Secret Weapon - Inhaled Pulmonary Vasodilators!
When managing the sickest patients with RV failure or hypoxemia, these can come in clutch.
#HRreloaded
When managing the sickest patients with RV failure or hypoxemia, these can come in clutch.
#HRreloaded
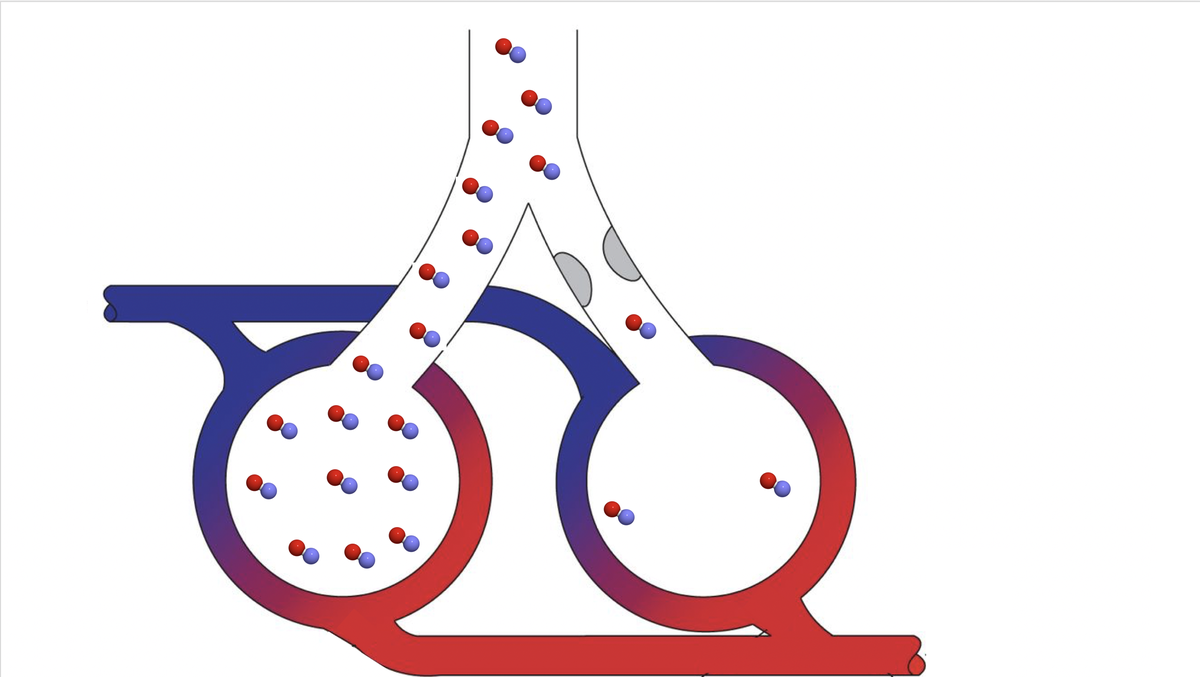
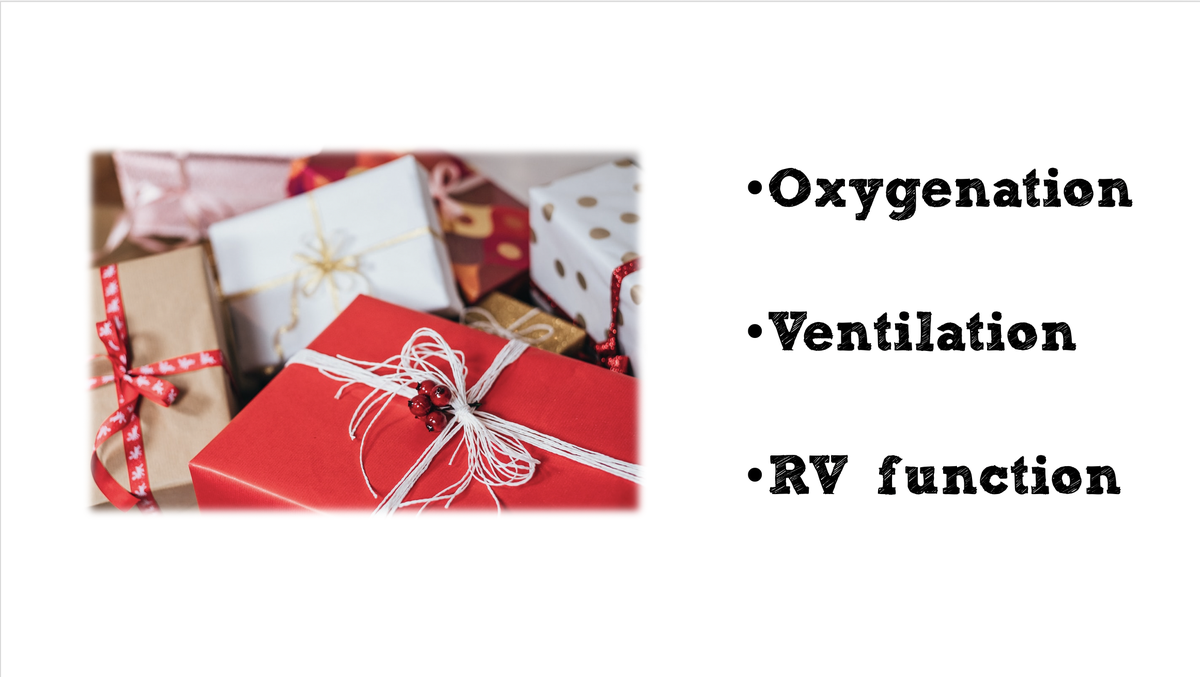
Inhaled pulm vasodilators do roughly three things physiologically. First, they pull blood towards the best-ventilated alveoli. This improves ventilation/perfusion matching and oxygenation. (Yep it always comes back to VQ matching.)
#HRreloaded
#HRreloaded
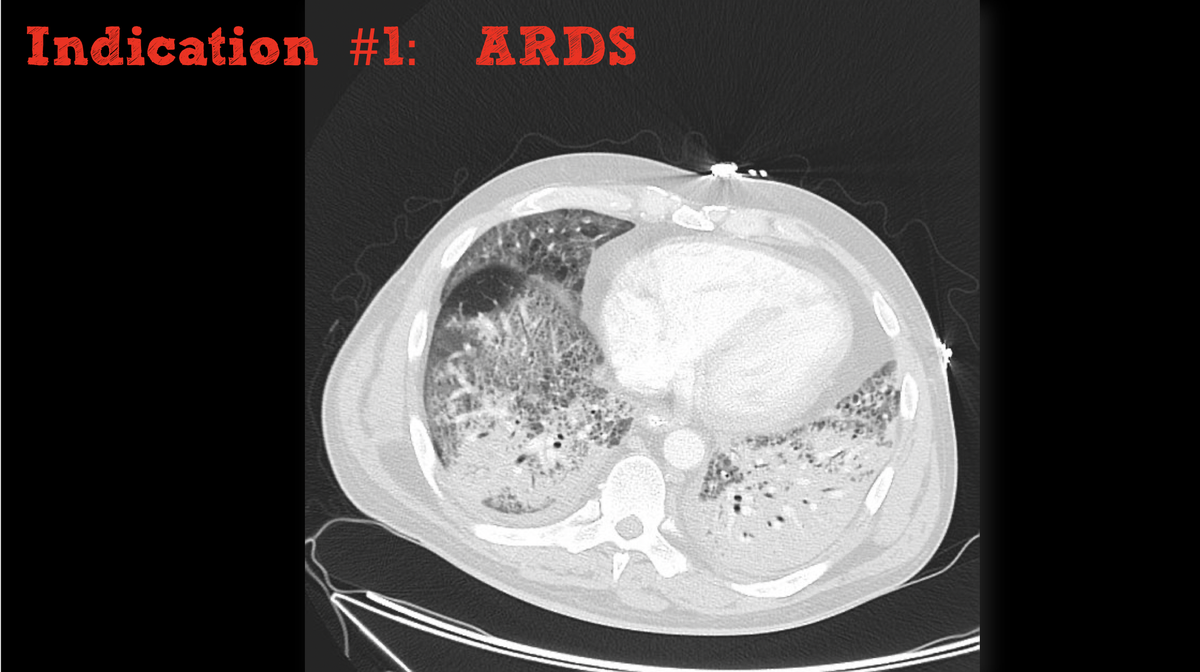
#2) Some patients with ARDS develop a right --> left shunt. these patients can be hard to treat, because increasing airway pressures (e.g. recruitment) may *increase* pulmonary vascular resistance and worsen the shunt! pulmonary vasodilators can reduce shunting
#HRreloaded
#HRreloaded
#3) inhaled vasodilators can reduce the pulmonary vascular resistance, thereby decreasing the afterload on the right ventricle. we do this all the time with the systemic vasodilators to bail out a failing LV. pulm vasodilators do this for the right-sided circulation
#HRreloaded
#HRreloaded
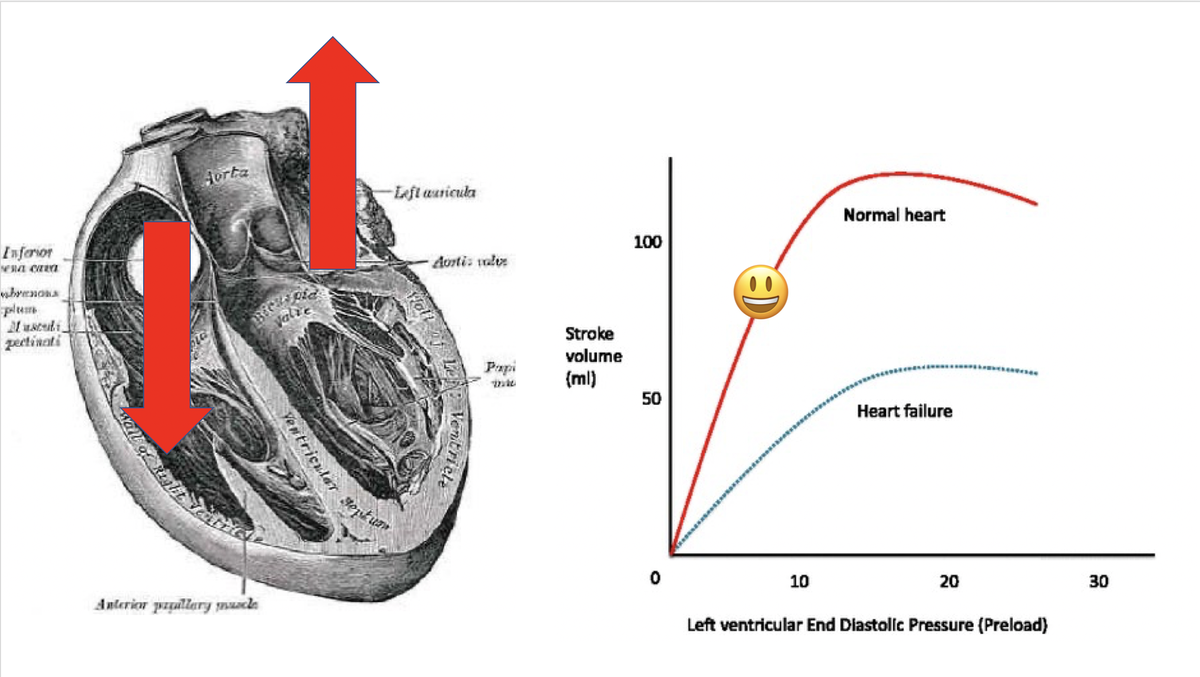
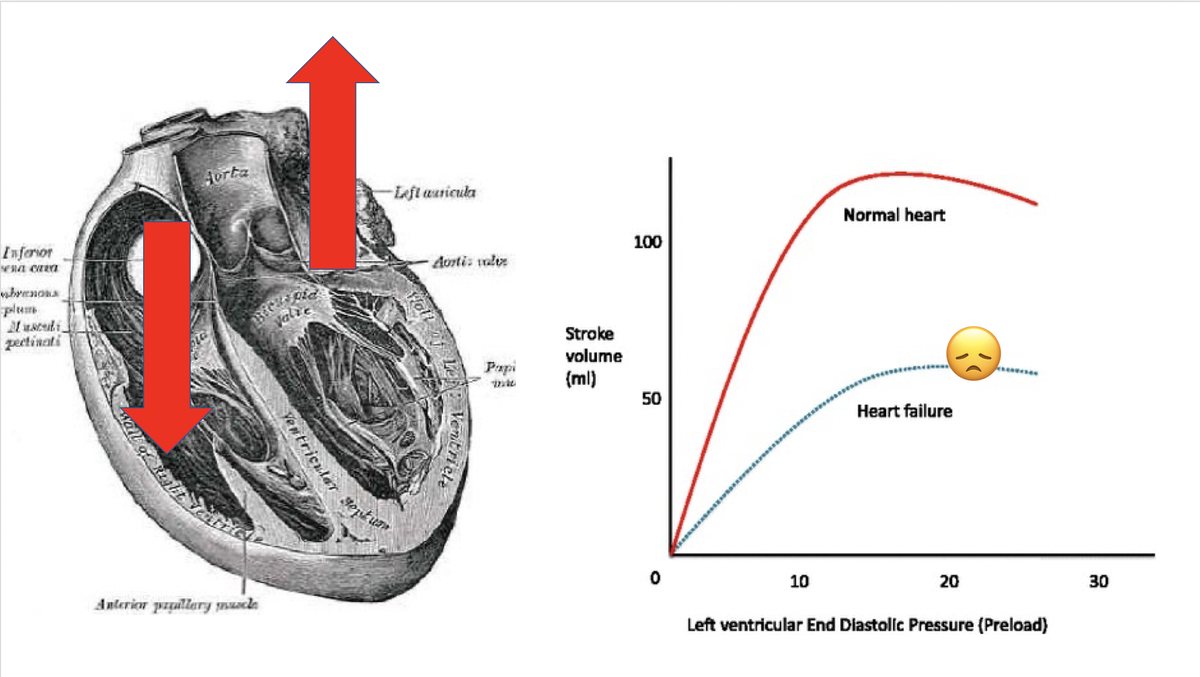
so in general pulm vasodilators bring lots of goodness, with a terrific side-effect profile. only real side effect to fear is exacerbation of left-sided heart failure due to increased blood flow across to the left side, exacerbating pulmonary edema
#HRreloaded
#HRreloaded
- physiology vs evidence!
- pulm vasodilators definitely work, but no EBM proving that they improve hard endpoints (e.g. mortality)
- use pulm vasodilators selectively in the sickest patients (not for everyone)
#HRreloaded
- pulm vasodilators definitely work, but no EBM proving that they improve hard endpoints (e.g. mortality)
- use pulm vasodilators selectively in the sickest patients (not for everyone)
#HRreloaded
- pulmonary vasodilators merely function as *bridge* to stabilize the patient and hopefully bring them to another therapy (or recovery)
- if there's nowhere to bridge the patient to, this won't work (one reason its hard to prove mortality benefit)
#HRreloaded
- if there's nowhere to bridge the patient to, this won't work (one reason its hard to prove mortality benefit)
#HRreloaded
Pulm vasodilators in ARDS
- Can improve oxygenation
- May bridge patients failing conventional therapy (e.g. buying time to prone or recruit with APRV)
- Doesn't modify underlying dz process
#HRreloaded
- Can improve oxygenation
- May bridge patients failing conventional therapy (e.g. buying time to prone or recruit with APRV)
- Doesn't modify underlying dz process
#HRreloaded
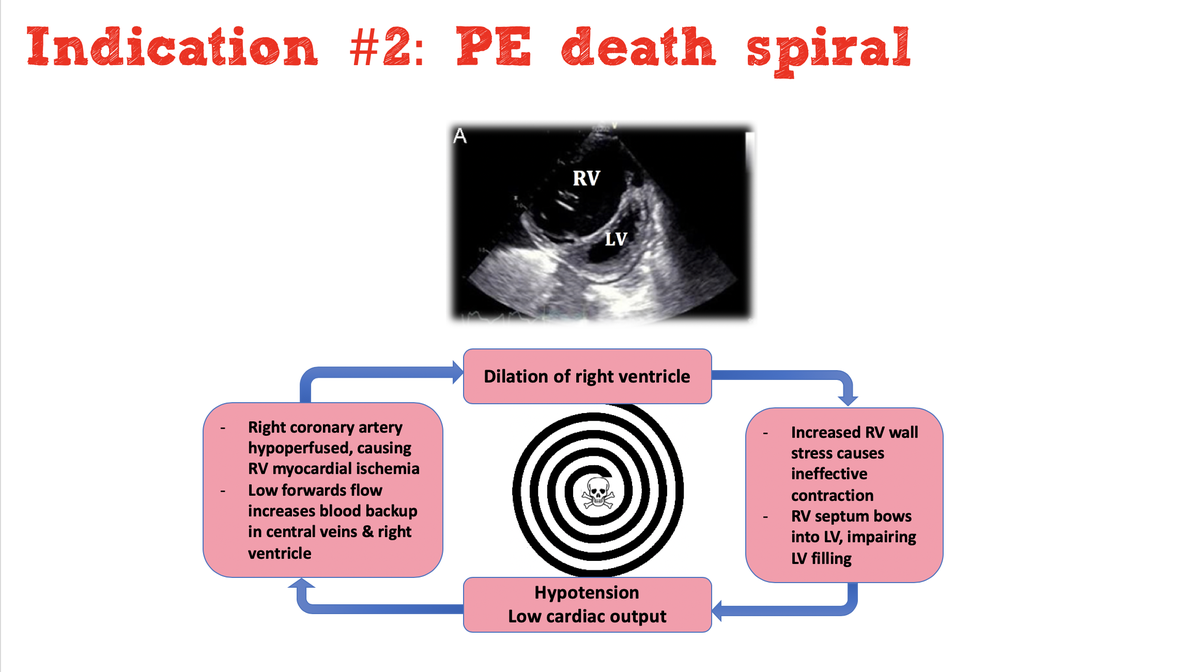
Pulm vasodilators in crashing PE
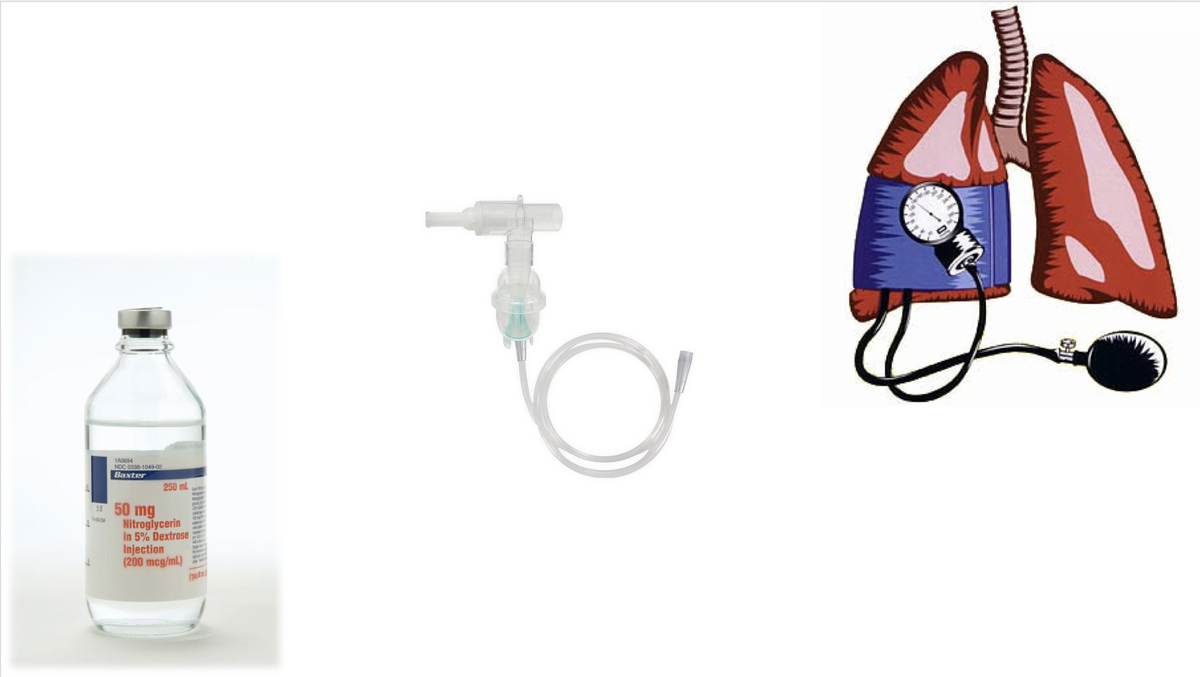
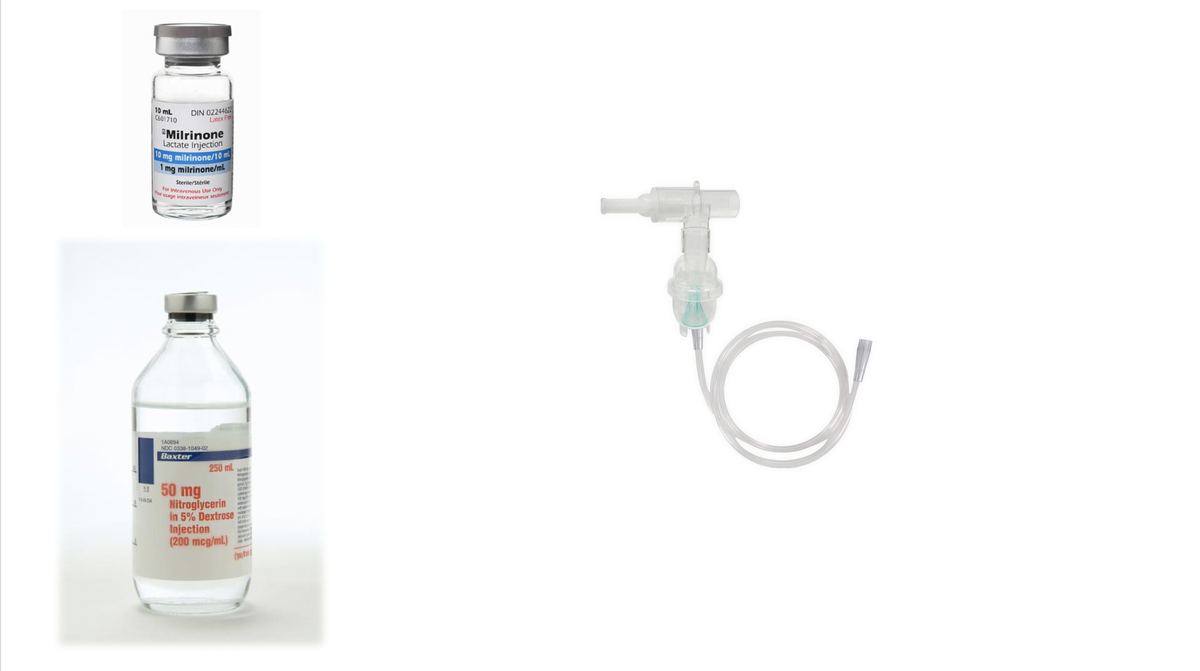
- Nitroglycerine or milrinone nebs can help rapidly stabilize
- Pulm vasodilators + epi are the fastest drugs to get to the bedside to prevent
- Bridge to other therapies (e.g. mixing up tPA, transport for IR procedure)
#HRreloaded
- Nitroglycerine or milrinone nebs can help rapidly stabilize
- Pulm vasodilators + epi are the fastest drugs to get to the bedside to prevent

- Bridge to other therapies (e.g. mixing up tPA, transport for IR procedure)
#HRreloaded
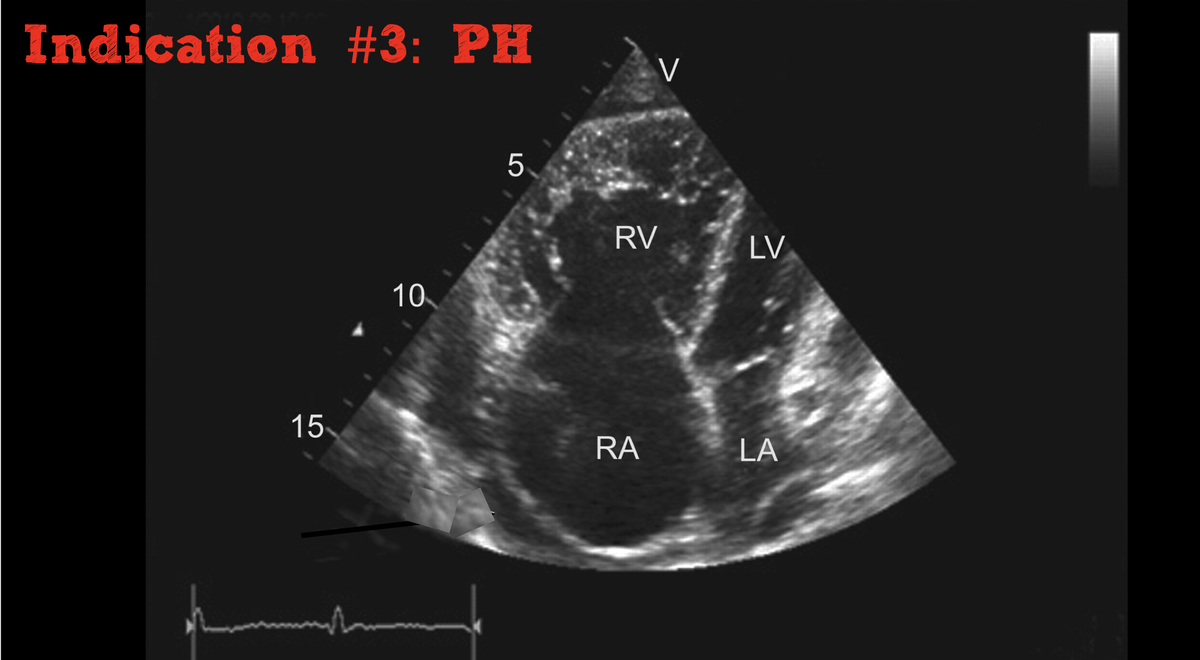
Pulm vasodilators in decompensated PH
- Can help stabilize on ventilator & prevent post-intubation cardiac arrest.
- Can help decompress RV & facilitate diuresis
#HRreloaded
- Can help stabilize on ventilator & prevent post-intubation cardiac arrest.
- Can help decompress RV & facilitate diuresis
#HRreloaded
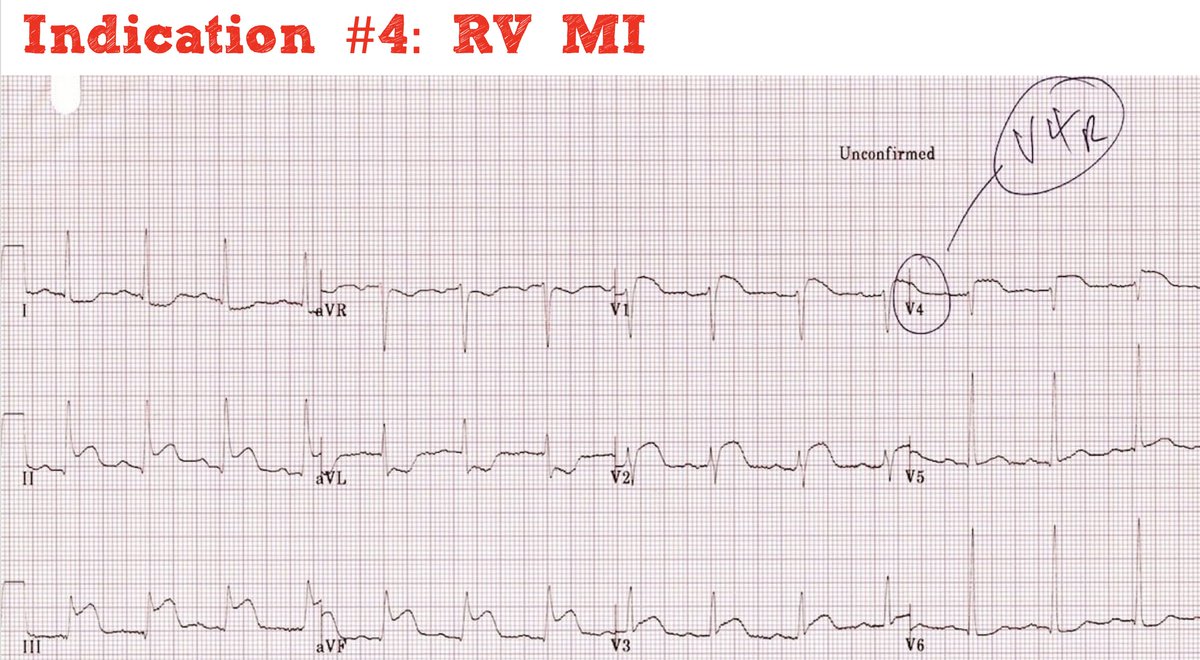
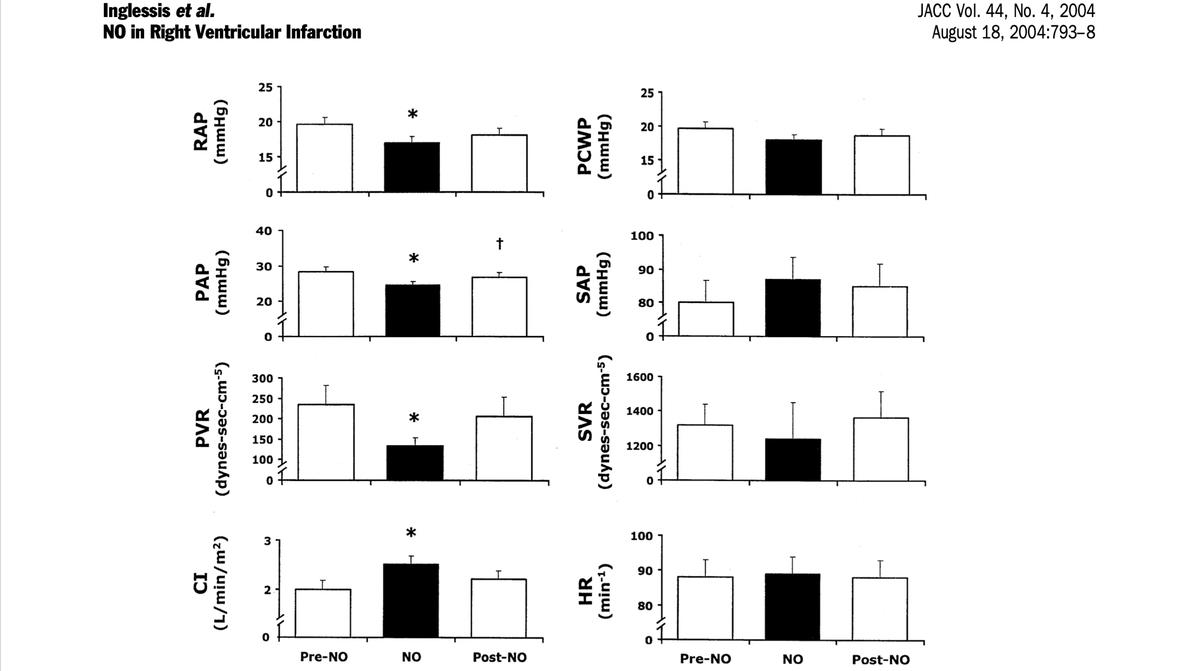
Pulm vasodilators in RV MI
- Maybe the most secret weapon of all (usually overlooked)
- RV assist device in a bottle
- Careful if LV failing as well (could exacerbate cardiogenic pulmonary edema)
#HRreloaded
- Maybe the most secret weapon of all (usually overlooked)
- RV assist device in a bottle
- Careful if LV failing as well (could exacerbate cardiogenic pulmonary edema)
#HRreloaded
No good evidence that any agent is better than any other agent (esp nitric oxide vs. epoprostenol). Use whatever your shop has and is comfortable with.
#HRreloaded
#HRreloaded
Milrinone or nitroglycerine can be given through a nebulizer, making them the fastest to deliver to a crashing patient. This may stabilize the patient long enough to set up nitric oxide or epoprostanol (which is trickier).
#HRreloaded
#HRreloaded
to go further down the rabbit hole of pulmonary vasodilators, take a look at our upcoming @iBookCC chapter. a podcast with @adamthomas will be released soon, but for now the text is up:
https://emcrit.org/ibcc/pulmvaso/
https://emcrit.org/ibcc/pulmvaso/
 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter