My attempt on "Decoding the HLA" with tweetorial & some slides/VisualArts @kidney_boy @NSMCInternship @Nephro_Sparks @hswapnil @rheault_m @RenalFellowNtwk @ssfarouk #Transplant
1/
1/
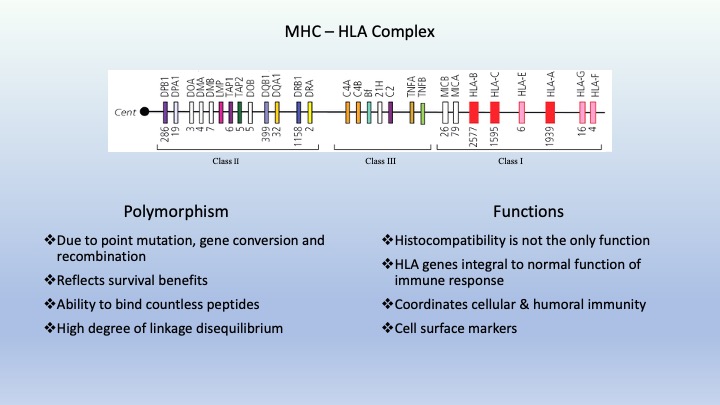
 MHC complex
MHC complex cluster of genes--> encodes HLA molecules
cluster of genes--> encodes HLA molecules located on chromosome 6p21
located on chromosome 6p21 over 200 genes; of which 40% involved in immune response
over 200 genes; of which 40% involved in immune response2/
 HLA Genes:
HLA Genes: main function is immune regulation
main function is immune regulation major barrier to transplant
major barrier to transplant gene products are histocompatibility molecules
gene products are histocompatibility molecules highly polymorphic
highly polymorphic significant linkage disequilibrium
significant linkage disequilibrium 
3/
 MHC-HLA genome-> divided into 3 regions
MHC-HLA genome-> divided into 3 regions Class I: molecules present on nucleated cells
Class I: molecules present on nucleated cells Class II: present on antigen presenting cells
Class II: present on antigen presenting cells Class III: are NOT histocompatibility genes
Class III: are NOT histocompatibility genes4/
 HLA Class I
HLA Class I  Classical: HLA-A, -B, -C antigens
Classical: HLA-A, -B, -C antigens Non-classical: HLA -E, -F, -G antigens
Non-classical: HLA -E, -F, -G antigens Class I like antigens: MICA, MICB
Class I like antigens: MICA, MICB 
5/
 HLA Class II
HLA Class II encodes HLA -DP, -DQ, -DR molecules
encodes HLA -DP, -DQ, -DR molecules expressed on antigen presenting cells
expressed on antigen presenting cells presents antigens to CD8 T cells
presents antigens to CD8 T cells 
6/
 HLA Class III
HLA Class III not involved in histocompatibility
not involved in histocompatibility encodes complement proteins like C2, C4, cytokines
encodes complement proteins like C2, C4, cytokines has both immune and non-immune genes
has both immune and non-immune genes 
7/
 HLA - Structure
HLA - Structure Class I has heavy glycoprotein alpha chain bound to beta 2 microglobulin (gene on chromosome 15). Alpha chain has three domains and is transmembrane
Class I has heavy glycoprotein alpha chain bound to beta 2 microglobulin (gene on chromosome 15). Alpha chain has three domains and is transmembrane Class II has both alpha & beta chains
Class II has both alpha & beta chains peptide groove is highly polymorphic region
peptide groove is highly polymorphic region 
8/
 HLA Class I Antigen Processing & Presentation
HLA Class I Antigen Processing & Presentation Altered self or/viral protein --> degraded intracellularly into peptides by proteases --> which fit into peptide groove--> transferred to cell surface to present to CD8 T cells
Altered self or/viral protein --> degraded intracellularly into peptides by proteases --> which fit into peptide groove--> transferred to cell surface to present to CD8 T cells 
9/
 HLA Class II Antigen Processing & Presentation:
HLA Class II Antigen Processing & Presentation: Exogenous antigen---> endocytosis--> degraded into lysosomes--> combines with MHC compartment-->attached to peptide groove--> transferred to cell surface--> present to CD4 T cells
Exogenous antigen---> endocytosis--> degraded into lysosomes--> combines with MHC compartment-->attached to peptide groove--> transferred to cell surface--> present to CD4 T cells
10/
 HLA typing:
HLA typing: to assess the HLA genotype
to assess the HLA genotype historically, it was done with serological microcytotoxicity using viable lymphocytes & panel of anti-sera
historically, it was done with serological microcytotoxicity using viable lymphocytes & panel of anti-sera Now, done with DNA-based HLA typing which is more reliable, precise & offers stable nomenclature
Now, done with DNA-based HLA typing which is more reliable, precise & offers stable nomenclature
11/
 HLA nomenclature
HLA nomenclature serological typing defines " antigens"
serological typing defines " antigens" DNA typing defines "alleles"
DNA typing defines "alleles" WHO nomenclature includes distinct fields seperated by colon ( : )for antigen, allele, specific protein, nucleotide substitution in coding & non-coding region
WHO nomenclature includes distinct fields seperated by colon ( : )for antigen, allele, specific protein, nucleotide substitution in coding & non-coding region
12/
 HLA Haplotype and Inheritance:
HLA Haplotype and Inheritance: HLA alleles from each parent is called haplotype
HLA alleles from each parent is called haplotype it is inherited in Mandelian fashion
it is inherited in Mandelian fashion co-domminantly expressed
co-domminantly expressed
13/
 HLA antibody
HLA antibody preformed antibodies against HLA antigens are major transplant barriers and has significant impact on allograft survival
preformed antibodies against HLA antigens are major transplant barriers and has significant impact on allograft survival14/
 Strategies to detect HLA Abs
Strategies to detect HLA Abs PRA: % panel reactive antibodies to assess sensitization in general
PRA: % panel reactive antibodies to assess sensitization in general Identification of specific antibodies in recipient
Identification of specific antibodies in recipient crossmatch when kidney is available
crossmatch when kidney is available
15/
 Crossmatch -->three methods
Crossmatch -->three methods standard complement dependent cytotoxicity CDC (1960s)
standard complement dependent cytotoxicity CDC (1960s) Flow T & B cells crossmatch (1980s)
Flow T & B cells crossmatch (1980s) Solid phase technologies using single or multiple alleles-
Solid phase technologies using single or multiple alleles-
16/
 Virtual Crossmatch
Virtual Crossmatch predicts presence of donor specific antibodies using solid phase without an actual crossmatch
predicts presence of donor specific antibodies using solid phase without an actual crossmatch compares recipient's HLA ab to donor HLA type to predict Xmatch results
compares recipient's HLA ab to donor HLA type to predict Xmatch results its use in lieu of 'wet' crossmatch is on the rise
its use in lieu of 'wet' crossmatch is on the rise
17/

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter