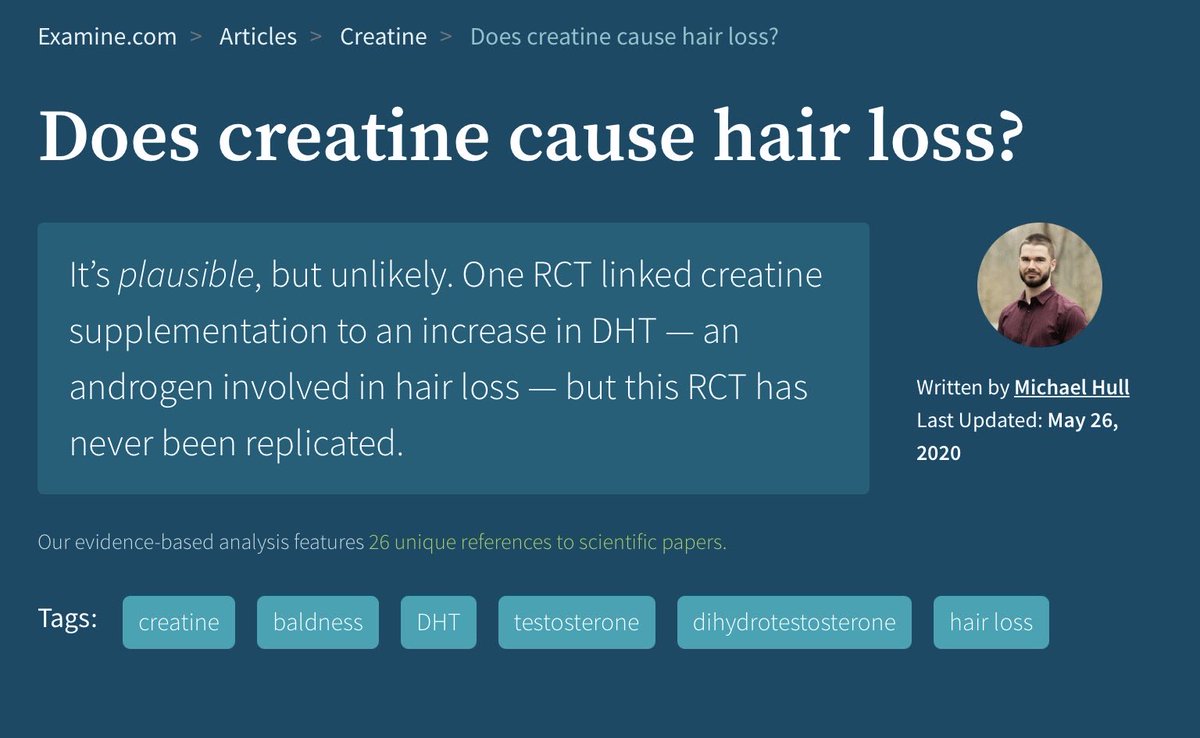
“There's one study that was done in rugby players actually, where they showed that there is an increased conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone, or DHT. DHT has been linked to male pattern baldness.”
https://examine.com/nutrition/does-creatine-cause-hairloss/
“There's one study that was done in rugby players actually, where they showed that there is an increased conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone, or DHT. DHT has been linked to male pattern baldness.”
https://examine.com/nutrition/does-creatine-cause-hairloss/
0:48:51
“There's been some great research by Rick Kreider...They actually showed the complete opposite, that creatine prevented muscle cramps, the opposite from a dehydration perspective.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14608430/
“There's been some great research by Rick Kreider...They actually showed the complete opposite, that creatine prevented muscle cramps, the opposite from a dehydration perspective.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14608430/
0:54:41
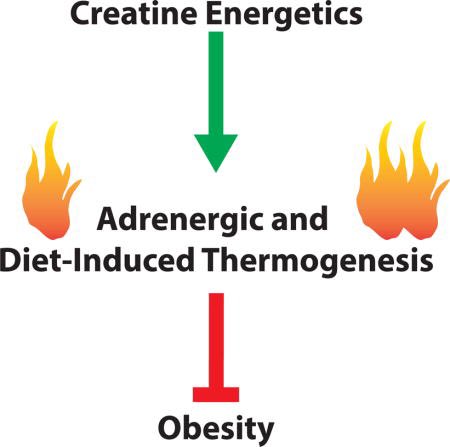
“There's some really interesting research in rats that shows that if you actually block the creatine transporter at adipose sites, it reduces whole body energy expenditure. They're actually suggesting that if you take creatine...you can increase energy expenditure”
“There's some really interesting research in rats that shows that if you actually block the creatine transporter at adipose sites, it reduces whole body energy expenditure. They're actually suggesting that if you take creatine...you can increase energy expenditure”
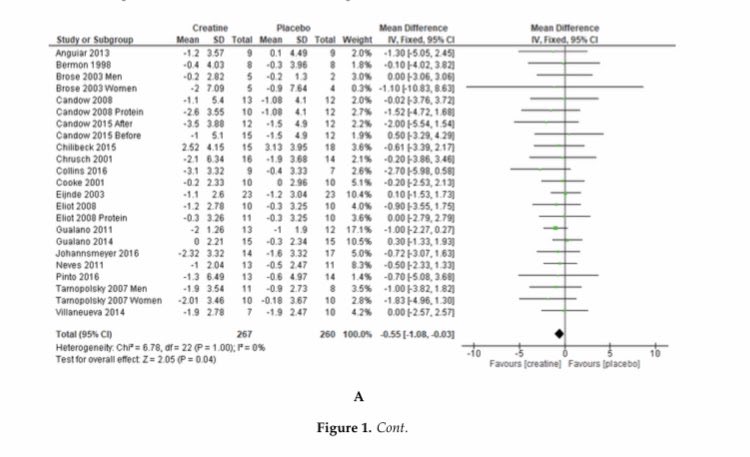
“those that took creatine, their percent body fat significantly were reduced and they lost about a 0.5 kilograms more fat mass when they took creatine, compared to when they took a placebo.”
https://res.mdpi.com/d_attachment/jfmk/jfmk-04-00062/article_deploy/jfmk-04-00062-v2.pdf
https://res.mdpi.com/d_attachment/jfmk/jfmk-04-00062/article_deploy/jfmk-04-00062-v2.pdf
0:54:23
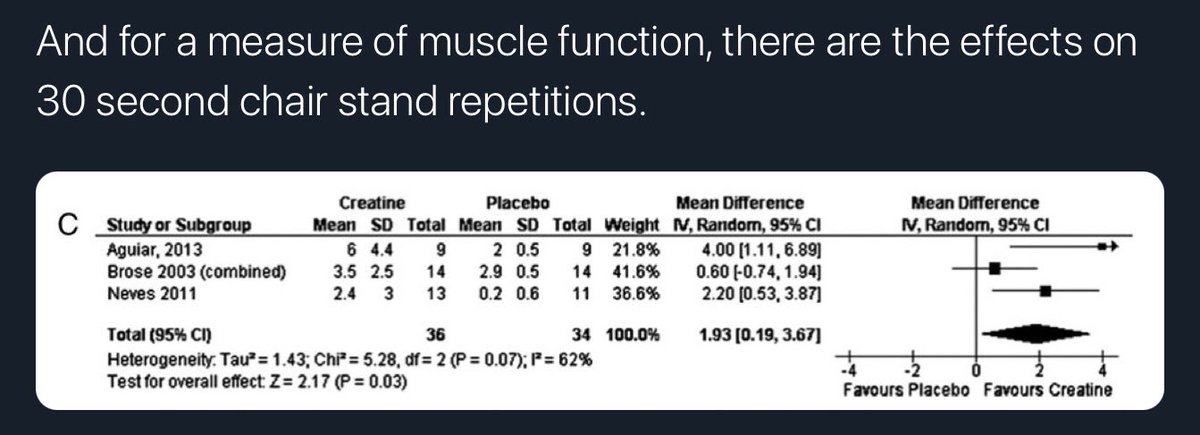
“those that took creatine & performed RT...actually gained 1.37 more kg of muscle mass, compared to if you just performed resistance training... it also improves sit to stand as well, which is a surrogate marker of falls risk.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29138605/
“those that took creatine & performed RT...actually gained 1.37 more kg of muscle mass, compared to if you just performed resistance training... it also improves sit to stand as well, which is a surrogate marker of falls risk.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29138605/
0:56:26
“There's definitely been studies done in children and adolescents and they haven't shown any harm of it. With the limited evidence that we have, it does seem to be safe for children, or adolescents.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6279854/
“There's definitely been studies done in children and adolescents and they haven't shown any harm of it. With the limited evidence that we have, it does seem to be safe for children, or adolescents.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6279854/
“ @LouiseMBurke for example, did a study in elite cyclists looking at a 120 kilometre time trials. They showed that their performance at the end of the race was better when they took creatine, which was pretty cool. It could be a benefit for endurance athletes as well.”
0:58:20
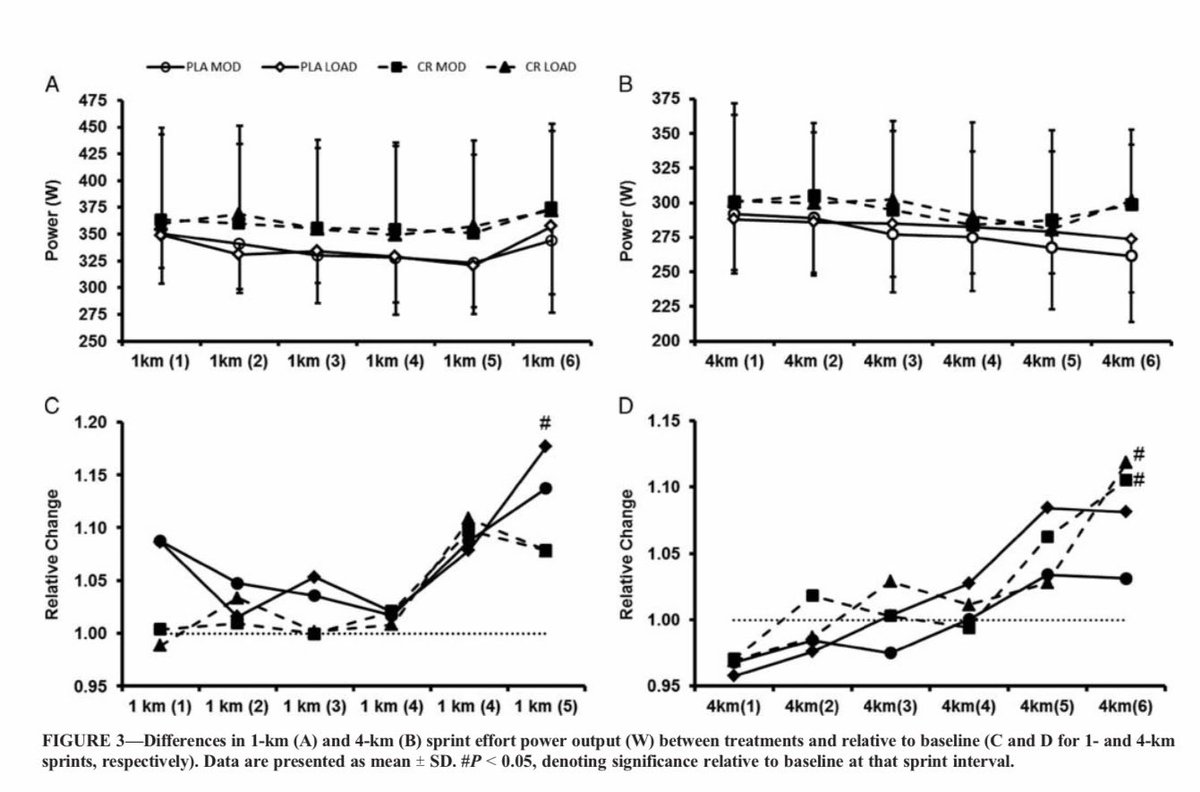
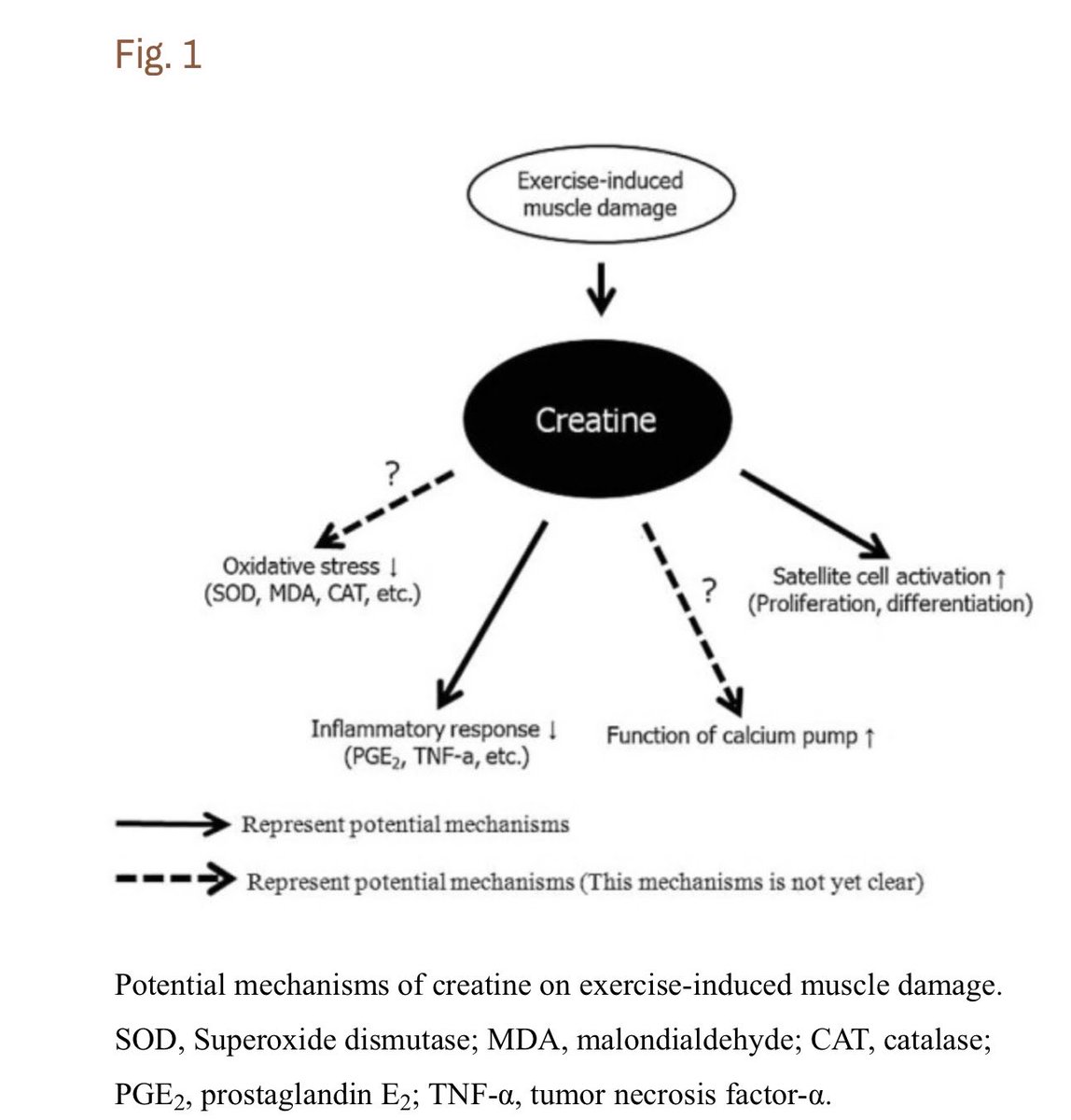
“There's one particular study where they looked at muscle damage following a marathon. Those that took creatine had less muscle damage.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4625651/pdf/jer-11-5-244.pdf
“There's one particular study where they looked at muscle damage following a marathon. Those that took creatine had less muscle damage.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4625651/pdf/jer-11-5-244.pdf
1:03:48
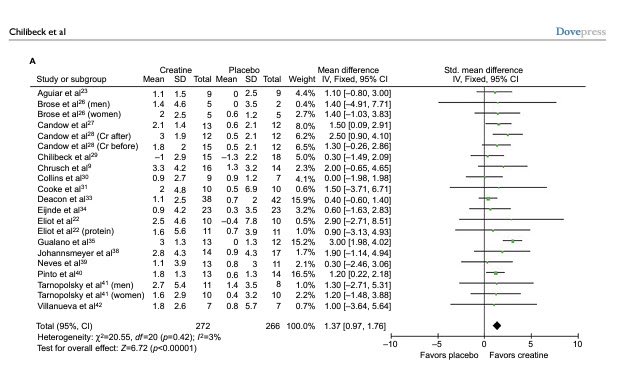
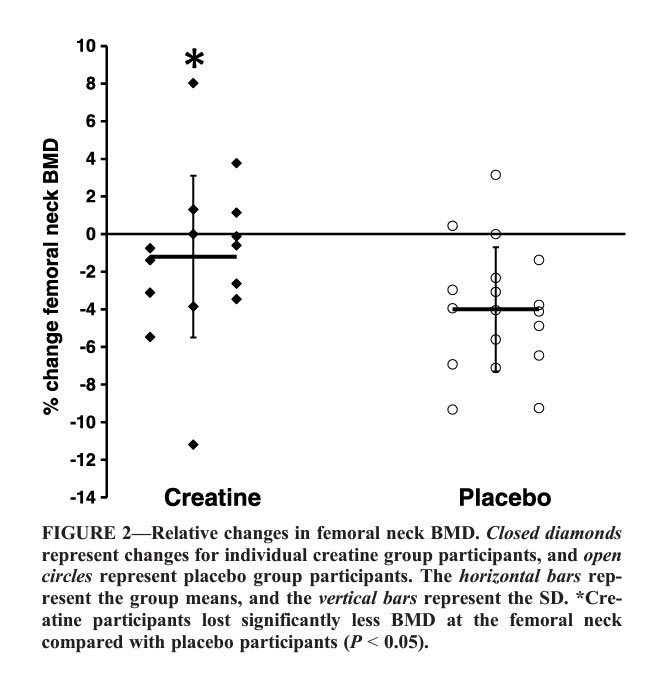
“There's definitely a lot of evidence to show that creatine can be effective in a female...it can enhance muscle mass, strength, but also bone health in that particular population.
https://journals.lww.com/acsm-msse/fulltext/2015/08000/effects_of_creatine_and_resistance_training_on.5.aspx
“There's definitely a lot of evidence to show that creatine can be effective in a female...it can enhance muscle mass, strength, but also bone health in that particular population.
https://journals.lww.com/acsm-msse/fulltext/2015/08000/effects_of_creatine_and_resistance_training_on.5.aspx
I’ll post the rest later...
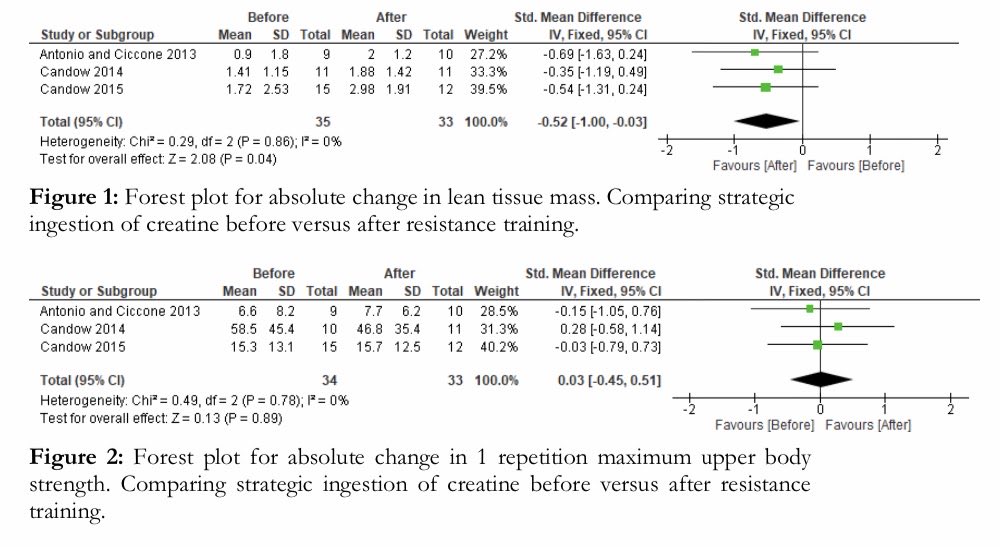
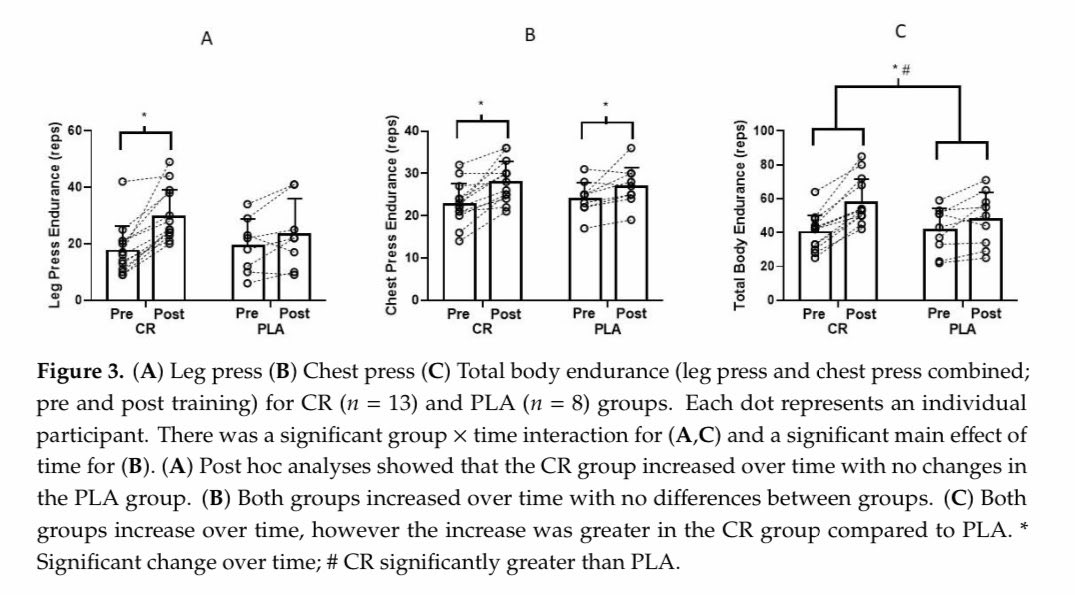
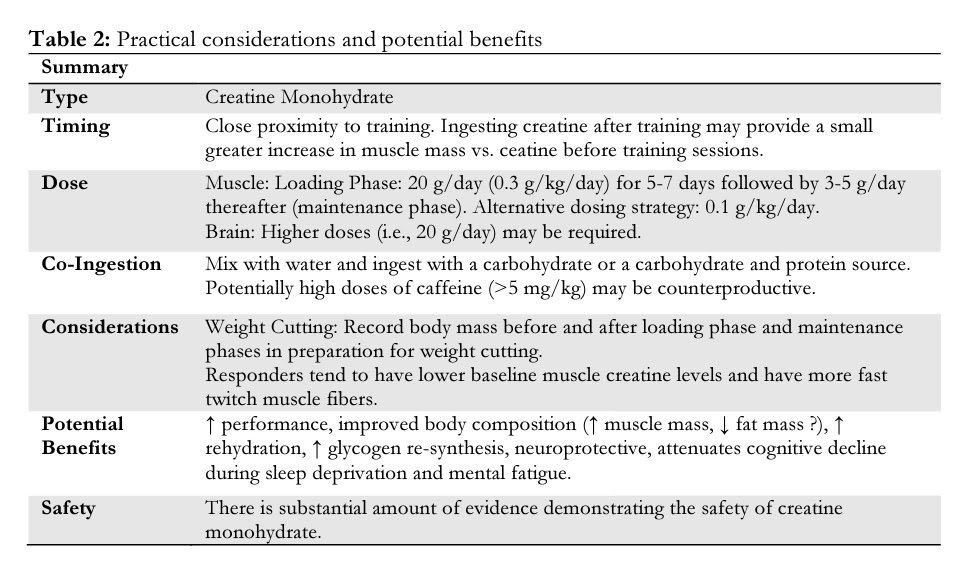
01:05:59
“There's been 3 pub’d studies looking at the effects of Cr before training vs after training. All three show a very slight advantage to after training. It's pretty small and it's hard to have strong evidence from those studies.”
https://www.journalofexerciseandnutrition.com/ManuscriptUploadsPDF/62.pdf
“There's been 3 pub’d studies looking at the effects of Cr before training vs after training. All three show a very slight advantage to after training. It's pretty small and it's hard to have strong evidence from those studies.”
https://www.journalofexerciseandnutrition.com/ManuscriptUploadsPDF/62.pdf
“I would suggest to take it close to your training, but it doesn't matter if you take it before training, during training, or after training.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7353308/pdf/nutrients-12-01880.pdf
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7353308/pdf/nutrients-12-01880.pdf
01:10:18
“Looking at creatine, it could be effective not only to enhance muscle and performance for fighters, but it could also be effective to enhance their cognition and perhaps, could also be protective for their brain as well.”
https://www.journalofexerciseandnutrition.com/ManuscriptUploadsPDF/115.pdf
“Looking at creatine, it could be effective not only to enhance muscle and performance for fighters, but it could also be effective to enhance their cognition and perhaps, could also be protective for their brain as well.”
https://www.journalofexerciseandnutrition.com/ManuscriptUploadsPDF/115.pdf
@laurent_bannock @ScottForbes14 please let me know if I left out anything noteworthy. No edit function but I appreciate any corrections as well. Thanks for the great podcast.

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter