THREAD
THREAD Paper just accepted in EPSL about solid-state sintering, led by Amy Ryan @UBCeoas! Solid-state sintering is a process in which crystalline clasts coalesce in the absence of fluids/melt. It occurs wherever granular materials are subjected to elevated PT over time 1/8
Paper just accepted in EPSL about solid-state sintering, led by Amy Ryan @UBCeoas! Solid-state sintering is a process in which crystalline clasts coalesce in the absence of fluids/melt. It occurs wherever granular materials are subjected to elevated PT over time 1/8
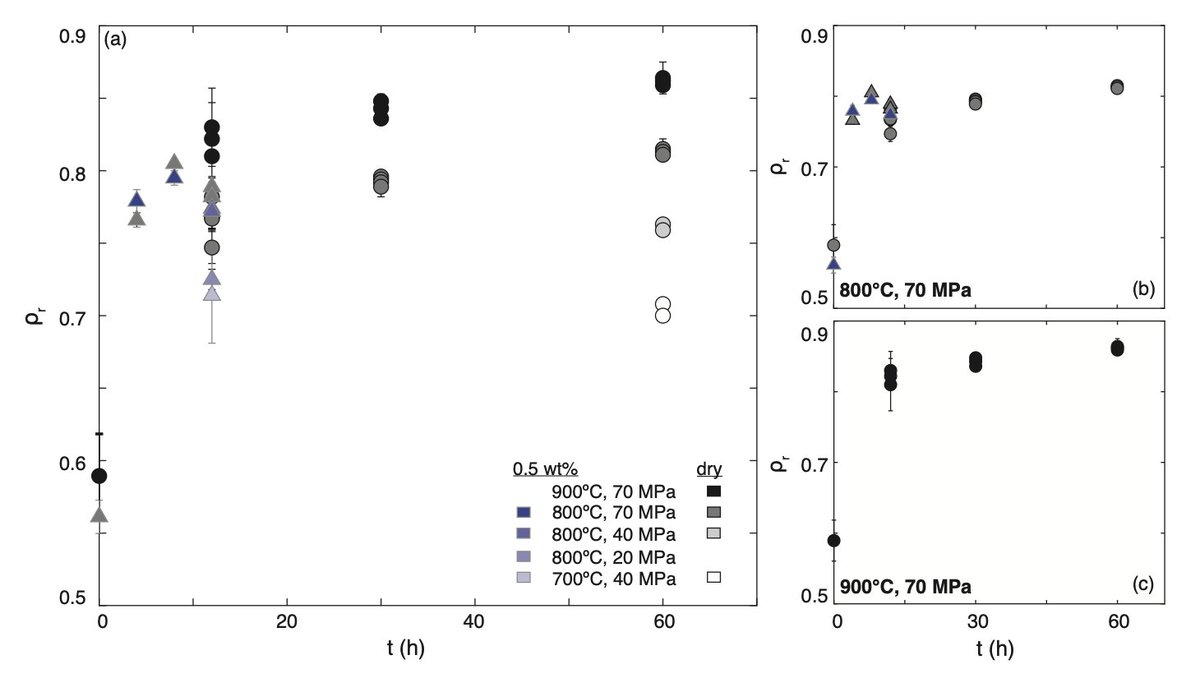
We first performed hot-pressing experiments on gouge to provide samples for which we know the PT conditions under which they formed 2/8
The density, porosity, and permeability of these samples was then measured in the laboratory. We find that density increases and porosity and permeability decrease as sintering pressure, temperature, and time increase 3/8
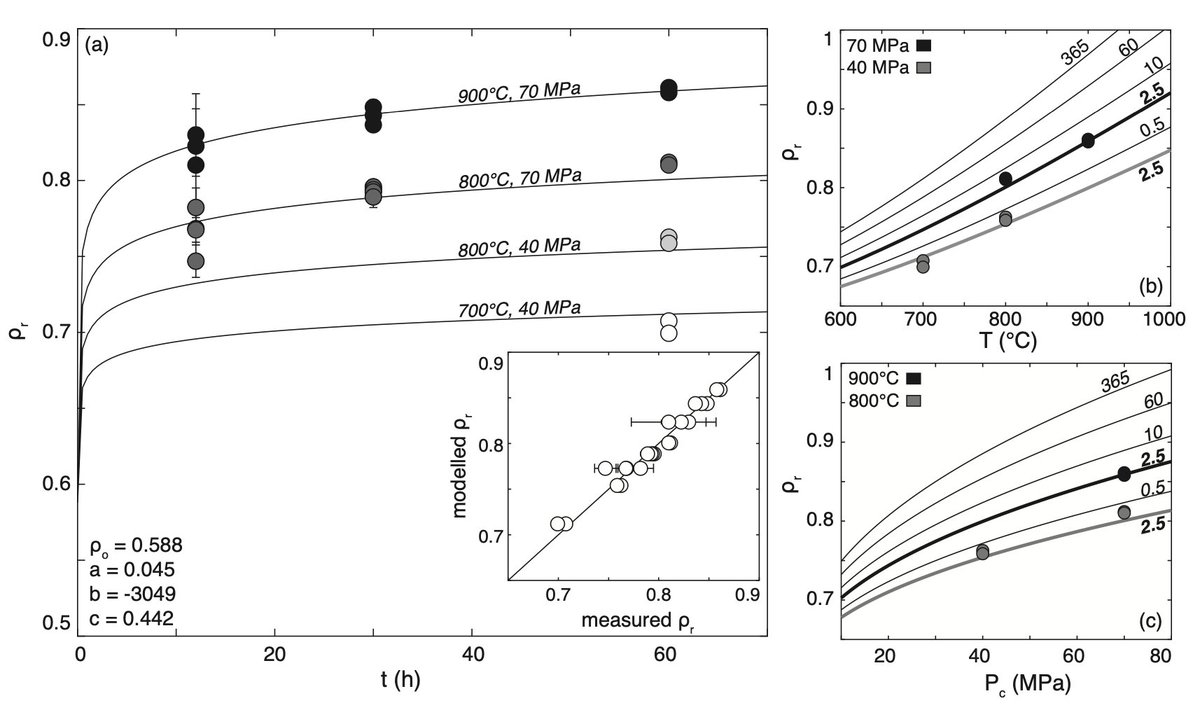
Side note - I particularly enjoyed this simple plot containing @LDR_Strasbourg data and a @FabianWadsworth model  4/8
4/8
 4/8
4/8
These data were then used to develop a robust densification model that predicts time-dependent porosity and permeability loss at a pressure-temperature range that includes volcanic and some upper-crustal environments 5/8
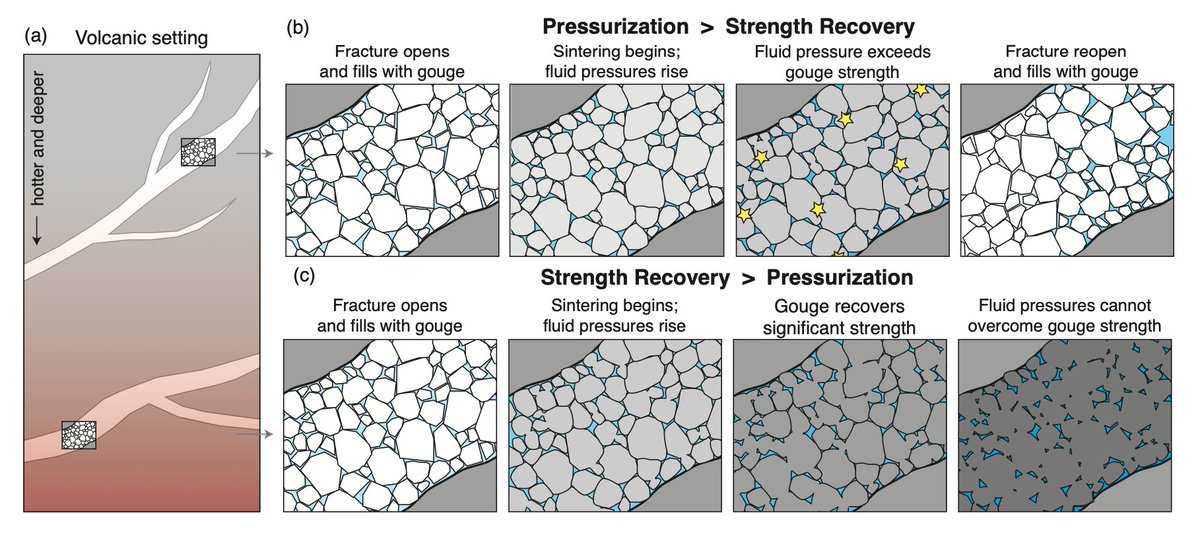
What's nuts is that solid-state sintering, once considered the custard cream to the bourbon cream of viscous sintering, causes large reductions in porosity and permeability over days to months, depending on pressure-temperature conditions 6/8
In terms of volcanoes, the short timescales of solid-state sintering-driven permeability loss and lithification can dictate the efficiency of outgassing and therefore modulate eruption style (i.e. explosive vs. effusive) Remember: in the absence of fluids/melt! 7/8
The paper is part of the fantastic Amy Ryan's @UBCeoas Ph.D thesis, with some help/guidance from Kelly Russell, @LDR_Strasbourg, Mark Zimmerman @UMNews, and @FabianWadsworth Link coming soon! 8/8

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter