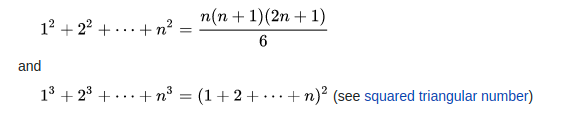#Thread
Aryabhatta(476–550CE)

The man who changed the whole Mathematics & Astronomy
-Place value system & zero
-Explanation of lunar & solar eclipse
-Calculate value of π
-Trigonometry
-Algebra
-rotation of Earth on its axis
-diameter of Earth
-reflection of light by moon
Aryabhatta(476–550CE)


The man who changed the whole Mathematics & Astronomy
-Place value system & zero
-Explanation of lunar & solar eclipse
-Calculate value of π
-Trigonometry
-Algebra
-rotation of Earth on its axis
-diameter of Earth
-reflection of light by moon
Aryabhatta's contribution in mathematics :
- Place value system and zero
- Approximation of π
- Trigonometry
- Algebra
- Indeterminate equations
- Place value system and zero
- Approximation of π
- Trigonometry
- Algebra
- Indeterminate equations
Place value system & 0 - The place-value system, first seen in the 3rd-CE Bakhshali Manuscript, was clearly in place in his work.
While he did not use a symbol for zero.
While he did not use a symbol for zero.
... The French mathematician Georges Ifrah argues that knowledge of zero was implicit in Aryabhata's place-value system as a place holder for the powers of ten with null coefficients.
Approximation of π - Aryabhata worked on the approximation for pi (π) & come to the conclusion that π is irrational.
His work in book Aryabhatiyam,|
The ratio of the circumference to the diameter is
((4 + 100) × 8 + 62000)/20000 = 62832/20000 = 3.1416, which is accurate.
His work in book Aryabhatiyam,|
The ratio of the circumference to the diameter is
((4 + 100) × 8 + 62000)/20000 = 62832/20000 = 3.1416, which is accurate.
In the second part of the Aryabhatiyam ,
,
चतुराधिकं शतमष्टगुणं द्वाषष्टिस्तथा सहस्राणाम्।अयुतद्वयस्य विष्कम्भस्यासन्नो वृत्तपरिणाहः॥
"Add four to 100, multiply by eight, and then add 62,000. By this rule the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 20,000 can be approached."
 ,
,चतुराधिकं शतमष्टगुणं द्वाषष्टिस्तथा सहस्राणाम्।अयुतद्वयस्य विष्कम्भस्यासन्नो वृत्तपरिणाहः॥
"Add four to 100, multiply by eight, and then add 62,000. By this rule the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 20,000 can be approached."
This implies that the ratio of the circumference to the diameter is ((4 + 100) × 8 + 62000)/20000 = 62832/20000 = 3.1416, which is accurate to five significant figures.
- Trigonometry :
In Ganitapada 6 , Aryabhata gives the AREA of a triangle as
, Aryabhata gives the AREA of a triangle as
"tribhujasya phalaśarīraṃ samadalakoṭī bhujārdhasaṃvargaḥ"
that translates to: "for a triangle, the result of a perpendicular with the half-side is the area."
In Ganitapada 6
 , Aryabhata gives the AREA of a triangle as
, Aryabhata gives the AREA of a triangle as"tribhujasya phalaśarīraṃ samadalakoṭī bhujārdhasaṃvargaḥ"
that translates to: "for a triangle, the result of a perpendicular with the half-side is the area."
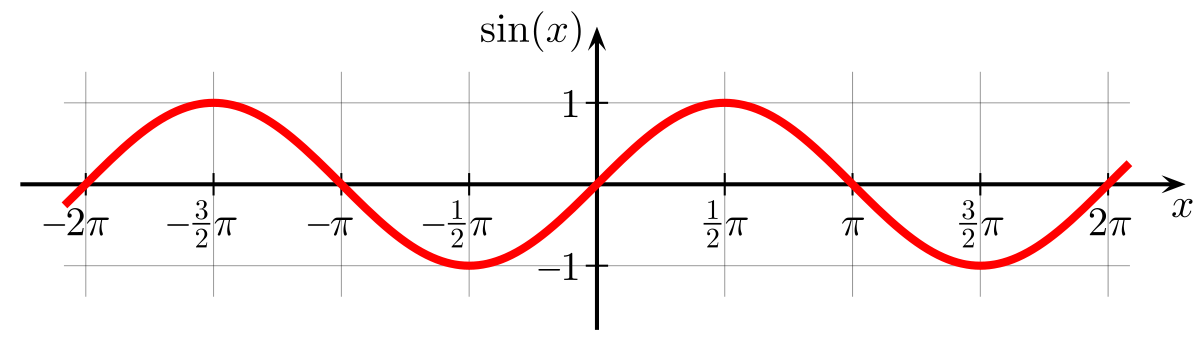
Aryabhata discussed the concept of sine (\\theta) in his work by the name of ardha-jya , which literally means "half-chord".
, which literally means "half-chord".
For simplicity, people started calling it "jya".
When Arabic writers translated his works from Sanskrit into Arabic, they referred it as "jiba".
 , which literally means "half-chord".
, which literally means "half-chord". For simplicity, people started calling it "jya".
When Arabic writers translated his works from Sanskrit into Arabic, they referred it as "jiba".
However, in Arabic writings, vowels are omitted, and it was abbreviated as "jb".
Later writers substituted it with "jaib", meaning "pocket" or "fold (in a garment)".
(In Arabic, jiba is a meaningless word.)
Later writers substituted it with "jaib", meaning "pocket" or "fold (in a garment)".
(In Arabic, jiba is a meaningless word.)
Later in the 12th century, when Gherardo of Cremona translated these writings from Arabic into Latin,
he replaced the Arabic "jaib" with its Latin counterpart,
"sinus", which means "cove" or "bay"; thence comes the English word sine.
he replaced the Arabic "jaib" with its Latin counterpart,
"sinus", which means "cove" or "bay"; thence comes the English word sine.
- Algebra :
In Aryabhatiya , Aryabhata
, Aryabhata provided elegant results for the summation of series of squares and cubes.
provided elegant results for the summation of series of squares and cubes.
In Aryabhatiya
 , Aryabhata
, Aryabhata provided elegant results for the summation of series of squares and cubes.
provided elegant results for the summation of series of squares and cubes.
- Indeterminate equations :
A problem of great interest to Indian mathematicians since ancient times has been to find integer solutions to Diophantine equations that have the form ax + by = c.
This is an example from Bhāskara's commentary on Aryabhatiya :
:
A problem of great interest to Indian mathematicians since ancient times has been to find integer solutions to Diophantine equations that have the form ax + by = c.
This is an example from Bhāskara's commentary on Aryabhatiya
 :
:
Find the number which gives 5 as the remainder when divided by 8, 4 as the remainder when divided by 9, and 1 as the remainder when divided by 7
That is, find N = 8x+5 = 9y+4 = 7z+1.
That is, find N = 8x+5 = 9y+4 = 7z+1.
It turns out that the smallest value for N is 85. In general, diophantine equations, such as this, can be notoriously difficult.
They were discussed extensively in ancient Vedic text Sulba Sutras , whose more ancient parts might date to 800 BCE.
, whose more ancient parts might date to 800 BCE.
They were discussed extensively in ancient Vedic text Sulba Sutras
 , whose more ancient parts might date to 800 BCE.
, whose more ancient parts might date to 800 BCE.
Aryabhata's method of solving such problems, elaborated by Bhaskara in 621 CE,is called the kuṭṭaka(कुट्टक) method.
Kuṭṭaka means "pulverizing" or "breaking into small pieces", & the method involves a recursive algorithm for writing the original factors in smaller numbers.
Kuṭṭaka means "pulverizing" or "breaking into small pieces", & the method involves a recursive algorithm for writing the original factors in smaller numbers.
This algorithm became the standard method for solving first-order diophantine equations in Indian mathematics, and initially the whole subject of algebra was called kuṭṭaka-gaṇita or simply kuṭṭaka (कुट्टक).
Aryabhatta's Contribution in Astronomy :
- Explanation of lunar & solar eclipse
- rotation of Earth on its axis
- diameter of Earth
- reflection of light by moon
- Motions of the solar system
- Sidereal periods
- Heliocentrism
- Explanation of lunar & solar eclipse
- rotation of Earth on its axis
- diameter of Earth
- reflection of light by moon
- Motions of the solar system
- Sidereal periods
- Heliocentrism
- Eclipses :
Solar & lunar eclipses were scientifically explained by Aryabhata.
- He states that the Moon and planets shine by reflected sunlight.
- Instead of the prevailing cosmogony in which eclipses were caused by Rahu & Ketu
(identified as the pseudo-planetary lunar nodes)
Solar & lunar eclipses were scientifically explained by Aryabhata.
- He states that the Moon and planets shine by reflected sunlight.
- Instead of the prevailing cosmogony in which eclipses were caused by Rahu & Ketu
(identified as the pseudo-planetary lunar nodes)
he explains eclipses in terms of shadows cast by and falling on Earth.
- Thus, the lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon enters into the Earth's shadow (verse gola.37).
He discusses at length the size and extent of the Earth's shadow (verses gola.38–48)
- Thus, the lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon enters into the Earth's shadow (verse gola.37).
He discusses at length the size and extent of the Earth's shadow (verses gola.38–48)
and then provides the computation and the size of the eclipsed part during an eclipse.
Later Indian astronomers improved on the calculations, but Aryabhata's methods provided the core.
Later Indian astronomers improved on the calculations, but Aryabhata's methods provided the core.
His computational paradigm was so accurate that 18thCE scientist Guillaume Gentil,during a visit to Pondicherry found the Indian computations of
found the Indian computations of
the duration of the lunar eclipse of 30-08-1765 to be short by 41 sec,whereas his charts (by Tobias Mayer,1752) were long by 68 sec
 found the Indian computations of
found the Indian computations of the duration of the lunar eclipse of 30-08-1765 to be short by 41 sec,whereas his charts (by Tobias Mayer,1752) were long by 68 sec
- Motions of the solar system :
Aryabhata correctly insisted that the earth rotates about its axis daily,
And that the apparent movement of the stars is a relative motion caused by the rotation of the earth, contrary to the then-prevailing view, that the sky rotated.
Aryabhata correctly insisted that the earth rotates about its axis daily,
And that the apparent movement of the stars is a relative motion caused by the rotation of the earth, contrary to the then-prevailing view, that the sky rotated.
This is indicated in the first chapter of the Aryabhatiya ,
,
where he gives the number of rotations of the earth in a yuga,
And made more explicit in his gola chapter :
 ,
, where he gives the number of rotations of the earth in a yuga,
And made more explicit in his gola chapter :
In the same way that someone in a boat going forward sees an unmoving [object] going backward,
so [someone] on the equator sees the unmoving stars going uniformly westward.
so [someone] on the equator sees the unmoving stars going uniformly westward.
The cause of rising and setting [is that] the sphere of the stars together with the planets [apparently] turns due west at the equator, constantly pushed by the cosmic wind.
Aryabhata described a geocentric model of the solar system, in which the Sun and Moon are each carried by epicycles.
They in turn revolve around the Earth. In this model, which is also found in the Paitāmahasiddhānta (c. CE 425)
They in turn revolve around the Earth. In this model, which is also found in the Paitāmahasiddhānta (c. CE 425)
the motions of the planets are each governed by two epicycles, a smaller manda (slow) and a larger śīghra (fast).
The order of the planets in terms of distance from earth is taken as: the Moon, Mercury, Venus, the Sun, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, and the asterisms."
The order of the planets in terms of distance from earth is taken as: the Moon, Mercury, Venus, the Sun, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, and the asterisms."
The positions and periods of the planets was calculated relative to uniformly moving points.
In the case of Mercury and Venus, they move around the Earth at the same mean speed as the Sun. In the case of Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn, they move around the Earth at specific speeds, representing each planet's motion through the zodiac.
Another element in Aryabhata's model, the śīghrocca, the basic planetary period in relation to the Sun, is seen by some historians as a sign of an underlying heliocentric model.
- Sidereal periods :
Considered in modern English units of time,
Aryabhata calculated the sidereal rotation -
(the rotation of the earth referencing the fixed stars) as 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4.1 seconds;
the modern value is 23:56:4.091.
Considered in modern English units of time,
Aryabhata calculated the sidereal rotation -
(the rotation of the earth referencing the fixed stars) as 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4.1 seconds;
the modern value is 23:56:4.091.

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter