1/
M protein ?!?
Ever ordered an SPEP and been uncertain whether to get a UPEP as well?
Should one obtain any other tests?
How does one interpret the results?
Read on for a quick journey evaluating M proteins.
#valuevignettes
M protein ?!?
Ever ordered an SPEP and been uncertain whether to get a UPEP as well?
Should one obtain any other tests?
How does one interpret the results?
Read on for a quick journey evaluating M proteins.
#valuevignettes
2/
SPEP is a screening test for monoclonal gammopathies+ related disorders.
Some indications include:
- Suspected plasma cell disorder (myeloma, amyloid)
- Unexplained
CRAB (Calcemia/ Renal disorder/ Anemia/ Bony lesions),
Neuropathy
- Bence Jones proteinuria
SPEP is a screening test for monoclonal gammopathies+ related disorders.
Some indications include:
- Suspected plasma cell disorder (myeloma, amyloid)
- Unexplained
CRAB (Calcemia/ Renal disorder/ Anemia/ Bony lesions),
Neuropathy
- Bence Jones proteinuria
3/
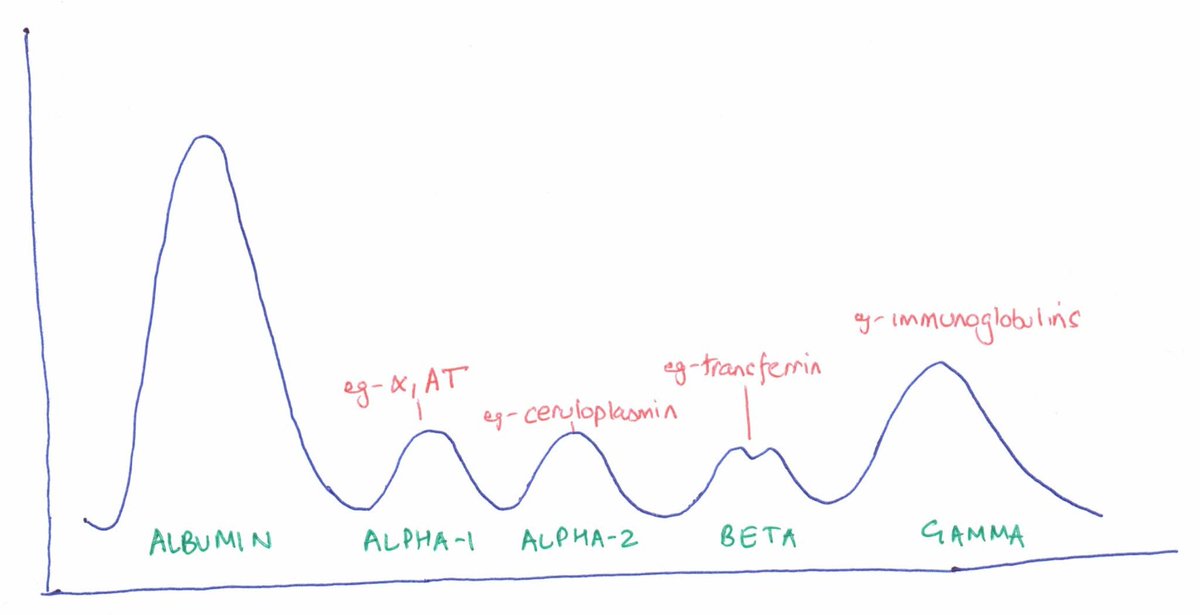
An SPEP separates serum proteins by their physical properties (charge, size) when electric current is applied.
A nice spread of ‘bands’ of different proteins/ classes forms.
Here is a ‘normal’ SPEP. Notice the different bands.
An SPEP separates serum proteins by their physical properties (charge, size) when electric current is applied.
A nice spread of ‘bands’ of different proteins/ classes forms.
Here is a ‘normal’ SPEP. Notice the different bands.
4/
The height of each band corresponds to its relative serum concentration.
Albumin being the predominant serum protein has the ‘tallest’ band.
Knowing the total serum protein concentration allows us to quantify each band (g/dL).
The height of each band corresponds to its relative serum concentration.
Albumin being the predominant serum protein has the ‘tallest’ band.
Knowing the total serum protein concentration allows us to quantify each band (g/dL).
5/
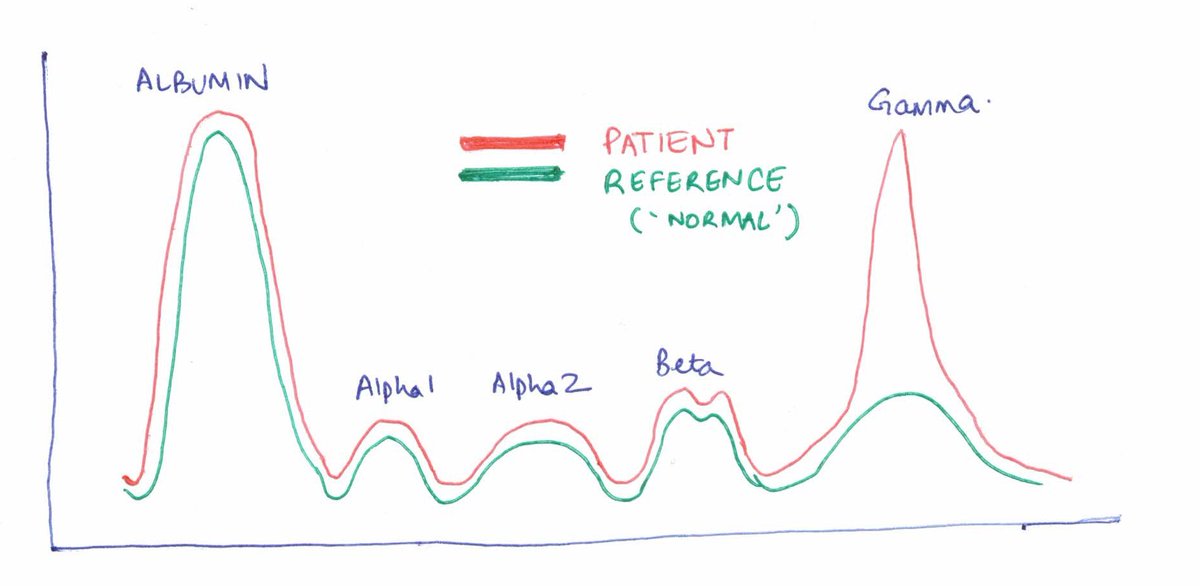
If a patient is severely hypoalbuminemic, the albumin band would ‘flatten’.
Conversely, if there is an expansion of immunoglobulins (or their chains), there would be a ‘peak’, usually in the gamma (and sometimes the beta or alpha 2) region.
If a patient is severely hypoalbuminemic, the albumin band would ‘flatten’.
Conversely, if there is an expansion of immunoglobulins (or their chains), there would be a ‘peak’, usually in the gamma (and sometimes the beta or alpha 2) region.
6/
If proteins in a band are monoclonal, they migrate closer together, giving a sharper band (M-spike).
Narrow band= potentially malignant clonal process= monoclonality?
Broad band= inflammatory process= polyclonality
The height of the band also allows us to quantify it.
If proteins in a band are monoclonal, they migrate closer together, giving a sharper band (M-spike).
Narrow band= potentially malignant clonal process= monoclonality?
Broad band= inflammatory process= polyclonality
The height of the band also allows us to quantify it.
7/
However, declaring a peak as narrow vs broad is subjective as you can imagine.
An SPEP can detect a ‘spike’ and quantify it, but cannot confirm its monoclonality or type of immunoglobulin.
Additionally, a small spike might be missed buried among the other bands.
However, declaring a peak as narrow vs broad is subjective as you can imagine.
An SPEP can detect a ‘spike’ and quantify it, but cannot confirm its monoclonality or type of immunoglobulin.
Additionally, a small spike might be missed buried among the other bands.
8/ To summarize,
SPEP can
1. Detect a spike
2. Determine its size (amount)
SPEP CANNOT
1. Confirm monoclonality
2. Comment on type (heavy/ light chain)
3. Always detect a small spike
SPEP can
1. Detect a spike
2. Determine its size (amount)
SPEP CANNOT
1. Confirm monoclonality
2. Comment on type (heavy/ light chain)
3. Always detect a small spike
9/
Enter the Serum Immunofixation test (IFX).
It can
1. Confirm monoclonality
2. Determine heavy/ light chain specificity
3. Detect smaller M spikes
An SPEP is repeated in several lanes. Monospecific antibodies against heavy and light chains are added– one to each lane.
Enter the Serum Immunofixation test (IFX).
It can
1. Confirm monoclonality
2. Determine heavy/ light chain specificity
3. Detect smaller M spikes
An SPEP is repeated in several lanes. Monospecific antibodies against heavy and light chains are added– one to each lane.
10/
Due to antigen (M protein)- antibody (reagent) crosslinking, an unwashable complex precipitates in one or more lanes, which is then stained and visualized.
Small spikes missed on SPEP can often be detected by IFX.
Here are sample SPEP and IFX reports in the EMR.
Due to antigen (M protein)- antibody (reagent) crosslinking, an unwashable complex precipitates in one or more lanes, which is then stained and visualized.
Small spikes missed on SPEP can often be detected by IFX.
Here are sample SPEP and IFX reports in the EMR.
11/
First time SPEPs should ideally be done in conjunction with IFX. These tests complement each other
An IFX should definitely follow if an M-spike is seen on SPEP.
But is combination SPEP/ IFX 100% sensitive in detecting M proteins?
First time SPEPs should ideally be done in conjunction with IFX. These tests complement each other
An IFX should definitely follow if an M-spike is seen on SPEP.
But is combination SPEP/ IFX 100% sensitive in detecting M proteins?
12/
The answer is no.
If extremely small amounts of light chains are produced (missed even on IFX), or a majority of M protein is excreted in urine (Bence Jones), then SPEP/ IFX can be false negative.
Then, we can use
1. Free light chains (FLC)
OR
2. 24-hour UPEP/ urine IFX
The answer is no.
If extremely small amounts of light chains are produced (missed even on IFX), or a majority of M protein is excreted in urine (Bence Jones), then SPEP/ IFX can be false negative.
Then, we can use
1. Free light chains (FLC)
OR
2. 24-hour UPEP/ urine IFX
13/
24 hour urine collections are cumbersome and FLC is an easier alternative.
There are 2 light chains- kappa and lambda. If one is produced in excess, the FLC RATIO is disturbed. A FLC ratio> 100 is diagnostic of myeloma.
24 hour urine collections are cumbersome and FLC is an easier alternative.
There are 2 light chains- kappa and lambda. If one is produced in excess, the FLC RATIO is disturbed. A FLC ratio> 100 is diagnostic of myeloma.
14/
A UPEP need not always be done as a ‘screening test’ for M protein.
However, if a plasma cell dyscrasia is diagnosed, one should obtain a baseline UPEP and urine IFX.
Results can influence therapy, and also serve as a baseline for monitoring therapy.
A UPEP need not always be done as a ‘screening test’ for M protein.
However, if a plasma cell dyscrasia is diagnosed, one should obtain a baseline UPEP and urine IFX.
Results can influence therapy, and also serve as a baseline for monitoring therapy.
15/
To summarize, if one *truly* suspects a plasma cell dyscrasia, obtaining SPEP + IFX + FLC/ UPEP is reasonable.
Overall sensitivity for M-protein
SPEP- 82%
With IFX -92%
With FLC or UPEP- 98%
To summarize, if one *truly* suspects a plasma cell dyscrasia, obtaining SPEP + IFX + FLC/ UPEP is reasonable.
Overall sensitivity for M-protein
SPEP- 82%
With IFX -92%
With FLC or UPEP- 98%
16/
If you has a ‘meh’ indication for testing—think whether you need an SPEP at all.
Remember that an SPEP alone cannot confirm/ characterize a monoclonal gammopathy.
Also, 18% of M proteins will be missed on SPEP alone.
If you has a ‘meh’ indication for testing—think whether you need an SPEP at all.
Remember that an SPEP alone cannot confirm/ characterize a monoclonal gammopathy.
Also, 18% of M proteins will be missed on SPEP alone.
17/
So next time you consult the hematology team, wow them with,
‘’A 68 year old man with unexplained anemia+ hypercalcemia has a 3.5 gm/dL IgG M-spike on SPEP/ IFX. FLC ratio is 2. The UPEP is pending. What do you think about a bone marrow biopsy for suspected myeloma?’’
So next time you consult the hematology team, wow them with,
‘’A 68 year old man with unexplained anemia+ hypercalcemia has a 3.5 gm/dL IgG M-spike on SPEP/ IFX. FLC ratio is 2. The UPEP is pending. What do you think about a bone marrow biopsy for suspected myeloma?’’

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter